All Exams >
NEET >
Biology Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Human Reproduction for NEET Exam
Spermatogenesis is induced by- a)FSH
- b)ICSH
- c)STH
- d)ATH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Spermatogenesis is induced by
a)
FSH
b)
ICSH
c)
STH
d)
ATH
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
FSH acts on the Sertoli cells and stimulate secretion of some factors which help in the process of spermatogenesis.
The middle piece of the sperm contains- a)proteins
- b)mitochondria
- c)centriole
- d)nucleus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The middle piece of the sperm contains
a)
proteins
b)
mitochondria
c)
centriole
d)
nucleus
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The middle piece of sperm contains mitochondria coiled around the axial filament. They provide energy for the movement of the sperm.
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option.
During copulation (coitus), semen is released by the penis into the vagina and is called (i) . The ovum released by the ovary is transported to the (ii) where (iii) takes place. During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of (iv) . The secretions of the (v) help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum.
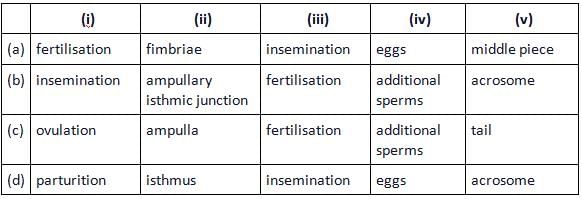
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option.
During copulation (coitus), semen is released by the penis into the vagina and is called (i) . The ovum released by the ovary is transported to the (ii) where (iii) takes place. During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of (iv) . The secretions of the (v) help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum.
During copulation (coitus), semen is released by the penis into the vagina and is called (i) . The ovum released by the ovary is transported to the (ii) where (iii) takes place. During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum and induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of (iv) . The secretions of the (v) help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Insemination is the process of the release of semen by the penis into the vagina during copulation. The sperm is released into the female reproductive part. This sperm released travels through the cervix enters to the ureter and reached the junction of the isthmus and ampulla and this is the region of fertilization or fusion. the sperm and the ovum should be transported to this junction at the same time. Zona pellucida that contacts the sperm brings about changes in the egg membrane and blocks the entry of additional sperms as a result. The secretions of the acrosome a part of the head of the sperm that includes enzymes to penetrate the ovum helps the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum.
So, the correct option is '(i) - insemination, (ii) - ampullary isthmic junction, (iii) - fertilization, (iv) - additional sperms, (v) - acrosome'.
The ligaments help the ovaries to be in place by:- a)Forming a connection with the pelvic wall and uterine wall
- b)Forming a connection with the pelvic wall
- c)Forming a connection with the uterine wall
- d)Forming a connection with the ovarian walls
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Forming a connection with the pelvic wall and uterine wall
b)
Forming a connection with the pelvic wall
c)
Forming a connection with the uterine wall
d)
Forming a connection with the ovarian walls

