All Exams >
A Level >
Biology A-Level >
All Questions
All questions of Classification, Biodiversity and Conservation for A Level Exam
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Biological organisation starts witha) Cellular levelb) Atomic levelc) Submicroscopic molecular leveld) Organismic levelCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Correct option is (c)
Biological organisation starts with submicroscopic molecular level, where four types of molecules, i.e. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acid are organised into organelles of cell.
Biological organisation starts with submicroscopic molecular level, where four types of molecules, i.e. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acid are organised into organelles of cell.
Animals undergo an inactive stage during the winter known as- a)Adaptation
- b)Hibernation
- c)Aestivation
- d)Acclimatisation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals undergo an inactive stage during the winter known as
a)
Adaptation
b)
Hibernation
c)
Aestivation
d)
Acclimatisation
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Aestivation: Aestivation is summer sleep and during aestivation, animals usually tend to rest in a shady and cool place. ... In aestivation, usually cold blooded animals like reptiles maintain their body temperature by reducing their metabolic activities and protecting themselves from very high temperature.
Ecosystem follows:- a)only first law of thermodynamics
- b)only second law of thermodynamics
- c)both first and second laws of thermodynamics
- d)only third law of thermodynamics
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ecosystem follows:
a)
only first law of thermodynamics
b)
only second law of thermodynamics
c)
both first and second laws of thermodynamics
d)
only third law of thermodynamics
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The first law, also known as Law of Conservation of Energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system. The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches absolute zero.
Organisms capable of maintaining constant body temperature are- a)Poikilothermal
- b)Conformers
- c)Stenothermal
- d)Homeothermal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms capable of maintaining constant body temperature are
a)
Poikilothermal
b)
Conformers
c)
Stenothermal
d)
Homeothermal
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Homeotherms: animals who maintain a constant internal body temperature across a wide range of environmental conditions. Most mammals and birds are homeotherms.
The common nitrogen-fixer in paddy fields is- a)Rhizobium
- b)Azospirillum
- c)Frankia
- d)Oscillatoria
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The common nitrogen-fixer in paddy fields is
a)
Rhizobium
b)
Azospirillum
c)
Frankia
d)
Oscillatoria
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Azospirillum is a nitrogen fixing bacterium in paddy fields. It is very useful soil and root bacterium. It is an associative symbiotic N2-fixing bacteria. When it is added to the soil, it multiplies in millions and can supply 20-40 Kg of nitrogen per hectare, per season. It also produces growth promoting substances like Indole Acetic Acid (IAA), gibberellins and promotes root proliferation. These substances improve the plant growth and yield.
Acclimatisation is- a)Pure-line selection
- b)Introduction
- c)Pure-line breeding
- d)Adaptation to new environment
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Acclimatisation is
a)
Pure-line selection
b)
Introduction
c)
Pure-line breeding
d)
Adaptation to new environment
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Acclimatization or acclimatisation (also called acclimation or acclimatation) is the process in which an individual organism adjusts to a change in its environment (such as a change in altitude, temperature, humidity, photoperiod, or pH), allowing it to maintain performance across a range of environmental conditions.
Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by- a)Decomposer
- b)Consumer
- c)Producer
- d)Parasite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by
a)
Decomposer
b)
Consumer
c)
Producer
d)
Parasite
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers. primary productivity depends on the producers inhabiting a particular area. Decomposers break down complex organic matter. Into inorganic substance like carbon dioxide water and nutrients. Parasitic species food on the body of other organisms.
. Which one of the following is considered as a pioneer community in xerarch?- a)Forest stage
- b)Perennial herb
- c)Annual herb
- d)Lichen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
. Which one of the following is considered as a pioneer community in xerarch?
a)
Forest stage
b)
Perennial herb
c)
Annual herb
d)
Lichen
|
|
Sanjana Sharma answered |
Xerarch Succession:
Xerarch succession is a type of ecological succession that occurs in a dry environment, such as a desert or a rocky terrain. Pioneer communities that start the succession process are those that are adapted to extreme conditions such as high temperatures, strong winds, and lack of water. These pioneer communities are usually small and simple, often consisting of lichens, mosses, or algae.
Pioneer Community in Xerarch:
The pioneer community in xerarch is the first community that establishes in a dry environment. The pioneer community is the first stage in the process of xerarch succession. The pioneer community is established by organisms that are adapted to live in harsh conditions. The pioneer community is usually small and simple, consisting of lichens, mosses, or algae.
Lichen as a Pioneer Community:
Lichens are considered as a pioneer community in xerarch succession. Lichens are composite organisms that consist of a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, often an alga or a cyanobacterium. Lichens are adapted to survive in harsh environments, such as deserts, rocky terrains, and polar regions. Lichens are the first organisms to colonize bare rock or soil in a xerarch succession. They secrete acids that dissolve the rock surface, making nutrients available for other organisms. Lichens also trap dust and organic matter, creating a small amount of soil that allows other plants to grow.
Conclusion:
In xerarch succession, lichens are considered as a pioneer community. Lichens are adapted to survive in harsh environments and are the first organisms to colonize bare rock or soil. Lichens secrete acids that dissolve the rock surface, making nutrients available for other organisms. Lichens also trap dust and organic matter, creating a small amount of soil that allows other plants to grow.
Xerarch succession is a type of ecological succession that occurs in a dry environment, such as a desert or a rocky terrain. Pioneer communities that start the succession process are those that are adapted to extreme conditions such as high temperatures, strong winds, and lack of water. These pioneer communities are usually small and simple, often consisting of lichens, mosses, or algae.
Pioneer Community in Xerarch:
The pioneer community in xerarch is the first community that establishes in a dry environment. The pioneer community is the first stage in the process of xerarch succession. The pioneer community is established by organisms that are adapted to live in harsh conditions. The pioneer community is usually small and simple, consisting of lichens, mosses, or algae.
Lichen as a Pioneer Community:
Lichens are considered as a pioneer community in xerarch succession. Lichens are composite organisms that consist of a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, often an alga or a cyanobacterium. Lichens are adapted to survive in harsh environments, such as deserts, rocky terrains, and polar regions. Lichens are the first organisms to colonize bare rock or soil in a xerarch succession. They secrete acids that dissolve the rock surface, making nutrients available for other organisms. Lichens also trap dust and organic matter, creating a small amount of soil that allows other plants to grow.
Conclusion:
In xerarch succession, lichens are considered as a pioneer community. Lichens are adapted to survive in harsh environments and are the first organisms to colonize bare rock or soil. Lichens secrete acids that dissolve the rock surface, making nutrients available for other organisms. Lichens also trap dust and organic matter, creating a small amount of soil that allows other plants to grow.
Cold-blooded animals fall under the category of- a)Psychotherms
- b)Ectotherms
- c)Thermophiles
- d)Endotherms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cold-blooded animals fall under the category of
a)
Psychotherms
b)
Ectotherms
c)
Thermophiles
d)
Endotherms
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
An ectotherm "outside" and "hot"), is an organism in which internal physiological sources of heat are of relatively small or quite negligible importance in controlling body temperature.] Such organisms (for example frogs) rely on environmental heat sources,which permit them to operate at very economical metabolic rates. Colloquially, some refer to these organisms as "cold blooded" though such a term is not technically correct, as the blood temperature of the organism varies with ambient environmental temperature. Some of these animals live in environments where temperatures are practically constant, as is typical of regions of the abyssal ocean and hence can be regarded as homeothermic ectotherms. In contrast, in places where temperature varies so widely as to limit the physiological activities of other kinds of ectotherms, many species habitually seek out external sources of heat or shelter from heat; for example, many reptiles regulate their body temperature by basking in the sun, or seeking shade when necessary in addition to a whole host of other behavioral thermoregulation mechanisms. For home captivity as pet, reptile owners can use a UVB/UVA light system to assist the animals' basking behaviour.
Which of the following is/are poikilotherm:?- a)Tapeworm and rabbits
- b)Elephants
- c)Humans and fishes
- d)Tapeworm and naked mole rat
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are poikilotherm:?
a)
Tapeworm and rabbits
b)
Elephants
c)
Humans and fishes
d)
Tapeworm and naked mole rat
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
- Poikilotherms or cold blooded animals are referred to as organisms that can change their body temperature according to the environment around.
- Tape worms and naked mole rats are examples of cold blooded animals.
Xerophytes are mostly- a)Succulents
- b)Water related
- c)Mesophytes
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Xerophytes are mostly
a)
Succulents
b)
Water related
c)
Mesophytes
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Plants adapted to living in dry environments such as succulents are termed xerophytes. However, not all xerophytes are succulents, since there are other ways of adapting to a shortage of water, e.g., by developing small leaves which may roll up or having leathery rather than succulent leaves.
Correct sequence for decomposition process is:
- a)fragmentation -> leaching -> catabolism -> mineralisation
- b)fragmentation -> leaching -> mineralisation -> humification
- c)leaching -> fragmentation -> humification -> mineralisation
- d)fragmentation -> catabolism -> leaching -> mineralisation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct sequence for decomposition process is:
a)
fragmentation -> leaching -> catabolism -> mineralisation
b)
fragmentation -> leaching -> mineralisation -> humification
c)
leaching -> fragmentation -> humification -> mineralisation
d)
fragmentation -> catabolism -> leaching -> mineralisation
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Decomposition is the process that involves the breakdown of complex organic matter or biomass from the body of dead plants and animals with the help of decomposers into inorganic raw materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and other nutrients.
The various processes involved in decomposition are as follows:
➢ Fragmentation
➢ Fragmentation
- It is the first step in the process of decomposition.
- It involves the breakdown of detritus into smaller pieces by the action of detritivores such as earthworms.
➢ Leaching
- It is a process where the water soluble nutrients go down into the soil layers and get locked as unavailable salts.
➢ Catabolism
- It is a process in which bacteria and fungi degrade detritus through various enzymes into smaller pieces.
➢ Humification
- The next step is humification which leads to the formation of a dark-coloured colloidal substance called humus, which acts as reservoir of nutrients for plants.
➢ Mineralization
- The humus is further degraded by the action of microbes, which finally leads to the release of inorganic nutrients into the soil.
- This process of releasing inorganic nutrients from the humus is known as mineralization.
Study of trends of human population is- a)Biography
- b)Kalography
- c)Demography
- d)Psychology
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study of trends of human population is
a)
Biography
b)
Kalography
c)
Demography
d)
Psychology

