All Exams >
SSC MTS / SSC GD >
Quantitative Aptitude for Competitive Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Trigonometry for SSC MTS / SSC GD Exam
A man standing on top of a tower sees a car coming towards the tower. If it takes 20 minutes for the angle of depression to change from 30° to 60°, what is the time remaining for the car to reach the tower?- a)20√3 minutes
- b)10 minutes
- c)10√3 minutes
- d)5 minutes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A man standing on top of a tower sees a car coming towards the tower. If it takes 20 minutes for the angle of depression to change from 30° to 60°, what is the time remaining for the car to reach the tower?
a)
20√3 minutes
b)
10 minutes
c)
10√3 minutes
d)
5 minutes

|
Quantronics answered |
Find the value of :- (log sin 1° + log sin 2° ………..+ log sin 89°) + (log tan 1° + log tan 2° + ……… + log tan 89°) - (log cos 1° + log cos 2° + ……… + log cos 89°)- a)log √2/(1+√2)
- b)-1
- c)1
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of :- (log sin 1° + log sin 2° ………..+ log sin 89°) + (log tan 1° + log tan 2° + ……… + log tan 89°) - (log cos 1° + log cos 2° + ……… + log cos 89°)
a)
log √2/(1+√2)
b)
-1
c)
1
d)
none of these

|
S.S Career Academy answered |
Writing the equation as :-
(log sin 1° - log cos 89°) + (log sin 2° - log cos 88°) + (log sin 3° - log cos 87°)………… + log tan 1°. log tan 89° + log tan 2°. log tan 88° + …….
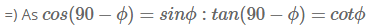
(log sin 1° - log cos 89°) + (log sin 2° - log cos 88°) + (log sin 3° - log cos 87°)………… + log tan 1°. log tan 89° + log tan 2°. log tan 88° + …….
=) (log sin 1° - log sin 1°) +(log sin 2° - log sin 2°)+……..+ log tan 1°cot 1° + log tan 2°cot 2°
=) log 1 = 0
=) log 1 = 0
A student is standing with a banner at the top of a 100 m high college building. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the student is 60° and from the same point, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 45°. Find the height of the student.- a)35 m
- b)73.2 m
- c)50 m
- d)75m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A student is standing with a banner at the top of a 100 m high college building. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the student is 60° and from the same point, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 45°. Find the height of the student.
a)
35 m
b)
73.2 m
c)
50 m
d)
75m
|
|
Abhiram Kumar answered |
Let BC be the height of the tower and DC be the height of the student.
Two poles of equal height are standing opposite to each other on either side of a road which is 100 m wide. Find a point between them on road, angles of elevation of their tops are 30∘ and 60∘. The height of each pole in meter, is:- a) 25√3
- b)20√3
- c)28√3
- d)30√3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two poles of equal height are standing opposite to each other on either side of a road which is 100 m wide. Find a point between them on road, angles of elevation of their tops are 30∘ and 60∘. The height of each pole in meter, is:
a)
25√3
b)
20√3
c)
28√3
d)
30√3

|
Adeshpal Singh answered |
Let the height of the poles be
For the pole where the angle of elevation is
For the pole where the angle of elevation is
We know that
Now, solve for
Equating the two expressions for
Solving for
Substitute
Therefore, the correct answer is:
Sin2014x + Cos2014x = 1, x in the range of [-5π, 5π], how many values can x take?- a)0
- b)10
- c)21
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sin2014x + Cos2014x = 1, x in the range of [-5π, 5π], how many values can x take?
a)
0
b)
10
c)
21
d)
11
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
We know that Sin2x + Cos2x = 1 for all values of x.
If Sin x or Cos x is equal to –1 or 1, then Sin2014x + Cos2014x will be equal to 1.
Sin x is equal to –1 or 1 when x = –4.5π or –3.5π or –2.5π or –1.5π or –0.5π or 0.5π or 1.5π or 2.5π or 3.5π or 4.5π.
Cosx is equal to –1 or 1 when x = –5π or –4π or –3π or –2π or –π or 0 or π or 2π or 3π or 4π or 5π.
For all other values of x, Sin2014 x will be strictly lesser than Sin2x.
For all other values of x, Cos2014 x will be strictly lesser than Cos2x.
We know that Sin2x + Cos2x is equal to 1. Hence, Sin2014x + Cos2014x will never be equal to 1 for all other values of x. Thus there are 21 values.
Answer choice (C)
If Sin x or Cos x is equal to –1 or 1, then Sin2014x + Cos2014x will be equal to 1.
Sin x is equal to –1 or 1 when x = –4.5π or –3.5π or –2.5π or –1.5π or –0.5π or 0.5π or 1.5π or 2.5π or 3.5π or 4.5π.
Cosx is equal to –1 or 1 when x = –5π or –4π or –3π or –2π or –π or 0 or π or 2π or 3π or 4π or 5π.