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The ligaments that support the ovaries help to keep them in place by forming connections with both the pelvic wall and the uterine wall. These ligaments ensure that the ovaries remain properly positioned within the female reproductive system.
The sperms undergo physiological maturation, acquiring increased motility and fertilizing capacity in- a)seminiferous tubules
- b)vasa efferentia
- c)epididymis
- d)vagina.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sperms undergo physiological maturation, acquiring increased motility and fertilizing capacity in
a)
seminiferous tubules
b)
vasa efferentia
c)
epididymis
d)
vagina.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In the head of the epididymis, the sperms undergo physiological maturation, acquiring increased motility and fertilizing capacity.
A human female is born with a million of eggs(primary oocyte) at the time of birth, only some 500 eggs get a chance of maturity. What is the destiny of rest of the eggs?- a)Rest of the eggs differentiate back to thecal and granulosa cells
- b)Rest of the eggs nurture the dominant follicular cell
- c)Rest of the eggs move out of the ovary and are destroyed by leucocytes
- d)Rest of the eggs break down and are absorbed i.e., degenerative follicular atresia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A human female is born with a million of eggs(primary oocyte) at the time of birth, only some 500 eggs get a chance of maturity. What is the destiny of rest of the eggs?
a)
Rest of the eggs differentiate back to thecal and granulosa cells
b)
Rest of the eggs nurture the dominant follicular cell
c)
Rest of the eggs move out of the ovary and are destroyed by leucocytes
d)
Rest of the eggs break down and are absorbed i.e., degenerative follicular atresia
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The total number of follicles in two ovaries of a normal young adult woman is about four lakhs but only about 500 eggs reach maturity because many ovarian follicles (during primary oocyte stage) undergo degeneration. This degenerative process of follicles is called follicular atresia and such follicles are known as atretic follicles.
Below is given the unorganised list of some important events in the human female reproductive cycle. Identify the correct sequence of these events and select the correct option.
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
- a)(i)→(iv)→(iii)→(v)→(ii)
- b)(ii)→(i)→(iii)→(iv)→(v)
- c)(iii)→(i)→(iv)→(ii)→(v)
- d)(i)→(iii)→(v)→(iv)→(ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Below is given the unorganised list of some important events in the human female reproductive cycle. Identify the correct sequence of these events and select the correct option.
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
a)
(i)→(iv)→(iii)→(v)→(ii)
b)
(ii)→(i)→(iii)→(iv)→(v)
c)
(iii)→(i)→(iv)→(ii)→(v)
d)
(i)→(iii)→(v)→(iv)→(ii)
|
|
Akash Menon answered |
(iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii)
Explanation:
The sequence of events in the human female reproductive cycle is as follows:
1. Secretion of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland
2. Growth of the follicle in the ovary
3. Ovulation, where the mature egg is released from the ovary
4. Growth of the corpus luteum, which is the remains of the follicle after ovulation
5. Sudden increase in the levels of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) which triggers ovulation
Therefore, the correct sequence of events is (iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii).
Explanation:
The sequence of events in the human female reproductive cycle is as follows:
1. Secretion of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland
2. Growth of the follicle in the ovary
3. Ovulation, where the mature egg is released from the ovary
4. Growth of the corpus luteum, which is the remains of the follicle after ovulation
5. Sudden increase in the levels of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) which triggers ovulation
Therefore, the correct sequence of events is (iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii).
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a mature human testis is- a)spermatogonia → spermatocyte → spermatid → sperms
- b)spermatid → spermatocyte → spermatogonia → sperms
- c)spermatogonia → spermatid → spermatocyte → sperms
- d)spermatocyte → spermatogonia → spermatid → sperms
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of spermatogenetic stages leading to the formation of sperms in a mature human testis is
a)
spermatogonia → spermatocyte → spermatid → sperms
b)
spermatid → spermatocyte → spermatogonia → sperms
c)
spermatogonia → spermatid → spermatocyte → sperms
d)
spermatocyte → spermatogonia → spermatid → sperms
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In human males, the primordial germ cells divide mitotically and produce spermatogonia. Some of the spermatogonia grow into large primary spermatocytes. Each primary spermatocyte undergoes first maturation division which is a reductional (meiotic) one. Thus, the primary spermatocyte divides into two haploid daughter cells called secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte now undergoes second maturation division which is a mitotic one. Thus, each secondary spermatocyte gives rise to two spermatids that undergo transformation to form two sperms. Overall, two secondary spermatocytes give rise to four sperms.
The nutritive cells found in seminiferous tubules are- a)Leydig's cells
- b)atretic follicular cells
- c)Sertoli cells
- d)chromaffin cells.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The nutritive cells found in seminiferous tubules are
a)
Leydig's cells
b)
atretic follicular cells
c)
Sertoli cells
d)
chromaffin cells.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Wall of each seminiferous tubule is formed of a single layered germinal epithelium. Majority of cells in this epithelium are male germ cells and at centain places, there are persent tall Sertoli cells. These cells act as nurse cells providing nutrition to the developing sperms.
Which one is correct for mammalian testis?- a)Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells
- b)Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells and Seminiferous tubules
- c)Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells
- d)Graffian follicles, Leydig's cells and Seminiferous tubules
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is correct for mammalian testis?
a)
Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells
b)
Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells and Seminiferous tubules
c)
Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells
d)
Graffian follicles, Leydig's cells and Seminiferous tubules
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Graafian follicles are present in human ovaries.
Consider the following statements each with two blanks.
(A) Seminiferous tubules produce (i) while Leydig's cells produce (ii).
(B) In females, urethra is small and conducts (iii) while in males it conducts urine and (iv).
(C) The process of formation of spermatozoa from spermatogonia is called (v) and the process of maturation of spermatids into spermatozoa is called (vi).
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (i) to (vi) in the statements?- a)(i) -spermatozoa, (ii)-testosterone, (v)-spermatogenesis, (vi)-spermiogenesis
- b)(i) -testosterone, (ii)-spermatozoa, (iii)-urine, (iv)-semen
- c)(i)-estrogen, (ii)-testosterone, (v)-spermiogenesis, (vi)-spermatogenesis
- d)(iii) -urine, (iv)-semen, (v)-spermiogenesis, (vi)-spermatogenesis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements each with two blanks.
(A) Seminiferous tubules produce (i) while Leydig's cells produce (ii).
(B) In females, urethra is small and conducts (iii) while in males it conducts urine and (iv).
(C) The process of formation of spermatozoa from spermatogonia is called (v) and the process of maturation of spermatids into spermatozoa is called (vi).
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (i) to (vi) in the statements?
(A) Seminiferous tubules produce (i) while Leydig's cells produce (ii).
(B) In females, urethra is small and conducts (iii) while in males it conducts urine and (iv).
(C) The process of formation of spermatozoa from spermatogonia is called (v) and the process of maturation of spermatids into spermatozoa is called (vi).
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (i) to (vi) in the statements?
a)
(i) -spermatozoa, (ii)-testosterone, (v)-spermatogenesis, (vi)-spermiogenesis
b)
(i) -testosterone, (ii)-spermatozoa, (iii)-urine, (iv)-semen
c)
(i)-estrogen, (ii)-testosterone, (v)-spermiogenesis, (vi)-spermatogenesis
d)
(iii) -urine, (iv)-semen, (v)-spermiogenesis, (vi)-spermatogenesis
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The seminiferous tubules are the location of the production of spermatozoa or sperms in the testicular lobule. The Leydig cells (interstitial cells) outside the seminiferous tubule synthesize and secrete testicular hormones called androgens or testosterone. Spermatogenesis is the process of immature male germ cells (spermatogonia) develop into mature sperms or spermatozoa. After this process, the conversion of the four equal haploid spermatids into spermatozoa (sperms) is called spermiogenesis.
So, the correct option is '(i)-spermatozoa, (ii)-testosterone, (v)-spermatogenesis, (vi)-spermiogenesis'.
Seminal plasma in humans is rich in- a)Fructose and certain enzymes but poor in calcium
- b)Fructose and calcium but has no enzyme
- c)Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes
- d)Glucose and certain enzymes but has no calcium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma in humans is rich in
a)
Fructose and certain enzymes but poor in calcium
b)
Fructose and calcium but has no enzyme
c)
Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes
d)
Glucose and certain enzymes but has no calcium
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Secretion of seminal vesicle, prostrate gland and bulbourethral gland Constitute seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes.
Which one is released from the ovary?- a)Primary oocyte
- b)Secondary oocyte
- c)Graafian follicle
- d)Oogonium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is released from the ovary?
a)
Primary oocyte
b)
Secondary oocyte
c)
Graafian follicle
d)
Oogonium
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Female gamete is released from the ovary in the secondary oocyte stage by rupturing the wall of the ovary.
Read the following statements about menstrual cycle and select two correct statements.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about menstrual cycle and select two correct statements.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iv)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy. During pregnancy, the levels of estrogen and progesterone are high in the blood, which are required for the maintenance of uterus and thus, menstruation does not occur. On 14th day of the menstrual cycle, there is rapid increase in LH (called LH surge), that induces ovulation. The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones and pituitary hormones. If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates by 16th week of pregnancy.
The last process that leads to pregnancy is called _________- a)fertilization
- b)cleavage
- c)lactation
- d)implantation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The last process that leads to pregnancy is called _________
a)
fertilization
b)
cleavage
c)
lactation
d)
implantation
|
|
Sanjana Reddy answered |
Implantation
Implantation is the final process that leads to pregnancy. It occurs when the fertilized egg, known as the blastocyst, attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. This process is essential for the embryo to receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother's body so it can continue to develop.
Key points:
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes several divisions to form a ball of cells called a blastocyst.
- The blastocyst travels through the fallopian tube and reaches the uterus, where it must implant into the thickened lining of the uterus known as the endometrium.
- Implantation usually occurs around 6-10 days after fertilization.
- Once the blastocyst is successfully implanted, it begins to release hormones that signal to the mother's body that she is pregnant.
- The placenta starts to develop, connecting the mother and the embryo and allowing for the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Implantation is a critical step in the process of pregnancy, as without successful implantation, the embryo will not be able to survive and develop. It marks the beginning of a complex and miraculous journey of growth and development that ultimately leads to the birth of a new life.
Implantation is the final process that leads to pregnancy. It occurs when the fertilized egg, known as the blastocyst, attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. This process is essential for the embryo to receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother's body so it can continue to develop.
Key points:
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes several divisions to form a ball of cells called a blastocyst.
- The blastocyst travels through the fallopian tube and reaches the uterus, where it must implant into the thickened lining of the uterus known as the endometrium.
- Implantation usually occurs around 6-10 days after fertilization.
- Once the blastocyst is successfully implanted, it begins to release hormones that signal to the mother's body that she is pregnant.
- The placenta starts to develop, connecting the mother and the embryo and allowing for the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Implantation is a critical step in the process of pregnancy, as without successful implantation, the embryo will not be able to survive and develop. It marks the beginning of a complex and miraculous journey of growth and development that ultimately leads to the birth of a new life.
Which of the following contains the actual genetic part of a sperm?- a)Whole of it
- b)Tail
- c)Middle piece
- d)Head
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following contains the actual genetic part of a sperm?
a)
Whole of it
b)
Tail
c)
Middle piece
d)
Head
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Head of the sperm is anterior, broad, flattened and oval structure. It consists of two parts, posterior large nucleus and anterior small cap-like acrosome. The nucleus consists of condensed DNA and basic proteins.
The given figure depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of the human female reproductive system. Which set of three parts out of I -VI have been correctly identified?- a)(II) endometrium, (III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae
- b)(III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae, (V) cervix
- c)(IV) oviducal funnel, (V)uterus,(VI)cervix
- d)(I) perimetrium, (II) myometrium, (III) Fallopian tube
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of the human female reproductive system. Which set of three parts out of I -VI have been correctly identified?
a)
(II) endometrium, (III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae
b)
(III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae, (V) cervix
c)
(IV) oviducal funnel, (V)uterus,(VI)cervix
d)
(I) perimetrium, (II) myometrium, (III) Fallopian tube
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
In the given figure, I-endometrium, II-perimetrium, III-infundibulum, IV-fimbriae, V-cervix, VI-vagina.
Given below are four statements (i)-(iv) regarding embryonic development in humans.
(i) Cleavage divisions bring about considerable increase in the mass of protoplasm.
(ii) With more cleavage divisions, the resultant blastomeres become smaller and smaller.
(iii) The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into two layers, trophoblast and endometrium.
(iv) Cleavage divisions result in a solid ball of cells called morula.
Which of the above two statements are correct?- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are four statements (i)-(iv) regarding embryonic development in humans.
(i) Cleavage divisions bring about considerable increase in the mass of protoplasm.
(ii) With more cleavage divisions, the resultant blastomeres become smaller and smaller.
(iii) The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into two layers, trophoblast and endometrium.
(iv) Cleavage divisions result in a solid ball of cells called morula.
Which of the above two statements are correct?
(i) Cleavage divisions bring about considerable increase in the mass of protoplasm.
(ii) With more cleavage divisions, the resultant blastomeres become smaller and smaller.
(iii) The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into two layers, trophoblast and endometrium.
(iv) Cleavage divisions result in a solid ball of cells called morula.
Which of the above two statements are correct?
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Cleavage is a series of rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote, characterised by absence of growth in daughter cells, which converts a single celled zygote into a multicellular structure called blastocyst. It starts in the Fallopian tube and is holoblastic. Interphase in cleavage division is short and don not involve growth so that the resulting blastomeres become smaller in size as their number increases. During cleavage, at 8-16 celled stage, a solid ball of cells called morula (as it look like mulberry) is formed.
Prostate glands are located below- a)gubernaculum
- b)seminal vesicles
- c)epididymis
- d)bulbourethral glands
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Prostate glands are located below
a)
gubernaculum
b)
seminal vesicles
c)
epididymis
d)
bulbourethral glands
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The prostate gland (small and walnut-shaped) is located beneath the seminal vesicle and secretes a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. The prostate is just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?- a)Progesterone
- b)Estrogen
- c)FSH
- d)FSH-RH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?
a)
Progesterone
b)
Estrogen
c)
FSH
d)
FSH-RH
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Progesterone is required for the maintenance of the endometrial lining of the uterus. As soon as the production of progesterone is reduced due to reduction in the production of LH from anterior lobe of the pituitary, the endometrium of the uterus breaks down and menstruation begins.
Study the graph carefully and correlate the hormone levels on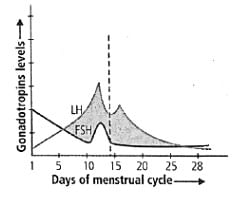 (i) 1-5 days
(i) 1-5 days
(ii) 12-14 days
(iii) 25-28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised).- a)(i) LH decreases and FSH increases
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level maintained and FSH level increases - b)(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH decreases and FSH increases
(iii) LH level increases and FSH level maintained - c)(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained - d)(i) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the graph carefully and correlate the hormone levels on