|
Savita Soni answered |
Yeah its right demography ,study of particular statics from birth to death ,mainly used for human population .
The final stable community in ecological succession is- a)Sere
- b)Climax
- c)Pioneers
- d)Carnivores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The final stable community in ecological succession is
a)
Sere
b)
Climax
c)
Pioneers
d)
Carnivores
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
The community begins with relatively few pioneering plants and animals and develops through increasing complexity until it becomes stable or self-perpetuating as a climax community. The "engine" of succession, the cause of ecosystem change, is the impact of establishedspecies upon their own environments.
Cuscuta is an example of
- a)Predation
- b)Brood parasitism
- c)ectoparasitism
- d)Parasite
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cuscuta is an example of
a)
Predation
b)
Brood parasitism
c)
ectoparasitism
d)
Parasite
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Explanation for correct option:
- When a parasite lives in the body of the host then it is referred to as ectoparasitism.
- Here the host-parasite relationship remains non-mutual.
- Cuscuta is a stem parasite that wraps around the host plants and remains attached to them.
- It is an example of ectoparasitism and in this type of parasitism the dependent organism or the parasite is dependent on the host for its food.
Which one of the following statements is CORRECT for secondary succession?
- a)It begins on a bare rock.
- b)It occurs on a deforested site.
- c)It follows primary succession.
- d)It is similar to primary succession except that it has a relatively fast pace.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is CORRECT for secondary succession?
a)
It begins on a bare rock.
b)
It occurs on a deforested site.
c)
It follows primary succession.
d)
It is similar to primary succession except that it has a relatively fast pace.
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
-
Option A: It begins on a bare rock. This is incorrect as it describes primary succession, not secondary.Option B: It occurs on a deforested site. This is correct. Secondary succession occurs in areas where a community has been removed; it is the series of community changes which take place on a previously colonized, but disturbed or damaged habitat.Option C: It follows primary succession. While secondary succession does come after primary succession, this statement on its own is not fully descriptive of secondary succession.Option D: It is similar to primary succession except that it has a relatively fast pace. This is also correct; however, it is less specific than Option B. Secondary succession is typically faster than primary succession because the soil already exists, and often some remnants of the previous community remain.The most accurate and specific statement for secondary succession is:Option B: It occurs on a deforested site.
Ecosystem is- a)Open
- b)Both open and close
- c)Close
- d)Neither opened nor closed
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ecosystem is
a)
Open
b)
Both open and close
c)
Close
d)
Neither opened nor closed
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
An ecosystem includes all of the living things (plants, animals and organisms) in a given area, interacting with each other, and also with their non-living environments (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere). Ecosystems are the foundations of the Biosphere and they determine the health of the entire earth system.
In a population curve, the rate of growth becomes steady towards the end of the exponential curve due to- a)Reproductive power is reduced
- b)Environmental stress
- c)Migration
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a population curve, the rate of growth becomes steady towards the end of the exponential curve due to
a)
Reproductive power is reduced
b)
Environmental stress
c)
Migration
d)
All of the above