For all other values of x, Sin2014 x will be strictly lesser than Sin2x.
For all other values of x, Cos2014 x will be strictly lesser than Cos2x.
We know that Sin2x + Cos2x is equal to 1. Hence, Sin2014x + Cos2014x will never be equal to 1 for all other values of x. Thus there are 21 values.
Answer choice (C)
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for "Trigonometry" under Quantitative Aptitude. You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic. The same topic is covered under various competitive examinations like - CAT, GMAT, Bank PO, SSC and other competitive examinations. Q. 3sinx + 4cosx + r is always greater than or equal to 0. What is the smallest value ‘r’ can to take?- a)5
- b)-5
- c)4
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for "Trigonometry" under Quantitative Aptitude. You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic. The same topic is covered under various competitive examinations like - CAT, GMAT, Bank PO, SSC and other competitive examinations.
Q. 3sinx + 4cosx + r is always greater than or equal to 0. What is the smallest value ‘r’ can to take?
a)
5
b)
-5
c)
4
d)
3

|
Dhruv Mehra answered |
3sinx + 4cosx ≥ -r
5(3/5sinx+4/5cosx) ≥ -r
35 = cosA => sinA =45
5(sinx cosA + sinA cosA) ≥ -r
5(sin(x + A)) ≥ -r
5sin (x + A) ≥ -r
-1 ≤ sin (angle) ≤ 1
5sin (x + A) ≥ -5
rmin = 5
Ram and Shyam are 10 km apart. They both see a hot air balloon passing in the sky making an angle of 60° and 30° respectively. What is the height at which the balloon could be flying?- a)
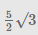
- b)5√3
- c)Both A and B
- d)Can’t be determined
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ram and Shyam are 10 km apart. They both see a hot air balloon passing in the sky making an angle of 60° and 30° respectively. What is the height at which the balloon could be flying?
a)
b)
5√3
c)
Both A and B
d)
Can’t be determined
|
|
Vikas Choudhury answered |
If cos A + cos2 A = 1 and a sin12 A + b sin10 A + c sin8 A + d sin6 A - 1 = 0. Find the value of a+b / c+d- a)4
- b)1
- c)6
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If cos A + cos2 A = 1 and a sin12 A + b sin10 A + c sin8 A + d sin6 A - 1 = 0. Find the value of a+b / c+d
a)
4
b)
1
c)
6
d)
3
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Correct Answer :- B
Explanation : Cos A = 1 - Cos2A
=> Cos A = Sin2A
=> Cos2A = Sin4A
=> 1 – Sin2A = Sin4A
=> 1 = Sin44A + Sin2A
=> 13 = (Sin4A + Sin2A)3
=> 1 = Sin12 A + Sin6A + 3Sin8A + 3Sin10A
=> Sin12A + Sin6A + 3Sin8A + 3Sin10A – 1 = 0
On comparing,
a = 1, b = 3 , c = 3 , d = 1
= a+b/c+d
Hence, the answer is 1
Consider a regular hexagon ABCDEF. There are towers placed at B and D. The angle of elevation from A to the tower at B is 30 degrees, and to the top of the tower at D is 45 degrees. What is the ratio of the heights of towers at B and D?- a)
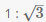
- b)
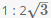
- c)
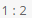
- d)
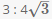
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a regular hexagon ABCDEF. There are towers placed at B and D. The angle of elevation from A to the tower at B is 30 degrees, and to the top of the tower at D is 45 degrees. What is the ratio of the heights of towers at B and D?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Machine Experts answered |
Let the hexagon ABCDEF be of side ‘a’. Line AD = 2a. Let towers at B and D be B’B and D’D respectively.
From the given data we know that ∠B´AB = 30° and ∠D´AB = 45°. Keep in mind that the Towers B’B and D´D are not in the same plane as the hexagon.
From the given data we know that ∠B´AB = 30° and ∠D´AB = 45°. Keep in mind that the Towers B’B and D´D are not in the same plane as the hexagon.