(i) 1-5 days
(ii) 12-14 days
(iii) 25-28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised).
(ii) 12-14 days
(iii) 25-28 days (if the ovum is not fertilised).
a)
(i) LH decreases and FSH increases
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level maintained and FSH level increases
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level maintained and FSH level increases
b)
(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH decreases and FSH increases
(iii) LH level increases and FSH level maintained
(ii) LH decreases and FSH increases
(iii) LH level increases and FSH level maintained
c)
(i) LH increases and FSH decreases
(ii) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
(ii) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
d)
(i) LH peaks and FSH peaks
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained
(ii) LH increases and FSH decreases
(iii) LH level decreases and FSH level maintained

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The menstrual cycle is a series of cyclic physiological changes that take place in the female primates. It is regulated by the various hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen, progesterone. The follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates the development of follicles which secretes estrogen. The rise in the level of estrogen stimulates the thickening of the endometrium in the uterus. LH is secreted by the pituitary gland which causes ovulation. The rise in LH level is followed by the rise in the progesterone which is responsible for developing the follicles into corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone which is necessary for the maintenance of the uterus lining for implantation. The rise in progesterone and estrogen results in the decrease of FSH and LH. If there is no pregnancy, then the level of progesterone and estrogen decreases which results in the breaking of the endometrium i.e., menstrual flow. After the start of menstruation, the level of FSH and LH rises to start the new cycle.
Lower narrow end of uterus is called - a)urethra
- b)cervix
- c)clitoris
- d)vulva
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lower narrow end of uterus is called
a)
urethra
b)
cervix
c)
clitoris
d)
vulva
|
|
Shalini Ahuja answered |
Understanding the Cervix
The cervix is an essential part of the female reproductive system. It serves as a crucial passage between the uterus and the vagina.
Location and Structure
- The cervix is located at the lower narrow end of the uterus.
- It connects the uterus to the vagina, forming a vital part of the birth canal.
- Structurally, the cervix is cylindrical and has a small opening called the cervical canal.
Functions of the Cervix
- Menstrual Flow: The cervix allows menstrual fluid to exit the uterus during menstruation.
- Sperm Passage: During intercourse, the cervix facilitates the entry of sperm into the uterus.
- Protection: It acts as a barrier to protect the uterus from infections, with its mucus changing in consistency throughout the menstrual cycle.
Role During Pregnancy
- The cervix plays a critical role in maintaining pregnancy by remaining closed to protect the developing fetus.
- During labor, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
Common Misconceptions
- The cervix is often confused with other structures:
- Urethra: The tube that carries urine from the bladder.
- Clitoris: A part of the external female genitalia involved in sexual arousal.
- Vulva: The external part of the female genitalia.
In conclusion, the cervix is a pivotal structure within the female reproductive system, functioning to connect and protect the uterus while facilitating reproduction.
The cervix is an essential part of the female reproductive system. It serves as a crucial passage between the uterus and the vagina.
Location and Structure
- The cervix is located at the lower narrow end of the uterus.
- It connects the uterus to the vagina, forming a vital part of the birth canal.
- Structurally, the cervix is cylindrical and has a small opening called the cervical canal.
Functions of the Cervix
- Menstrual Flow: The cervix allows menstrual fluid to exit the uterus during menstruation.
- Sperm Passage: During intercourse, the cervix facilitates the entry of sperm into the uterus.
- Protection: It acts as a barrier to protect the uterus from infections, with its mucus changing in consistency throughout the menstrual cycle.
Role During Pregnancy
- The cervix plays a critical role in maintaining pregnancy by remaining closed to protect the developing fetus.
- During labor, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
Common Misconceptions
- The cervix is often confused with other structures:
- Urethra: The tube that carries urine from the bladder.
- Clitoris: A part of the external female genitalia involved in sexual arousal.
- Vulva: The external part of the female genitalia.
In conclusion, the cervix is a pivotal structure within the female reproductive system, functioning to connect and protect the uterus while facilitating reproduction.
The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation, called colostrum, is essential for the new born as colostrums contains:- a)Large amount of glucose
- b)Anti-infective antibodies
- c)Fats
- d)Various hormones
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation, called colostrum, is essential for the new born as colostrums contains:
a)
Large amount of glucose
b)
Anti-infective antibodies
c)
Fats
d)
Various hormones

|
Bs Academy answered |
The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called colostrum which contains several antibodies absolutely essential to develop resistance for the new born babies.
During oogenesis, each diploid , primary oocyte produces- a)four functional sperms
- b)two functional eggs and two polar bodies
- c)four functional polar bodies
- d)one functional egg and three polar bodies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During oogenesis, each diploid , primary oocyte produces
a)
four functional sperms
b)
two functional eggs and two polar bodies
c)
four functional polar bodies
d)
one functional egg and three polar bodies
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In human females, certain cells in the germinal epithelium divide by mitosis to produce a large number of oogonia (diploid). The oogonia multiply by mitotic divisions to form primary oocytes (diploid). Each primary oocyte undergoes two maturation divisions. In the first meiotic division the primary oocyte divides into two very unequal haploid daughter cells- a large secondary oocyte and a small first polar body. In the second maturation division (mitotic), the first polar body may divide to form two second polar bodies and the secondary oocyte divides to form two unequal daughter cells, a large ootid and a small polar body. The ootid grows into a haploid ovum. Thus, from one oogonium, one ovum and three polar bodies are formed.
So, the correct answer is 'One functional egg and three polar bodies'.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given.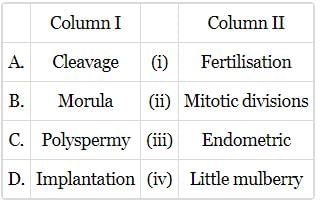
- a)A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (i), D - (iii)
- b)A - (i), B - (iv), C - (ii), D - (iii)
- c)A - (iv), B - (ii), C - (i), D - (iii)
- d)A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given.

a)
A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (i), D - (iii)
b)
A - (i), B - (iv), C - (ii), D - (iii)
c)
A - (iv), B - (ii), C - (i), D - (iii)
d)
A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i)

|
Navina Rajavelu answered |
Epididymis is located on the….of the testis.- a)Anterior surface
- b)Posterior surface
- c)Lateral surface
- d)Anterolateral surface
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Anterior surface
b)
Posterior surface
c)
Lateral surface
d)
Anterolateral surface

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The epididymis is located on the posterior surface of the testis, where it plays a key role in the storage and maturation of sperm.
Read the following statements about the uterus and identify which are correct and which are incorrect:Statement A: The uterus is single and is also known as the womb.
Statement B: The shape of the uterus is like an inverted pear and is supported by ligaments attached to the pelvic wall.
Statement C: The cervix opens directly into the uterine cavity, bypassing the vagina.
Statement D: The wall of the uterus has three layers: perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium.
Statement E: The myometrium is responsible for strong contractions during the menstrual cycle.
Statement F: The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle.- a)Correct: A, D, E, F; Incorrect: B, C
- b)Correct: A, B, C, D; Incorrect: E, F
- c)Correct: A, C, D, F; Incorrect: B, E
- d)Correct: A, B, D, F; Incorrect: C, E
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about the uterus and identify which are correct and which are incorrect:
Statement A: The uterus is single and is also known as the womb.
Statement B: The shape of the uterus is like an inverted pear and is supported by ligaments attached to the pelvic wall.
Statement C: The cervix opens directly into the uterine cavity, bypassing the vagina.
Statement D: The wall of the uterus has three layers: perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium.
Statement E: The myometrium is responsible for strong contractions during the menstrual cycle.
Statement F: The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle.
Statement B: The shape of the uterus is like an inverted pear and is supported by ligaments attached to the pelvic wall.
Statement C: The cervix opens directly into the uterine cavity, bypassing the vagina.
Statement D: The wall of the uterus has three layers: perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium.
Statement E: The myometrium is responsible for strong contractions during the menstrual cycle.
Statement F: The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle.
a)
Correct: A, D, E, F; Incorrect: B, C
b)
Correct: A, B, C, D; Incorrect: E, F
c)
Correct: A, C, D, F; Incorrect: B, E
d)
Correct: A, B, D, F; Incorrect: C, E

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- Statement A is correct: The uterus is indeed single and is known as the womb.
- Statement B is correct: The uterus is shaped like an inverted pear and is supported by ligaments attached to the pelvic wall.
- Statement C is incorrect: The cervix opens into the vagina, not directly into the uterine cavity.
- Statement D is correct: The uterus has three layers: perimetrium (external), myometrium (middle), and endometrium (inner).
- Statement E is incorrect: The myometrium exhibits strong contractions during delivery, not during the menstrual cycle.
- Statement F is correct: The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle.
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct statements.
(i) hPL plays a major role in parturition.
(ii) Fetus shows movements first time in the 7th month of pregnancy.
(iii) Signal for parturition comes from fully developed fetus and placenta.
(iv) Embryo's heart is formed by the 3rd month of pregnancy.- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(iii) only
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct statements.
(i) hPL plays a major role in parturition.
(ii) Fetus shows movements first time in the 7th month of pregnancy.
(iii) Signal for parturition comes from fully developed fetus and placenta.
(iv) Embryo's heart is formed by the 3rd month of pregnancy.
(i) hPL plays a major role in parturition.
(ii) Fetus shows movements first time in the 7th month of pregnancy.
(iii) Signal for parturition comes from fully developed fetus and placenta.
(iv) Embryo's heart is formed by the 3rd month of pregnancy.
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(iii) only
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Signal for parturition comes from fully developed fetus and placenta. Oxytocin and relaxis play major role in parturition fetus shows movements first time during fifth month pregnancy. Embryo's hearth is formed after the first month pregnancy.
For human female which of the following is incorrect?- a)Menstrual cycle takes 28 days on an average
- b)Menopause occurs at 45−55 years of age
- c)The eggs released during pregnancy die
- d)Menstruation takes 4 days on an average
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For human female which of the following is incorrect?
a)
Menstrual cycle takes 28 days on an average
b)
Menopause occurs at 45−55 years of age
c)
The eggs released during pregnancy die
d)
Menstruation takes 4 days on an average
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
During pregnancy, high levels of progesterone inhibits FSH and LH secretion. In absence of these hormones, there is no chance of ovulation and thus no pregnancy.
During the development of embryo, which of the following occurs first?- a)Differentiation of organ
- b)Differentiation of tissue
- c)Differentiation of organ system
- d)Differentiation of cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During the development of embryo, which of the following occurs first?
a)
Differentiation of organ
b)
Differentiation of tissue
c)
Differentiation of organ system
d)
Differentiation of cells
|
|
Mahi Mukherjee answered |
Differentiation of Cells
During the development of an embryo, the process of differentiation of cells occurs first. This is an essential stage in embryonic development where cells become specialized and acquire distinct functions. The differentiation of cells is a carefully regulated process that allows the embryo to develop into a complex organism with various specialized tissues and organs.
Process of Differentiation
The process of cell differentiation involves various molecular and genetic mechanisms that determine the fate of each cell. This process begins shortly after fertilization when the zygote, a single-celled organism, undergoes multiple rounds of cell division. As the cells divide, they start to differentiate into specific cell types.
Stem Cells
Initially, the cells in the embryo are undifferentiated and are known as stem cells. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to give rise to different types of specialized cells. They can divide and produce more stem cells or differentiate into specific cell types depending on the signals they receive from their environment.
Cell Fate Determination
The fate of a cell is determined by a combination of intrinsic factors, such as its genetic makeup, and extrinsic factors, such as signals from neighboring cells and the surrounding environment. These signals can activate specific genes and cellular pathways, leading to the development of different cell types.
Sequential Differentiation
During embryonic development, cells first differentiate into primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. From these germ layers, different tissues and organs develop. The process of differentiation occurs in a sequential manner, with the formation of basic tissues preceding the development of more complex organs.
Formation of Tissues and Organs
Once cells have differentiated into specific cell types, they organize themselves into tissues with similar functions. For example, cells that have differentiated into muscle cells come together to form muscle tissue, while cells that have differentiated into nerve cells form nervous tissue.
Conclusion
In summary, the differentiation of cells is the first step in the development of an embryo. Through a complex process regulated by genetic and environmental factors, cells acquire specific identities and functions. This initial differentiation sets the stage for the subsequent development of tissues, organs, and organ systems in the growing embryo.
During the development of an embryo, the process of differentiation of cells occurs first. This is an essential stage in embryonic development where cells become specialized and acquire distinct functions. The differentiation of cells is a carefully regulated process that allows the embryo to develop into a complex organism with various specialized tissues and organs.
Process of Differentiation
The process of cell differentiation involves various molecular and genetic mechanisms that determine the fate of each cell. This process begins shortly after fertilization when the zygote, a single-celled organism, undergoes multiple rounds of cell division. As the cells divide, they start to differentiate into specific cell types.
Stem Cells
Initially, the cells in the embryo are undifferentiated and are known as stem cells. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to give rise to different types of specialized cells. They can divide and produce more stem cells or differentiate into specific cell types depending on the signals they receive from their environment.
Cell Fate Determination
The fate of a cell is determined by a combination of intrinsic factors, such as its genetic makeup, and extrinsic factors, such as signals from neighboring cells and the surrounding environment. These signals can activate specific genes and cellular pathways, leading to the development of different cell types.
Sequential Differentiation
During embryonic development, cells first differentiate into primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. From these germ layers, different tissues and organs develop. The process of differentiation occurs in a sequential manner, with the formation of basic tissues preceding the development of more complex organs.
Formation of Tissues and Organs
Once cells have differentiated into specific cell types, they organize themselves into tissues with similar functions. For example, cells that have differentiated into muscle cells come together to form muscle tissue, while cells that have differentiated into nerve cells form nervous tissue.
Conclusion
In summary, the differentiation of cells is the first step in the development of an embryo. Through a complex process regulated by genetic and environmental factors, cells acquire specific identities and functions. This initial differentiation sets the stage for the subsequent development of tissues, organs, and organ systems in the growing embryo.
Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as- a)chorion
- b)zona pellucida
- c)corona radiata
- d)vitelline membrane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as
a)
chorion
b)
zona pellucida
c)
corona radiata
d)
vitelline membrane
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Immediately after ovulation, the layer that forms around the ovum is called corona radiata. It is formed by the granulosa cells of cumulus oophorus. Corona radiata probably increases the likelihood that the ovum will be picked up in the uterine tube.
Breast feeding suspends pregnancy due to- a)Post pregnancy lower levels of FSH and LH
- b)Post pregnancy higher levels of FSH and LH which puts a negative check on ovulation
- c)Inhibiting the release of FSH by prolactin and thus countering the effects of FSH on the ovarian follicles
- d)Increasing the release of inhibin by prolactin and thus countering the effects of FSH on the ovarian follicles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Breast feeding suspends pregnancy due to
a)
Post pregnancy lower levels of FSH and LH
b)
Post pregnancy higher levels of FSH and LH which puts a negative check on ovulation
c)
Inhibiting the release of FSH by prolactin and thus countering the effects of FSH on the ovarian follicles
d)
Increasing the release of inhibin by prolactin and thus countering the effects of FSH on the ovarian follicles
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
During breast feeding, prolactin hormone (required for the release of milk) present in the blood, inhibits the release of LH from pituitary. This will counter the effect of LH on the ovarian follicles and therefore no ovulation will occur. Hence, no pregnancy occurs during this period
Fertilisation in humans is practically feasible only if:- a)The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary-isthmic junction of the fallopian tube
- b)The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary-isthmic junction of the cervix
- c)The sperms are transported into the cervix within 48 hours of the release of the ovum in the uterus
- d)The sperms are transported into the vagina just after the release of the ovum in the fallopian tube
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary-isthmic junction of the fallopian tube
b)
The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary-isthmic junction of the cervix
c)
The sperms are transported into the cervix within 48 hours of the release of the ovum in the uterus
d)
The sperms are transported into the vagina just after the release of the ovum in the fallopian tube
|
|
Nandini Sharma answered |
Fertilisation in Humans
Fertilisation in humans is a critical process that occurs under specific conditions within the female reproductive system. The successful union of sperm and ovum is essential for conception.
Optimal Site for Fertilisation
- The ampullary-isthmic junction of the fallopian tube is the ideal location for fertilisation.
- This region provides the optimal environment for sperm and egg to meet, ensuring a high chance of successful fertilisation.
Timing of Ovum Release
- The ovum is typically released during ovulation, which occurs approximately once a menstrual cycle.
- The sperm must reach the ampullary-isthmic junction shortly after ovulation to increase the likelihood of fertilisation.
Simultaneous Transport
- For fertilisation to be feasible, both the ovum and sperm need to be present at the ampullary-isthmic junction at the same time.
- Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, but the ovum is viable for only about 12-24 hours after ovulation.
Conclusion
- Thus, option 'A' is correct: the simultaneous transport of sperm and ovum to the ampullary-isthmic junction is crucial for fertilisation.
- Other options do not provide the correct environment or timing necessary for successful fertilisation, highlighting the importance of precise conditions in human reproduction.
Fertilisation in humans is a critical process that occurs under specific conditions within the female reproductive system. The successful union of sperm and ovum is essential for conception.
Optimal Site for Fertilisation
- The ampullary-isthmic junction of the fallopian tube is the ideal location for fertilisation.
- This region provides the optimal environment for sperm and egg to meet, ensuring a high chance of successful fertilisation.
Timing of Ovum Release
- The ovum is typically released during ovulation, which occurs approximately once a menstrual cycle.
- The sperm must reach the ampullary-isthmic junction shortly after ovulation to increase the likelihood of fertilisation.
Simultaneous Transport
- For fertilisation to be feasible, both the ovum and sperm need to be present at the ampullary-isthmic junction at the same time.
- Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, but the ovum is viable for only about 12-24 hours after ovulation.
Conclusion
- Thus, option 'A' is correct: the simultaneous transport of sperm and ovum to the ampullary-isthmic junction is crucial for fertilisation.
- Other options do not provide the correct environment or timing necessary for successful fertilisation, highlighting the importance of precise conditions in human reproduction.
External genital organs are developed during _________- a)First trimester
- b)First month of pregnancy
- c)Second trimester
- d)Third trimester
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
External genital organs are developed during _________
a)
First trimester
b)
First month of pregnancy
c)
Second trimester
d)
Third trimester

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Limbs and digits, along with external genitalia, are formed during the first trimester.
- This is a period of 12 weeks after pregnancy.
The correct sequence of the various phases of a typical menstrual cycle is:
- a)Menstrual → Follicular → Secretory → Ovulatory
- b)Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory
- c)Ovulatory → Follicular → Secretory → Menstrual
- d)Menstrual → Secretory → Follicular → Ovulatory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of the various phases of a typical menstrual cycle is:
a)
Menstrual → Follicular → Secretory → Ovulatory
b)
Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory
c)
Ovulatory → Follicular → Secretory → Menstrual
d)
Menstrual → Secretory → Follicular → Ovulatory

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The correct sequence of the various phases of a typical menstrual cycle is:
- Menstrual
- Follicular
- Ovulatory
- Secretory
Explanation:
- Menstrual phase: Shedding of the uterine lining
- Follicular phase: Maturation of follicles in the ovary
- Ovulatory phase: Release of an egg from the ovary
- Secretory phase: Preparation of the uterus for possible pregnancy by thickening the lining
Therefore, the correct sequence is Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory, which corresponds to option B.
- Menstrual
- Follicular
- Ovulatory
- Secretory
Explanation:
- Menstrual phase: Shedding of the uterine lining
- Follicular phase: Maturation of follicles in the ovary
- Ovulatory phase: Release of an egg from the ovary
- Secretory phase: Preparation of the uterus for possible pregnancy by thickening the lining
Therefore, the correct sequence is Menstrual → Follicular → Ovulatory → Secretory, which corresponds to option B.
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized, which one of the following is unlikely?- a)Corpus luteum will degenrate
- b) Progesterone secretion rapidly declines
- c)Estrogen secretion further decreases
- d)Primary follicle starts developing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized, which one of the following is unlikely?
a)
Corpus luteum will degenrate
b)
Progesterone secretion rapidly declines
c)
Estrogen secretion further decreases
d)
Primary follicle starts developing

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized the estrogen secretion does not decrease further while corpus luteum will disintegrate. Primary follicle starts developing and progesterone secretion rapidly declines.
Topic in NCERT: MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Line in NCERT: "In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates."
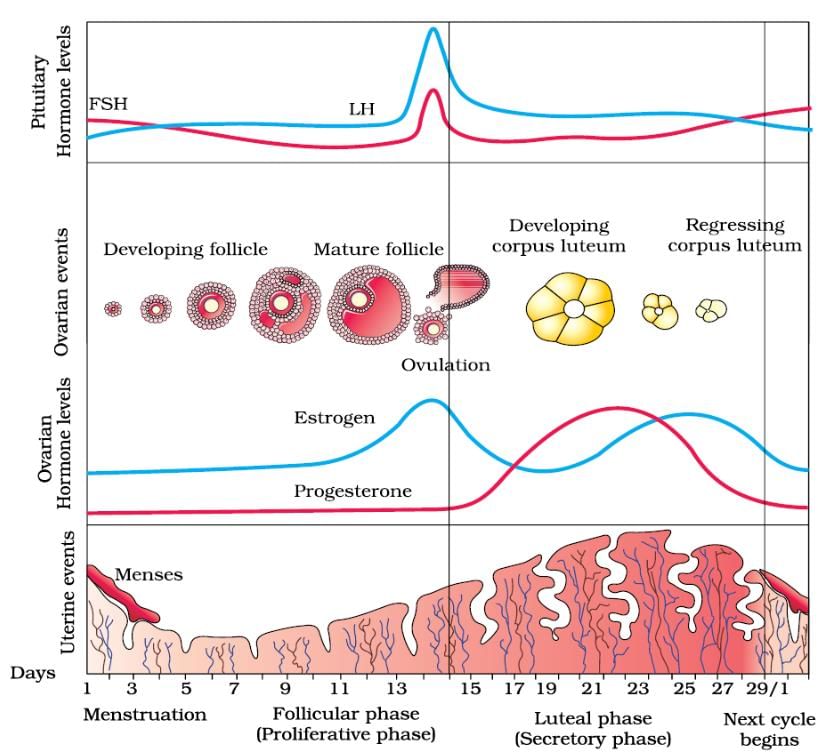

Urine test during pregnancy determines the presence- a)human chorionic gonadotropin hormone
- b)estrogen
- c)progesterone
- d)luteinising hormone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Urine test during pregnancy determines the presence
a)
human chorionic gonadotropin hormone
b)
estrogen
c)
progesterone
d)
luteinising hormone
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
During pregnancy, human chorionic gonadotropin hormone is released by trophoblastic cells which passes out in urine. Thus, if this hormone appears in urine test, it means the woman is pregnant. This hormone maintains the corpus luteum and stimulates it to secrete progesterone which is required for the maintenance of the uterus.
How many sperms are formed from 4 primary spermatocytes?- a)4
- b)1
- c)16
- d)32
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many sperms are formed from 4 primary spermatocytes?
a)
4
b)
1
c)
16
d)
32
|
|
Anjali Ahuja answered |
Formation of Sperms
During the process of spermatogenesis, spermatogonial cells undergo several stages of division and differentiation to ultimately form mature sperm cells known as spermatozoa. The process begins with the division of spermatogonial cells called primary spermatocytes.
Formation of Primary Spermatocytes
Primary spermatocytes are formed through mitotic division of spermatogonial cells. Each spermatogonial cell undergoes DNA replication and cell division to form two identical daughter cells. One of these daughter cells remains as a spermatogonial cell, while the other undergoes further differentiation to form a primary spermatocyte. Therefore, for every spermatogonial cell that divides, one primary spermatocyte is formed.
Division of Primary Spermatocytes
Primary spermatocytes then enter the first meiotic division, also known as meiosis I. During this division, each primary spermatocyte undergoes DNA replication followed by two rounds of cell division, resulting in the formation of four haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes. These secondary spermatocytes contain only half the number of chromosomes as the original primary spermatocytes.
Formation of Sperm Cells
The secondary spermatocytes then enter the second meiotic division, also known as meiosis II. During this division, each secondary spermatocyte undergoes another round of DNA replication followed by cell division. This division results in the formation of four haploid spermatids. Each spermatid contains half the number of chromosomes as the original primary spermatocytes and is morphologically distinct from the primary spermatocytes.
Conclusion
In summary, four primary spermatocytes are formed from spermatogonial cells through mitotic division. Each primary spermatocyte then undergoes two rounds of meiotic division to form four haploid spermatids. Therefore, four spermatids or sperm cells are formed from the original four primary spermatocytes. Hence, the correct answer is option C) 16.
During the process of spermatogenesis, spermatogonial cells undergo several stages of division and differentiation to ultimately form mature sperm cells known as spermatozoa. The process begins with the division of spermatogonial cells called primary spermatocytes.
Formation of Primary Spermatocytes
Primary spermatocytes are formed through mitotic division of spermatogonial cells. Each spermatogonial cell undergoes DNA replication and cell division to form two identical daughter cells. One of these daughter cells remains as a spermatogonial cell, while the other undergoes further differentiation to form a primary spermatocyte. Therefore, for every spermatogonial cell that divides, one primary spermatocyte is formed.
Division of Primary Spermatocytes
Primary spermatocytes then enter the first meiotic division, also known as meiosis I. During this division, each primary spermatocyte undergoes DNA replication followed by two rounds of cell division, resulting in the formation of four haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes. These secondary spermatocytes contain only half the number of chromosomes as the original primary spermatocytes.
Formation of Sperm Cells
The secondary spermatocytes then enter the second meiotic division, also known as meiosis II. During this division, each secondary spermatocyte undergoes another round of DNA replication followed by cell division. This division results in the formation of four haploid spermatids. Each spermatid contains half the number of chromosomes as the original primary spermatocytes and is morphologically distinct from the primary spermatocytes.
Conclusion
In summary, four primary spermatocytes are formed from spermatogonial cells through mitotic division. Each primary spermatocyte then undergoes two rounds of meiotic division to form four haploid spermatids. Therefore, four spermatids or sperm cells are formed from the original four primary spermatocytes. Hence, the correct answer is option C) 16.
The roots that originate from the base of the stem are:- a)Fibrous roots
- b)Primary roots
- c)Prop roots
- d)Lateral roots
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The roots that originate from the base of the stem are:
a)
Fibrous roots
b)
Primary roots
c)
Prop roots
d)
Lateral roots
|
|
Mahi Nair answered |
Fibrous Roots:
Fibrous roots are the roots that originate from the base of the stem. These are also known as adventitious roots. They are formed from the stem or leaves of the plant. Fibrous roots are found in monocots, whereas dicots have a taproot system.
Characteristics of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots are thin and hair-like.
- They grow in a cluster or group.
- They do not penetrate deep into the soil.
- They are responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- They provide anchorage to the plant.
Examples of Plants with Fibrous Roots:
- Grass
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- Sugarcane
Importance of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots help in preventing soil erosion.
- They increase the surface area of the root system, which enhances the absorption of water and nutrients.
- They provide support to the plant, preventing it from falling.
- Fibrous roots help in stabilizing the soil and preventing landslides.
Conclusion:
Fibrous roots are important for the growth and development of plants. They play a vital role in providing support, preventing soil erosion, and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
Fibrous roots are the roots that originate from the base of the stem. These are also known as adventitious roots. They are formed from the stem or leaves of the plant. Fibrous roots are found in monocots, whereas dicots have a taproot system.
Characteristics of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots are thin and hair-like.
- They grow in a cluster or group.
- They do not penetrate deep into the soil.
- They are responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- They provide anchorage to the plant.
Examples of Plants with Fibrous Roots:
- Grass
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- Sugarcane
Importance of Fibrous Roots:
- Fibrous roots help in preventing soil erosion.
- They increase the surface area of the root system, which enhances the absorption of water and nutrients.
- They provide support to the plant, preventing it from falling.
- Fibrous roots help in stabilizing the soil and preventing landslides.
Conclusion:
Fibrous roots are important for the growth and development of plants. They play a vital role in providing support, preventing soil erosion, and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
Rakesh and Reshma have difficulty conceiving a baby. They consulted a sex therapist. Sperm count of Rakesh was normal but the doctor observed that the motility of his sperm was less. What part of sperm do you think has the issue?- a)Tail
- b)Mitochondria
- c)Nucleus
- d)Acrosome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rakesh and Reshma have difficulty conceiving a baby. They consulted a sex therapist. Sperm count of Rakesh was normal but the doctor observed that the motility of his sperm was less. What part of sperm do you think has the issue?
a)
Tail
b)
Mitochondria
c)
Nucleus
d)
Acrosome

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
- They are essential for producing energy required for movement of tail.
- This is essential for movement through the genital tract and oviduct before sperm encounters the egg.
- Rakesh might have less or poorly functional mitochondria, which prevent his normal count of sperms from moving along the genital tract.
After birth, colostrum is released from mammary glands which is rich in- a)fat and low in proteins
- b)proteins and low in fat
- c)proteins, antibodies and low in fat
- d)proteins, fat and low in antibodies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
After birth, colostrum is released from mammary glands which is rich in
a)
fat and low in proteins
b)
proteins and low in fat
c)
proteins, antibodies and low in fat
d)
proteins, fat and low in antibodies
|
|
Aarav Shah answered |
Colostrum Composition:
Colostrum is the first milk produced by the mammary glands after giving birth. It is a crucial fluid that provides essential nutrients and antibodies to newborns. The composition of colostrum is unique and differs from mature milk.
Rich in Proteins:
- Colostrum is rich in proteins such as immunoglobulins, specifically IgA, IgG, and IgM. These antibodies play a vital role in providing passive immunity to the newborn, protecting them from infections.
- Other proteins present in colostrum include lactoferrin, lysozyme, and cytokines, which help in boosting the immune system of the infant.
Low in Fat:
- Compared to mature milk, colostrum is lower in fat content. This is because colostrum is designed to be easily digestible for the newborn's developing digestive system.
- The low-fat content in colostrum ensures that the infant receives essential nutrients without burdening their digestive system.
Other Components:
- Apart from proteins and antibodies, colostrum also contains growth factors like insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which promote the growth and development of the newborn.
- Colostrum is also rich in vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates, which provide additional nourishment to the infant.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, colostrum is rich in proteins and antibodies, making it a vital source of nutrition and immunity for newborns. Its unique composition, with a high protein content and low fat content, ensures that the infant receives the necessary nutrients and protection during the early stages of life.
Colostrum is the first milk produced by the mammary glands after giving birth. It is a crucial fluid that provides essential nutrients and antibodies to newborns. The composition of colostrum is unique and differs from mature milk.
Rich in Proteins:
- Colostrum is rich in proteins such as immunoglobulins, specifically IgA, IgG, and IgM. These antibodies play a vital role in providing passive immunity to the newborn, protecting them from infections.
- Other proteins present in colostrum include lactoferrin, lysozyme, and cytokines, which help in boosting the immune system of the infant.
Low in Fat:
- Compared to mature milk, colostrum is lower in fat content. This is because colostrum is designed to be easily digestible for the newborn's developing digestive system.
- The low-fat content in colostrum ensures that the infant receives essential nutrients without burdening their digestive system.
Other Components:
- Apart from proteins and antibodies, colostrum also contains growth factors like insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which promote the growth and development of the newborn.
- Colostrum is also rich in vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates, which provide additional nourishment to the infant.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, colostrum is rich in proteins and antibodies, making it a vital source of nutrition and immunity for newborns. Its unique composition, with a high protein content and low fat content, ensures that the infant receives the necessary nutrients and protection during the early stages of life.
At what stage of life is oogenesis initiated in a humanfemale?- a)At puberty
- b)During menarch
- c)During menopause
- d)During embryonic development
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At what stage of life is oogenesis initiated in a humanfemale?
a)
At puberty
b)
During menarch
c)
During menopause
d)
During embryonic development
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Oogenesis is the process of formation of functional haploid ova from the diploid germinal cells in the ovary. Oogenesis begins during embryonic development but is completed only at puberty of the secondary oocyte with the sperm.
What is the correct sequence for parturition to occur?- a)Signal from fetus and placenta → Uterine contractions → Release of oxytocin → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Parturition
- b)Uterine contractions → Release of oxytocin → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Signal from fetus and placenta → Parturition
- c)Signal from fetus and placenta → Release of oxytocin → Uterine contractions → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Parturition
- d)Release of oxytocin → Uterine contractions → Signal from fetus and placenta → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Parturition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct sequence for parturition to occur?
a)
Signal from fetus and placenta → Uterine contractions → Release of oxytocin → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Parturition
b)
Uterine contractions → Release of oxytocin → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Signal from fetus and placenta → Parturition
c)
Signal from fetus and placenta → Release of oxytocin → Uterine contractions → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Parturition
d)
Release of oxytocin → Uterine contractions → Signal from fetus and placenta → Rise in oxytocin secretion → Powerful contractions → Parturition

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Parturition starts with the signal released by the fetus and the placenta.
- These act on the pituitary to release oxytocin.
- Oxytocin acts as a stimulant leading to contractions of the uterine muscles.
- The uterine contractions feedbacks to release more oxytocin from the pituitary.
- This results in more powerful contractions of the uterus until the baby is delivered in the process of parturition.
If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from- a)testes to epididymis
- b)epididymis to vas deferens
- c)ovary to uterus
- d)vagina to uterus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from
a)
testes to epididymis
b)
epididymis to vas deferens
c)
ovary to uterus
d)
vagina to uterus
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Vasa efferentia are fine ciliated ductules that arise from the seminiferous tubules of testis (where sperms are formed) and open into epididymis which is a mass of long narrow closely coiled tubule lying along the inner side of testis. Epididymis stores the sperms. Thus, if vasa efferentia get blocked, sperms will not be transposed from testes to epididymis.
Given below are three statements each with one or two blanks. Select the option which correctly fills up the blanks in any two statements.
(A) In human beings, menstrual cycle ceases around 50 years of age; this is termed as (i).
(B) The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called (i) which contains several (ii) absolutely essential to develop resistance for the new-born babies.
(C) At the completion of the (i) division, the primary oocyte divides into secondary oocyte and (ii).- a)(A)−(i) menarche; (B)−(i) lactation, (ii) minerals
- b)(B)−(i) colostrum, (ii) antibodies, (C)−(i) first meiotic, (ii) first polar body
- c)(A)−(i) menopause; (C)−(i) second meiotic, (ii) second polar body
- d)(A)−(i) menopause; (B)−(i) corpus luteum, (ii) antibodies
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are three statements each with one or two blanks. Select the option which correctly fills up the blanks in any two statements.
(A) In human beings, menstrual cycle ceases around 50 years of age; this is termed as (i).
(B) The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called (i) which contains several (ii) absolutely essential to develop resistance for the new-born babies.
(C) At the completion of the (i) division, the primary oocyte divides into secondary oocyte and (ii).
(A) In human beings, menstrual cycle ceases around 50 years of age; this is termed as (i).
(B) The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called (i) which contains several (ii) absolutely essential to develop resistance for the new-born babies.
(C) At the completion of the (i) division, the primary oocyte divides into secondary oocyte and (ii).
a)
(A)−(i) menarche; (B)−(i) lactation, (ii) minerals
b)
(B)−(i) colostrum, (ii) antibodies, (C)−(i) first meiotic, (ii) first polar body
c)
(A)−(i) menopause; (C)−(i) second meiotic, (ii) second polar body
d)
(A)−(i) menopause; (B)−(i) corpus luteum, (ii) antibodies