|
Kritika Singh answered |
It is given in Ecology NCERT due to environmental stress...
Humus will never be:
- a)Good for plant growth.
- b)Resistant to microbial action.
- c)Reservoir of nutrients.
- d)all of these
- e)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Humus will never be:
a)
Good for plant growth.
b)
Resistant to microbial action.
c)
Reservoir of nutrients.
d)
all of these
e)
None of these.
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
- Humus is a dark brown amorphous gummy substance formed by partial decomposition of plant and animal matter.
- It is not good for plant growth.
- Humus is quite resistant to microbial action.
- It is a reservoir of nutrients and is helpful in the maintenance of soil moisture as well as aeration.
Hence, None of these statements is correct about Humus.
Which of the following is correct?a)GPP + NPP = Rb)NPP – R = GPPc)GPP – R = NPPd)NPP – GPP = RCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Net primary productivity (NPP) is equal to Gross primary productivity (GPP) minus Respiration loss (R). NPP is the available biomass for the consumption of heterotrophs in the ecosystem.
Which one of the following is a denitrifying bacterium?- a)Pseudomonas
- b)Escherichia coli
- c)Nitrobacter
- d)Nitrosomonas
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a denitrifying bacterium?
a)
Pseudomonas
b)
Escherichia coli
c)
Nitrobacter
d)
Nitrosomonas
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Denitrifying bacteria, microorganisms whose action results in the conversion of nitrates in soil to free atmospheric nitrogen, thus depleting soil fertility and reducing agricultural productivity. Thiobacillus denitrificans, Micrococcus denitrificans, and some species of Serratia, Pseudomonas, and Achromobacter are implicated as denitrifiers. Pseudomonas aeruginosa can, under anaerobic conditions (as in swampy or water-logged soils), reduce the amount of fixed nitrogen (as fertilizer) by up to 50 percent. Without denitrification, however, the Earth’s supply of nitrogen would eventually accumulate in the oceans, since nitrates are highly soluble and are continuously leached from the soil into nearby bodies of water. See also nitrogen cycle.
Orchid shows commensalism as interaction with:- a)bee
- b)mango tree
- c)both mango tree and bee
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Orchid shows commensalism as interaction with:
a)
bee
b)
mango tree
c)
both mango tree and bee
d)
none of these

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Commensalism is interaction in which one species is benefited by other is neither benefited nor harmed. Orchids growing on mango tree do not harm the mango plants but get shelter.
The scientist who put price tag of US$ 33 trillion a year for nature’s life-support services was- a)Robert hook and his colleagues.
- b)Robert Contanza and his colleagues.
- c)William Contanza and his colleagues.
- d)William Haber and his colleagues.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The scientist who put price tag of US$ 33 trillion a year for nature’s life-support services was
a)
Robert hook and his colleagues.
b)
Robert Contanza and his colleagues.
c)
William Contanza and his colleagues.
d)
William Haber and his colleagues.

|
Krish Saha answered |
Robert Constanza and his colleagues have recently put price tag of US$ 33 trillion a year for nature’s life support services for fundamental services.
Exponential growth occurs in the population in which sufficient
- a)Water is abundant.
- b)Sufficient area is available.
- c)All of the these.
- d)Food and other nutrient are available.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exponential growth occurs in the population in which sufficient
a)
Water is abundant.
b)
Sufficient area is available.
c)
All of the these.
d)
Food and other nutrient are available.

|
Krish Saha answered |
Exponential growth occurs in the population in which sufficient food and nutrients are available in sufficient amount. The rate of growth is very fast in this kinds of growth.
Exponential growth in a population occurs when:
- Food and nutrients are plentiful.
- Water is abundant.
- There is sufficient living space.
These conditions ensure that individuals can reproduce rapidly without facing resource limitations, leading to a fast and continuous increase in population size. Thus, the correct answer is C: All of these.
A natural reservoir of phosphorus is- a)Fossils
- b)Rock
- c)Sea water
- d)Animal bones
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A natural reservoir of phosphorus is
a)
Fossils
b)
Rock
c)
Sea water
d)
Animal bones
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The natural reservoir of phosphate is rock which contains phosphorus in the form of phosphates when rocks are weathered, minute amounts of these phosphate dissolve in soil solution and are absorbed by the roots of the plants. Herbivores and other animals obtain this element from plants.
The birth and death rates of four counteries are given below. which one will have the least population growth rate?
- a)P
- b)Q
- c)R
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The birth and death rates of four counteries are given below. which one will have the least population growth rate?

a)
P
b)
Q
c)
R
d)
S
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Growth rate = Birth rate - death rate
For country P, it is 10/1000. For country Q, It is 15/1000
For country R, it is 17/1000. For country S, It is 7/1000
Hence, country S has the least population growth rate
For country P, it is 10/1000. For country Q, It is 15/1000
For country R, it is 17/1000. For country S, It is 7/1000
Hence, country S has the least population growth rate
A detritus food chain will start with which of the following?- a)Protozoans
- b)Rhizophora species
- c)Bacteria & fungi
- d)Earthworm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A detritus food chain will start with which of the following?
a)
Protozoans
b)
Rhizophora species
c)
Bacteria & fungi
d)
Earthworm

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
A detritus food chain begins with dead organic matter. It is made of decomposers which are heterotrophic organism fungi and bacteria.Rhizophora species is a saprophyticheterotrophs.
Which one of the following is the most important service provided by ecosystems?- a)soil formation
- b)aesthetic values
- c)pollination
- d)water purification
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the most important service provided by ecosystems?
a)
soil formation
b)
aesthetic values
c)
pollination
d)
water purification

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
Ecosystem services includes all activities performed by nature to benefits of human beings. The most important ecological service includes soil formation. Soil is essential for growth of plants that provide food to all living forms.
A statement 933 females per 1000 males depict:- a)ecological ages
- b)generation time
- c)sex ratio
- d)biotic potential
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A statement 933 females per 1000 males depict:
a)
ecological ages
b)
generation time
c)
sex ratio
d)
biotic potential

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Sex ratio is the no of female available per thousands of male in a population. Sex ratio is decline due to female feticides alarmingly in some part of India.
Available organic matter for herbivores is represented by:- a)Secondary productivity
- b)GPP
- c)NPP
- d)All the these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Available organic matter for herbivores is represented by:
a)
Secondary productivity
b)
GPP
c)
NPP
d)
All the these

|
Charvi Shah answered |
The organic matter available for herbivores is called net primary productivity (NPP). Total amount of organic matter fix during photosynthesis is called Gross primary productivity (GPP).
Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?- a)Dry weight
- b)Number of individuals
- c) Fresh weight
- d)Rate of energy flow
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?
a)
Dry weight
b)
Number of individuals
c)
Fresh weight
d)
Rate of energy flow

|
Sanvi Patel answered |
Option c) Fresh weight is correct because
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of the relationship between different organisms. It shows the biomass at each trophic level of an ecosystem. It is of three types, pyramid of numbers, the pyramid of energy and the pyramid of biomass. The pyramid of numbers indicates the total number of individuals at each trophic level. The pyramid of energy indicates the rate of energy flow. Pyramid of biomass indicates the dry weight of living organisms at each trophic level.
There are only 4 or 5 trophic levels in food chain of an ecosystem due to :- a)Limited number of members in biotic community
- b)Loss of energy at successive levels
- c)Carrying capacity
- d)Environmental resistance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are only 4 or 5 trophic levels in food chain of an ecosystem due to :
a)
Limited number of members in biotic community
b)
Loss of energy at successive levels
c)
Carrying capacity
d)
Environmental resistance

|
Krish Saha answered |
In most of the food chain of ecosystem only 4 to 5 trophic levels are present because loss of energy at successive levels is very high. Only 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level.
Which of the following could be most intense and strongest?
- a)natural selection
- b)intra-specific competition
- c)inter-specific competition
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following could be most intense and strongest?
a)
natural selection
b)
intra-specific competition
c)
inter-specific competition
d)
none

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Inter-specific competition could be most intense and strongest as it occurs between organisms having same types of requirement of food, water etc. They may have competition for food, shelter, water, space or mat also.
A sedentary sea anaemone gets attached to the shell lining of hermit crab. The association is- a)Symbiosis
- b)Ectoparasitism
- c)Commensalism
- d)Amensalism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A sedentary sea anaemone gets attached to the shell lining of hermit crab. The association is
a)
Symbiosis
b)
Ectoparasitism
c)
Commensalism
d)
Amensalism

|
Nupur Juyal answered |
The association is commensalism but it's a part of symbiosis...so both a and c should be correct answer...hermit crab gets protection from predators by stings of sea anaemone whereas sea anaemone doesn't significantly get benefitted(yes it do get benefitted by the food provided by hermit crab but that's not significant) so we can called it as commensalism symbiosis association
Organism/s living as both producer as well as consumer is/are:- a)Algae & fungi
- b)Nepenthes & Drocera
- c)Cuscuta
- d)Phytoplankton
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Organism/s living as both producer as well as consumer is/are:
a)
Algae & fungi
b)
Nepenthes & Drocera
c)
Cuscuta
d)
Phytoplankton

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Nepenthes (pitcher plant) and Drocera are insectivores plants to compensate theirprotein requirement. They have green leaves that perform photosynthesis process. So, they act as both producer as well as consumer.
Phosphorus will not make part of:- a)nucleic acids
- b)ATP
- c)teeth
- d)amino acids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phosphorus will not make part of:
a)
nucleic acids
b)
ATP
c)
teeth
d)
amino acids

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Phosphorus is not present in amino acids. Nucleic acids, ATP and Teeth contain phosphorus. Amino acids polymerases to form protein.
Which of the following ecological pyramid is always erect and upright?- a)pyramid of biomass
- b)pyramid of energy
- c)pyramid of number
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ecological pyramid is always erect and upright?
a)
pyramid of biomass
b)
pyramid of energy
c)
pyramid of number
d)
none of these

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Pyramid of energy is always erect and upright because the amount of energy get reduce at each trophic level from prouder to consumers.
Small fish get stuck near the bottom of a shark and derive their nutrition from it? This kind of association is called- a)Parasitism
- b)Symbiosis
- c)Predation
- d)Commensalism
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Small fish get stuck near the bottom of a shark and derive their nutrition from it? This kind of association is called
a)
Parasitism
b)
Symbiosis
c)
Predation
d)
Commensalism
|
|
Sonal Chakraborty answered |
Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits from the association, while the other is neither harmed nor helped. In this type of association, one species derives benefits from the other without causing any harm to the host.
Explanation:
In the given scenario, the small fish gets stuck near the bottom of a shark and derives its nutrition from it. The small fish is not harming the shark, nor is it providing any benefits to the shark. Therefore, this is an example of commensalism.
The small fish is using the shark as a shelter and also gets access to food particles that are present near the shark's mouth. The shark is not affected by the presence of the small fish, and it does not derive any benefit from it either.
In summary, commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits from the association, while the other is neither harmed nor helped. The small fish getting stuck near the bottom of a shark and deriving its nutrition from it is an example of commensalism.
Explanation:
In the given scenario, the small fish gets stuck near the bottom of a shark and derives its nutrition from it. The small fish is not harming the shark, nor is it providing any benefits to the shark. Therefore, this is an example of commensalism.
The small fish is using the shark as a shelter and also gets access to food particles that are present near the shark's mouth. The shark is not affected by the presence of the small fish, and it does not derive any benefit from it either.
In summary, commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits from the association, while the other is neither harmed nor helped. The small fish getting stuck near the bottom of a shark and deriving its nutrition from it is an example of commensalism.
The decomposition of organic matter is brought about by- a)Protozoans
- b)Plants
- c)Microorganisms
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The decomposition of organic matter is brought about by
a)
Protozoans
b)
Plants
c)
Microorganisms
d)
None of the above

|
Shruti Bora answered |
Microorganisms like bacteria etc decompose organic matter.
Which of the following is not an ecological parameter?- a)Stratification
- b)Number
- c)Energy
- d)Biomass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an ecological parameter?
a)
Stratification
b)
Number
c)
Energy
d)
Biomass

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Ecological parameter includes, biomass, energy and number of individual in the ecosystem. Stratification is not a part of ecological parameter.
A large regional unit characterised by a major vegetation type and associated fauna found in a specific climate zone constitutes- a)Biological community
- b)Ecosystem
- c)Biome
- d)Habitat
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A large regional unit characterised by a major vegetation type and associated fauna found in a specific climate zone constitutes
a)
Biological community
b)
Ecosystem
c)
Biome
d)
Habitat
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
A biome is a community of plants and animals that have common characteristics for the environment they exist in. They can be found over a range of continents. Biomes are distinct biological communities that have formed in response to a shared physical climate."Biome" is a broader term than "habitat"; any biome can comprise a variety of habitats.
While a biome can cover large areas, a microbiome is a mix of organisms that coexist in a defined space on a much smaller scale. For example, the human microbiome is the collection of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that are present on or in a human body.
A 'biota' is the total collection of organisms of a geographic region or a time period, from local geographic scales and instantaneous temporal scales all the way up to whole-planet and whole-timescale spatiotemporal scales. The biotas of the Earth make up the biosphere.
Term ecosystem was introduced by :- a)Charles Elton
- b)Haeckel
- c)Lindemann
- d)Tansley
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Term ecosystem was introduced by :
a)
Charles Elton
b)
Haeckel
c)
Lindemann
d)
Tansley

|
Shounak Nair answered |
Term ecosystem was introduced by Tansley. Ecosystem is the functionalunit of nature where living and non-living components interact with each other.
In which of the following places, succession will occur in short time?- a)on a bare rock
- b)in heavily overgrazed pasture
- c)in a small oligotrophic lake
- d)area exposed by a retreating glacier
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following places, succession will occur in short time?
a)
on a bare rock
b)
in heavily overgrazed pasture
c)
in a small oligotrophic lake
d)
area exposed by a retreating glacier

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
Succession will occur in short time in heavily overgrazed pasture. If organic compound are already available in the place new organisms will develops faster as compare to bare land without organic matter.
In an ecosystem, the cycling of nutrients is known as- a)Biogeochemical cycle
- b)Geological cycle
- c)Chemical cycle
- d)Geochemical cycle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an ecosystem, the cycling of nutrients is known as
a)
Biogeochemical cycle
b)
Geological cycle
c)
Chemical cycle
d)
Geochemical cycle

|
Aditi Rai answered |
Cycling of nutrients. from bio..mean living thing. to geo ....mean soil. chemical.......in the form of chemicals. all 3 are included...so option A is corrrect
Human population follows the- a)J-shaped growth curve
- b)Z-shaped growth curve
- c)S-shaped growth curve
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Human population follows the
a)
J-shaped growth curve
b)
Z-shaped growth curve
c)
S-shaped growth curve
d)
All of the above

|
Harshitha Chavan answered |
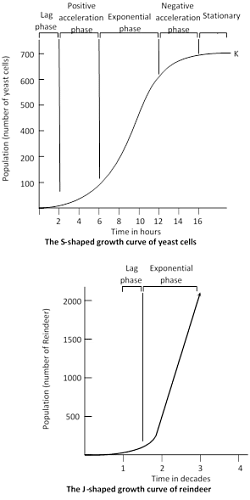
Logarithmic or Exponential phase : It is characterized by rapid growth in population which continues till enough food is available. But with the increase in reindeer population, there is corresponding decrease in the availability of food and space, which finally become exhausted, which leads to mass starvation and mortality. This sudden increase in mortality is called population crash. Lemming of Tundra, some insect, algal blooms and annual plants also show J-shaped curves. The population growth curve is S- shaped in most of the organisms, Human population also shows S-shaped curve.

The birth rate if 7 new plants are added to previous year plant population of 23 Salvinia plants will be:- a)0.3
- b)0.25
- c)0.4
- d)0.5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The birth rate if 7 new plants are added to previous year plant population of 23 Salvinia plants will be:
a)
0.3
b)
0.25
c)
0.4
d)
0.5

|
Rohan Unni answered |
The birth rate of a population = new individual added / previous population. Here birth rate= 7/23=0.3043. Hence, birth rate of Salvinia plants is equal to 0.3.
Exponential growth pattern in a population results into:- a)Sigmoid curve
- b)U-shaped curve
- c)J-shaped curve
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exponential growth pattern in a population results into:
a)
Sigmoid curve
b)
U-shaped curve
c)
J-shaped curve
d)
None of these

|
Shalini Saha answered |
Exponential growth pattern in population results into j-shaped curve. During exponential growth faster growth occurs and j-shaped curve is formed when time v/s growth is drawn.
Chapter doubts & questions for Classification, Biodiversity and Conservation - Biology A-Level 2024 is part of A Level exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the A Level exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for A Level 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Classification, Biodiversity and Conservation - Biology A-Level in English & Hindi are available as part of A Level exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for A Level Exam by signing up for free.
Biology A-Level
280 videos|166 docs|147 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