If Cos x – Sin x = √2 Sin x, find the value of Cos x + Sin x:- a)√2 Cos x
- b)√2 Cosec x
- c)√2 Sec x
- d)√2 Sin x Cos x
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If Cos x – Sin x = √2 Sin x, find the value of Cos x + Sin x:
a)
√2 Cos x
b)
√2 Cosec x
c)
√2 Sec x
d)
√2 Sin x Cos x
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Cos x – Sin x = √2 Sin x
=> Cos x = Sin x + √2 Sin x
=> Cos x = Sin x + √2 Sin x
=> Sin x = Cosx/(√2+1) * Cos x
=> Sin x = (√2−1)/(√2−1) * 1/(√2+1) * Cos x
=> Sin x = (√2−1)/((√2)2−(1)2)* Cos x
=> Sin x = (√2 - 1) Cos x
=> Sin x = √2 Cos x – Cos x
=> Sin x + Cos x = √2 Cos x
=> Cos x = Sin x + √2 Sin x
=> Cos x = Sin x + √2 Sin x
=> Sin x = Cosx/(√2+1) * Cos x
=> Sin x = (√2−1)/(√2−1) * 1/(√2+1) * Cos x
=> Sin x = (√2−1)/((√2)2−(1)2)* Cos x
=> Sin x = (√2 - 1) Cos x
=> Sin x = √2 Cos x – Cos x
=> Sin x + Cos x = √2 Cos x
Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
You are standing on the corner of a square whose side length is 25 feet. Standing on the opposite corner from you is a tall tree. The angle of elevation from your position to the top of the tree is exactly 60°. How tall is the tree?- a)25√ 2
- b)25√ 3
- c)25√ 6
- d)50√ 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
You are standing on the corner of a square whose side length is 25 feet. Standing on the opposite corner from you is a tall tree. The angle of elevation from your position to the top of the tree is exactly 60°. How tall is the tree?
a)
25√ 2
b)
25√ 3
c)
25√ 6
d)
50√ 3
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
First find the distance of the diagonal d along the ground from corner to corner. Using Pythagorean theorem with sides 25 and 25, we get:
252 + 252 = d2
2 × 252 = d2
d = 25√ 2 .
Then to obtain the height h of the tree, use the tangent ratio with angle 60°.
tan 60° = x / (25√ 2 )
√ 3 = x / (25√ 2 )
x = 25√ 2 × √ 3 = 25√ 6
The tops of two poles of height 30 m and 14 m are connected by a string. If the wire makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal, find the length of the wire.- a)36 m
- b)34 m
- c)30 m
- d)32 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The tops of two poles of height 30 m and 14 m are connected by a string. If the wire makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal, find the length of the wire.
a)
36 m
b)
34 m
c)
30 m
d)
32 m

|
Impact Learning answered |
The tops of two poles of height 30 m and 14 m are connected by a string. If the wire makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal.
Calculation: Let the length of the wire be h.
Height of pole 1 = 30 m AB = 30 - 14 = 16 m
In ΔABC, Sin30° = AB/AC ⇒ 1/2 = 16/h
⇒ h = 32 m
⇒ h = 32 m
∴ The length of the wire is 32 m.
A right angled triangle has a height ‘p’, base ‘b’ and hypotenuse ‘h’. Which of the following value can h2 not take, given that p and b are positive integers?- a)74
- b)52
- c)13
- d)23
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A right angled triangle has a height ‘p’, base ‘b’ and hypotenuse ‘h’. Which of the following value can h2 not take, given that p and b are positive integers?
a)
74
b)
52
c)
13
d)
23
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
We know that,
h2 = p2 + b2 Given, p and b are positive integer, so h2 will be sum of two perfect squares.
We see
a) 72 + 52 = 74
b) 62 + 42 = 52
c) 32 + 22 = 13
d) Can’t be expressed as a sum of two perfect squares
h2 = p2 + b2 Given, p and b are positive integer, so h2 will be sum of two perfect squares.
We see
a) 72 + 52 = 74
b) 62 + 42 = 52
c) 32 + 22 = 13
d) Can’t be expressed as a sum of two perfect squares
Therefore the answer is Option D.
Anil looked up at the top of a lighthouse from his boat and found the angle of elevation to be 30 degrees. After sailing in a straight line 50 m towards the lighthouse, he found that the angle of elevation changed to 45 degrees. Find the height of the lighthouse.- a)25
- b)25√3
- c)25(√3-1)
- d)25(√3+1)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anil looked up at the top of a lighthouse from his boat and found the angle of elevation to be 30 degrees. After sailing in a straight line 50 m towards the lighthouse, he found that the angle of elevation changed to 45 degrees. Find the height of the lighthouse.
a)
25
b)
25√3
c)
25(√3-1)
d)
25(√3+1)
|
|
Sagar Sharma answered |
Let's assume that the height of the lighthouse is "h" meters.
When Anil is at point A (on his boat), the angle of elevation to the top of the lighthouse is 30 degrees.
When Anil sails 50 meters towards the lighthouse and reaches point B, the angle of elevation to the top of the lighthouse is 45 degrees.
We can form a right-angled triangle ABC, where AB is the distance Anil sailed towards the lighthouse (50 meters), BC is the height of the lighthouse (h meters), and angle BAC is 30 degrees.
Using the tangent function, we can write:
tan(30) = BC / AB
tan(30) = h / 50
Solving for h, we get:
h = 50 * tan(30)
h = 50 * (1/√3)
h = 50/√3
h = (50/√3) * (√3/√3) [Multiplying numerator and denominator by √3]
h = (50√3) / 3
So, the height of the lighthouse is approximately 28.87 meters.