|
EduRev NEET answered |
(A) In human beings, the menstrual cycle ceases around 50 years of age; this is termed as "menopause." Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. During menopause, the ovaries stop releasing eggs, and the levels of certain hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, decrease.
(B) The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called "colostrum." Colostrum is a specialized form of breast milk that is rich in essential nutrients and antibodies. It contains several bioactive compounds absolutely essential to develop resistance for newborn babies. These antibodies help protect the infant from infections and provide important nutrients for their early growth and development.
(C) At the completion of the "meiosis I" division, the primary oocyte divides into the "secondary oocyte" and a smaller cell called the "first polar body." Meiosis is the process by which germ cells (eggs and sperm) are formed. In meiosis I, the primary oocyte undergoes a reduction in chromosome number, resulting in the formation of the secondary oocyte and the first polar body. The secondary oocyte is the cell that can potentially be fertilized by a sperm, while the first polar body usually degenerates and does not play a direct role in reproduction.
Which of the following is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male?- a)Sperm count
- b)Sperm motility
- c)Sperm height
- d)Sperm production rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male?
a)
Sperm count
b)
Sperm motility
c)
Sperm height
d)
Sperm production rate
|
|
Lekshmi Menon answered |
Sperm height is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male. The correct answer is option 'C'. Let's discuss each option to understand why.
a) Sperm count:
Sperm count refers to the number of sperm cells present in a given sample. It is an important factor in determining male fertility because a higher sperm count increases the chances of successful fertilization. Low sperm count, also known as oligospermia, can reduce the probability of conception. Therefore, sperm count is a crucial feature for male fertility.
b) Sperm motility:
Sperm motility refers to the ability of sperm cells to swim and move effectively. It is an essential factor in fertility because sperm cells need to move through the female reproductive tract to reach the egg for fertilization. If the sperm cells do not have proper motility, they may not be able to navigate through the female reproductive system and fertilize an egg. Therefore, sperm motility is a critical feature for male fertility.
c) Sperm height:
Sperm height is not a recognized factor in determining male fertility. The concept of sperm height is not commonly used or recognized in scientific literature or medical practice. It is likely an incorrect or misleading term. As a result, sperm height does not play a role in determining male fertility.
d) Sperm production rate:
Sperm production rate refers to the rate at which sperm cells are produced by the male reproductive system. It is an essential factor in fertility because a sufficient production of healthy sperm cells is necessary for successful fertilization. If the production rate is low, it can lead to a reduced number of sperm cells available for fertilization. Therefore, sperm production rate is a crucial feature for male fertility.
In conclusion, among the options given, sperm height is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male. Sperm count, sperm motility, and sperm production rate are all important factors that contribute to male fertility.
a) Sperm count:
Sperm count refers to the number of sperm cells present in a given sample. It is an important factor in determining male fertility because a higher sperm count increases the chances of successful fertilization. Low sperm count, also known as oligospermia, can reduce the probability of conception. Therefore, sperm count is a crucial feature for male fertility.
b) Sperm motility:
Sperm motility refers to the ability of sperm cells to swim and move effectively. It is an essential factor in fertility because sperm cells need to move through the female reproductive tract to reach the egg for fertilization. If the sperm cells do not have proper motility, they may not be able to navigate through the female reproductive system and fertilize an egg. Therefore, sperm motility is a critical feature for male fertility.
c) Sperm height:
Sperm height is not a recognized factor in determining male fertility. The concept of sperm height is not commonly used or recognized in scientific literature or medical practice. It is likely an incorrect or misleading term. As a result, sperm height does not play a role in determining male fertility.
d) Sperm production rate:
Sperm production rate refers to the rate at which sperm cells are produced by the male reproductive system. It is an essential factor in fertility because a sufficient production of healthy sperm cells is necessary for successful fertilization. If the production rate is low, it can lead to a reduced number of sperm cells available for fertilization. Therefore, sperm production rate is a crucial feature for male fertility.
In conclusion, among the options given, sperm height is not an essential feature of sperms that determine the fertility of a male. Sperm count, sperm motility, and sperm production rate are all important factors that contribute to male fertility.
Which human male accessory reproductive duct receives a duct from the seminal vesicle?- a)Rete testis
- b)Vas deferens
- c)Epididymis
- d)Urethra
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Rete testis
b)
Vas deferens
c)
Epididymis
d)
Urethra

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The vas deferens is the duct that receives a duct from the seminal vesicle. The vas deferens joins with the duct from the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct, which then leads to the urethra. This process is essential for the transport of sperm and seminal fluid during ejaculation.
The third stage of parturition is called "after-birth". In this stage- a)excessive bleeding occurs
- b)fetus is born and cervix and vagina contraction to normal condition happens
- c)fetus is born and contraction of uterine wall prevents excessive bleeding
- d)placenta is expelled out
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The third stage of parturition is called "after-birth". In this stage
a)
excessive bleeding occurs
b)
fetus is born and cervix and vagina contraction to normal condition happens
c)
fetus is born and contraction of uterine wall prevents excessive bleeding
d)
placenta is expelled out
|
|
Aarav Shah answered |
Explanation:
After-birth stage:
- The after-birth stage, also known as the third stage of parturition, involves the expulsion of the placenta from the uterus after the delivery of the baby.
- This stage is crucial to prevent excessive bleeding and to ensure the mother's health and well-being post-delivery.
Process of placenta expulsion:
- After the baby is born, the uterus continues to contract to help expel the placenta.
- These contractions help detach the placenta from the uterine wall and push it out through the vagina.
- The placenta is usually expelled within 15-30 minutes after the baby is born.
Prevention of excessive bleeding:
- The contraction of the uterine wall during this stage helps in compressing the blood vessels that were connected to the placenta.
- This compression prevents excessive bleeding and helps the uterus return to its normal size.
Signs of successful after-birth stage:
- Once the placenta is expelled, the healthcare provider will examine it to ensure that it is complete.
- Any remaining tissue may need to be removed to prevent complications.
In conclusion, the after-birth stage is a critical part of the birthing process as it ensures the safe delivery of the placenta and helps prevent postpartum complications such as excessive bleeding.
After-birth stage:
- The after-birth stage, also known as the third stage of parturition, involves the expulsion of the placenta from the uterus after the delivery of the baby.
- This stage is crucial to prevent excessive bleeding and to ensure the mother's health and well-being post-delivery.
Process of placenta expulsion:
- After the baby is born, the uterus continues to contract to help expel the placenta.
- These contractions help detach the placenta from the uterine wall and push it out through the vagina.
- The placenta is usually expelled within 15-30 minutes after the baby is born.
Prevention of excessive bleeding:
- The contraction of the uterine wall during this stage helps in compressing the blood vessels that were connected to the placenta.
- This compression prevents excessive bleeding and helps the uterus return to its normal size.
Signs of successful after-birth stage:
- Once the placenta is expelled, the healthcare provider will examine it to ensure that it is complete.
- Any remaining tissue may need to be removed to prevent complications.
In conclusion, the after-birth stage is a critical part of the birthing process as it ensures the safe delivery of the placenta and helps prevent postpartum complications such as excessive bleeding.
hCG, hPL and relaxin are produced in women- a)at the time of puberty
- b)only during pregnancy
- c)at the time of menopause
- d)during menstruation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
hCG, hPL and relaxin are produced in women
a)
at the time of puberty
b)
only during pregnancy
c)
at the time of menopause
d)
during menstruation
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
During pregnancy, placenta acts as an endocrine gland and secretes some hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), chorionic thyrotropin, chorionic corticotropin and relaxin.
Which of the following hormones is not a secretion product of human placenta?- a)Human chorionic gonadotropin
- b)Prolactin
- c)Estrogen
- d)Progesterone
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormones is not a secretion product of human placenta?
a)
Human chorionic gonadotropin
b)
Prolactin
c)
Estrogen
d)
Progesterone
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Prolactin is secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland. After parturition, secretion and storage of milk in mammary glands is under the influence of this hormone.
Chapter doubts & questions for Human Reproduction - Biology Class 12 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Human Reproduction - Biology Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