Therefore, the correct option is:
b) 25
When Anil is at point A (on his boat), the angle of elevation to the top of the lighthouse is 30 degrees.
When Anil sails 50 meters towards the lighthouse and reaches point B, the angle of elevation to the top of the lighthouse is 45 degrees.
We can form a right-angled triangle ABC, where AB is the distance Anil sailed towards the lighthouse (50 meters), BC is the height of the lighthouse (h meters), and angle BAC is 30 degrees.
Using the tangent function, we can write:
tan(30) = BC / AB
tan(30) = h / 50
Solving for h, we get:
h = 50 * tan(30)
h = 50 * (1/√3)
h = 50/√3
h = (50/√3) * (√3/√3) [Multiplying numerator and denominator by √3]
h = (50√3) / 3
So, the height of the lighthouse is approximately 28.87 meters.
Therefore, the correct option is:
b) 25
Given that cos x + cos y = 1, the range of sin x - sin y is- a)[-1, 1]
- b)[-2, 2]
- c)[0, √3]
- d)[-√3, √3]
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given that cos x + cos y = 1, the range of sin x - sin y is
a)
[-1, 1]
b)
[-2, 2]
c)
[0, √3]
d)
[-√3, √3]

|
EduRev CAT answered |
Let’s say sin x – sin y = k. So we intend to find the range of k.
We have cos x + cos y = 1
So, k2 + 12 = (sin x - sin y )2 + (cos x + cosy )2
k2 + 12 = (sin x)2 + (sin y)2 – 2(sin x)(sin y) + (cos x)2 + (cos y)2 + 2(cos x)(cos y)
k2 + 12= sin2 x + cos2 x + sin2 y + cos2 y + 2(cos x)(cos y) – 2(sin x)(sin y)
k2 + 12 = 1 + 1 + 2(cos x)(cos y) – 2(sin x)(sin y) {Because, sin2 x + cos2 x = 1}
k2 + 12= 2 + 2[(cos x)(cos y) – (sin x)(sin y)] {Because, (cos x)(cos y) – (sin x)(sin y) = cos(x + y)}
k2 = 1 + 2(cos(x + y))
The maximum value that a cos function can take is 1, and the minimum value is -1.
Therefore the maximum value that k2 can take is 1+2(1) = 3,
and the minimum value that k2 can take is 1+2(-1) = -1,
This is impossible, k2 is always non-negative.
The minimum value that k2 can take is 0.
Therefore (k2)max = 3 and (k2)min = 0.
To get the range of k, we concentrate on (k2)max.
(k2)max = 3, implies that the extreme values of k are:
k = +√3 or -√3
So, the values of k range between +√3 and -√3, both +√3 and -√3 inclusive.
k = sin x – sin y, Remember!!
Therefore, Range of sin x – sin y = [-√3, √3]
We have cos x + cos y = 1
So, k2 + 12 = (sin x - sin y )2 + (cos x + cosy )2
k2 + 12 = (sin x)2 + (sin y)2 – 2(sin x)(sin y) + (cos x)2 + (cos y)2 + 2(cos x)(cos y)
k2 + 12= sin2 x + cos2 x + sin2 y + cos2 y + 2(cos x)(cos y) – 2(sin x)(sin y)
k2 + 12 = 1 + 1 + 2(cos x)(cos y) – 2(sin x)(sin y) {Because, sin2 x + cos2 x = 1}
k2 + 12= 2 + 2[(cos x)(cos y) – (sin x)(sin y)] {Because, (cos x)(cos y) – (sin x)(sin y) = cos(x + y)}
k2 = 1 + 2(cos(x + y))
The maximum value that a cos function can take is 1, and the minimum value is -1.
Therefore the maximum value that k2 can take is 1+2(1) = 3,
and the minimum value that k2 can take is 1+2(-1) = -1,
This is impossible, k2 is always non-negative.
The minimum value that k2 can take is 0.
Therefore (k2)max = 3 and (k2)min = 0.
To get the range of k, we concentrate on (k2)max.
(k2)max = 3, implies that the extreme values of k are:
k = +√3 or -√3
So, the values of k range between +√3 and -√3, both +√3 and -√3 inclusive.
k = sin x – sin y, Remember!!
Therefore, Range of sin x – sin y = [-√3, √3]
Chapter doubts & questions for Trigonometry - Quantitative Aptitude for Competitive Exams 2025 is part of SSC MTS / SSC GD exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the SSC MTS / SSC GD exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for SSC MTS / SSC GD 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Trigonometry - Quantitative Aptitude for Competitive Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of SSC MTS / SSC GD exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC MTS / SSC GD Exam by signing up for free.
Quantitative Aptitude for Competitive Exams
203 videos|110 docs|114 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup