All Exams >
Grade 12 >
Biology for Grade 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Reproduction in Organisms for Grade 12 Exam
The chances of survival of the young one is greater in ______ animals
- a)Terrestrial
- b)Oviparous
- c)Viviparous
- d)Aerial
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chances of survival of the young one is greater in ______ animals
a)
Terrestrial
b)
Oviparous
c)
Viviparous
d)
Aerial
|
|
Sagar Sen answered |
Viviparous animals have a greater chance of survival of their young ones compared to other animals.
Explanation:
Viviparous animals are those animals that give birth to live young. They retain the developing embryo within their body and provide all the necessary nutrients and protection until the young ones are fully developed. The young ones are then born through the birth canal.
The chances of survival of the young ones of viviparous animals are greater due to the following reasons:
1. Nourishment: The young ones receive all the necessary nutrients from the mother. They are protected within the mother's body, and this ensures that they have access to all the necessary nutrients and oxygen required for their growth and development.
2. Protection: The mother protects the young ones from predators and other environmental factors that may harm them.
3. Adaptability: The young ones of viviparous animals are born fully developed and are better adapted to survive in their environment. They are able to move and feed on their own, which increases their chances of survival.
4. Maternal Care: Viviparous animals exhibit maternal care, which involves the mother providing additional protection and care to the young ones. This increases the chances of survival even further.
Therefore, viviparous animals have a greater chance of survival of their young ones compared to other animals.
Explanation:
Viviparous animals are those animals that give birth to live young. They retain the developing embryo within their body and provide all the necessary nutrients and protection until the young ones are fully developed. The young ones are then born through the birth canal.
The chances of survival of the young ones of viviparous animals are greater due to the following reasons:
1. Nourishment: The young ones receive all the necessary nutrients from the mother. They are protected within the mother's body, and this ensures that they have access to all the necessary nutrients and oxygen required for their growth and development.
2. Protection: The mother protects the young ones from predators and other environmental factors that may harm them.
3. Adaptability: The young ones of viviparous animals are born fully developed and are better adapted to survive in their environment. They are able to move and feed on their own, which increases their chances of survival.
4. Maternal Care: Viviparous animals exhibit maternal care, which involves the mother providing additional protection and care to the young ones. This increases the chances of survival even further.
Therefore, viviparous animals have a greater chance of survival of their young ones compared to other animals.
Embryo sac is formed inside______.
- a)Seed
- b)Ovule
- c)Endosperm
- d)Embryo
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Embryo sac is formed inside______.
a)
Seed
b)
Ovule
c)
Endosperm
d)
Embryo
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
An oval structure within an ovule of an angiosperm that contains the egg. Together with the fertilized egg, it develops into a seed. The embryo sac is the female gametophyte of angiosperms, consisting of eight nuclei: the egg and two adjacent and short-lived synergids that are near the micropyle (the opening where the pollen nuclei will enter), two central nuclei (which will combine with one of the pollen nuclei to form the endosperm), and three antipodal nuclei at the end of the embryo sac opposite the micropyle. Like the synergids, these nuclei degenerate at or shortly after fertilization
The product of sexual reproduction generally generatesA: Longer viability of seedsB: New genetic combination leading to variationC: Large biomassD: Prolonged dormancyCorrect answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The product of sexual reproduction generally generates
A: Longer viability of seeds
B: New genetic combination leading to variation
C: Large biomass
D: Prolonged dormancy
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
- Sexual reproduction leads to new genetic combination leading to variation in new products.
- The longer viability of seeds, prolonged dormancy and large biomass are not related to sexual reproduction.
Cleistogamous flowers are:
- a)Wind pollinated
- b)Insect pollinated
- c)Cross pollinated
- d)Self pollinated
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cleistogamous flowers are:
a)
Wind pollinated
b)
Insect pollinated
c)
Cross pollinated
d)
Self pollinated
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
- The most important event of sexual reproduction is fusion of gametes, in a process called fertilisation or syngamy.
- This process results in the formation of a zygote. If the zygote is not formed then the next generation of organisms are not produced.
Period of pregnancy is called- a)Gestation period
- b)Pre-patent period
- c)Blastulation
- d)Incubation period
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Period of pregnancy is called
a)
Gestation period
b)
Pre-patent period
c)
Blastulation
d)
Incubation period
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Pregnancy, also known as gravidity or gestation. The pregnancy period is classified into three Trimester.
They are as follows:
- First Trimester (0 to 13 Weeks).
- Second Trimester (14 to 26 Weeks) is often called the "golden period" because many of the unpleasant effects of early pregnancy disappear.
- Third Trimester (27 to 40 Weeks).
Development of fruit without fertilization is called? - a)Cell division
- b)Cell culture
- c)Parthenocarpy
- d)Parthenogenesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Development of fruit without fertilization is called?
a)
Cell division
b)
Cell culture
c)
Parthenocarpy
d)
Parthenogenesis
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- Parthenocarpy is the method of fertilizing fruit without development.
- In botany and horticulture, parthenocarpy(literally meaning "virgin fruit") is the natural or artificially induced production of fruit without fertilization of ovules, which makes the fruit seedless.
- Stenospermocarpy may also produce apparently seedless fruit, but the seeds are actually aborted while they are still small.
- Parthenocarpy (or stenospermocarpy) occasionally occurs as a mutation in nature; if it affects every flower the plant can no longer sexually reproduce but might be able to propagate by apomixis or by vegetative means.
Which of the following is a hermaphrodite?- a)Cockroach
- b)Earthworm
- c)Aphids
- d)Ant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a hermaphrodite?
a)
Cockroach
b)
Earthworm
c)
Aphids
d)
Ant
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- In biology, a hermaphrodite is an organism that has complete or partial reproductive organs and produces gametes normally associated with both male and female sexes.
- Many taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the "female" or "male." For example, the great majority of tunicates, pulmonate snails, opisthobranch snails, earthworms and slugs are hermaphrodites.
- Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species and to a lesser degree in other vertebrates. Most plants are also hermaphrodites.
Man is- a)Hermaphrodite
- b)Bisexual
- c)Protogynous
- d)Unisexual
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Man is
a)
Hermaphrodite
b)
Bisexual
c)
Protogynous
d)
Unisexual

|
Aarohi Singhania answered |
R u crazy a man is bisexual
In grafting, the portion to be grafted on the main plant is called______.
- a)Stock
- b)Scion
- c)Stem
- d)Adventitious bud
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In grafting, the portion to be grafted on the main plant is called______.
a)
Stock
b)
Scion
c)
Stem
d)
Adventitious bud

|
Neha Thakur answered |
Stock is root system while Scion is shoot system so...ans. is option 'B'
Menstrual cycle is completed in- a)28 days
- b)31 days
- c)27 days
- d)30 days
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Menstrual cycle is completed in
a)
28 days
b)
31 days
c)
27 days
d)
30 days
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The menstrual cycle starts on the first day of the menstrual period (referred to as day one) and ends the day before the next period begins. While the length of the menstrual cycle is often 28 days, it can vary between women and from one cycle to the next. It is common for women to experience cycles that last anywhere from 20 to 40 days. Cycles longer than six weeks are considered unusual.
In males, urethra carries______.
- a)Urine only
- b)Sperms only
- c)None of the above
- d)Both of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In males, urethra carries______.
a)
Urine only
b)
Sperms only
c)
None of the above
d)
Both of these
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body. In males, it has the additional function of ejaculating semen when the man reaches orgasm. When the penis is erect during sex, the flow of urine is blocked from the urethra, allowing only semen to be ejaculated at orgasm.
Which of the following organism do not shows binary fission? - a)Euglena
- b)Plasmodium
- c)Paramecium
- d)Amoeba
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organism do not shows binary fission?
a)
Euglena
b)
Plasmodium
c)
Paramecium
d)
Amoeba
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Plasmodium exhibits multiple fission..so option B
When seeds are attached to the parent plant, the type of germination is known asA: HypogealB: EpigealC: ViviparyD: OviparyCorrect answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When seeds are attached to the parent plant, the type of germination is known as
A: Hypogeal
B: Epigeal
C: Vivipary
D: Ovipary
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Usually plants multiply by dispersion of seed through agencies like air, water, bird droppings or seed simply falls on ground near the parent plant and gives rise, to a new plant.
But in certain conditions seed cannot germinate if it falls down, like in the case of marshy areas or sea coast. Mangrove plants show vivipary i.e. seeds germinate while they are still attached to the parent plant.
The seedling then, falls into water (due to increase in its weight) and develops roots. E.g. Rhizophora, Sonneratia etc.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The period from birth to death of an organism represents_________.
- A:
Juvenile period
- B:
Adulthood
- C:
Life span
- D:
Reproductive life
The answer is c.
The period from birth to death of an organism represents_________.
Juvenile period
Adulthood
Life span
Reproductive life

|
Rishika Chauhan answered |
The period from Birth of an individual to its natural death is called life span. Different organisms have different life span starting from one day to hundreds of years.
Budding is a method of asexual reproduction found in ______.- a)Hydra
- b)Sponges
- c)Penicillium
- d)Amoeba
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Budding is a method of asexual reproduction found in ______.
a)
Hydra
b)
Sponges
c)
Penicillium
d)
Amoeba
|
|
Palak Roy answered |
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops from an outgrowth or bud on the parent. This method of reproduction is found in many organisms, including some plants, fungi, and animals. In the context of this question, budding is specifically found in Hydra, which is a freshwater cnidarian.
Explanation:
Budding is a process by which a new individual develops from a small outgrowth or bud on the parent. This outgrowth grows and eventually detaches from the parent to become a separate individual. Budding is a form of asexual reproduction because the new individual is genetically identical to the parent.
Budding in Hydra:
Hydra is a small, freshwater cnidarian that exhibits budding. Hydra can reproduce both sexually and asexually, but budding is a common method of asexual reproduction in this organism. In Hydra, the bud develops as a small outgrowth on the parent's body. The bud grows and eventually detaches from the parent to become a new, independent individual.
Advantages of Budding:
Budding has several advantages as a method of reproduction:
1. It allows for rapid reproduction because new individuals can develop quickly from the parent.
2. It allows organisms to reproduce without the need for a mate, which can be beneficial in environments where mates are scarce.
3. It produces genetically identical offspring, which can be advantageous in stable environments where the parent's traits are well-suited to the environment.
Conclusion:
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction that is found in many organisms, including Hydra. This process allows for rapid reproduction and the production of genetically identical offspring. Budding is a beneficial method of reproduction in certain environments, and it is one of the ways that organisms have evolved to ensure their continued survival.
Explanation:
Budding is a process by which a new individual develops from a small outgrowth or bud on the parent. This outgrowth grows and eventually detaches from the parent to become a separate individual. Budding is a form of asexual reproduction because the new individual is genetically identical to the parent.
Budding in Hydra:
Hydra is a small, freshwater cnidarian that exhibits budding. Hydra can reproduce both sexually and asexually, but budding is a common method of asexual reproduction in this organism. In Hydra, the bud develops as a small outgrowth on the parent's body. The bud grows and eventually detaches from the parent to become a new, independent individual.
Advantages of Budding:
Budding has several advantages as a method of reproduction:
1. It allows for rapid reproduction because new individuals can develop quickly from the parent.
2. It allows organisms to reproduce without the need for a mate, which can be beneficial in environments where mates are scarce.
3. It produces genetically identical offspring, which can be advantageous in stable environments where the parent's traits are well-suited to the environment.
Conclusion:
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction that is found in many organisms, including Hydra. This process allows for rapid reproduction and the production of genetically identical offspring. Budding is a beneficial method of reproduction in certain environments, and it is one of the ways that organisms have evolved to ensure their continued survival.
In diploid organism, gametes are produced by meiosis division but in haploid organism gametes are produced by: - a)Mitosis
- b)Meiosis
- c)Both a and b
- d)Reduction division
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In diploid organism, gametes are produced by meiosis division but in haploid organism gametes are produced by:
a)
Mitosis
b)
Meiosis
c)
Both a and b
d)
Reduction division

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Gametogenesis refers to the formation of the gametes.
- In sexual reproduction formation of gametes is very important since offspring is formed only after the fusion of the gametes.
- Gamete transfer refers to bringing the 2 gametes together.
Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 10 of topic "1.2.1 Pre-fertilisation Events” of chapter 1.
How many daughter cells are produced when a bacterial cell reproduces asexually?- a)2
- b)1
- c)4
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many daughter cells are produced when a bacterial cell reproduces asexually?
a)
2
b)
1
c)
4
d)
3
|
|
Ananya Basak answered |
Bacterial cell reproduction
Bacterial cell reproduction is a process by which bacterial cells divide and produce new cells. Bacteria can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In asexual reproduction, bacterial cells divide and produce identical daughter cells.
Number of daughter cells
When a bacterial cell reproduces asexually, it produces two identical daughter cells. Therefore, the correct answer is option a) 2.
Process of asexual reproduction
The process of asexual reproduction in bacteria is called binary fission. It involves the following steps:
1. DNA replication: The bacterial cell replicates its DNA.
2. Cell elongation: The bacterial cell elongates and increases in size.
3. Chromosome segregation: The replicated DNA moves to opposite ends of the cell.
4. Cell division: The cell membrane and cell wall grow inward and divide the cell into two identical daughter cells.
Advantages of asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction in bacteria has several advantages, including:
1. Rapid reproduction: Bacteria can reproduce quickly and produce large numbers of offspring.
2. Adaptability: Bacteria can adapt quickly to changing environments through mutations in their DNA.
3. Efficiency: Asexual reproduction is a very efficient way for bacteria to produce offspring, as there is no need for mating or the exchange of genetic material.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a bacterial cell produces two identical daughter cells when it reproduces asexually through binary fission. Asexual reproduction in bacteria has several advantages, including rapid reproduction, adaptability, and efficiency.
Bacterial cell reproduction is a process by which bacterial cells divide and produce new cells. Bacteria can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In asexual reproduction, bacterial cells divide and produce identical daughter cells.
Number of daughter cells
When a bacterial cell reproduces asexually, it produces two identical daughter cells. Therefore, the correct answer is option a) 2.
Process of asexual reproduction
The process of asexual reproduction in bacteria is called binary fission. It involves the following steps:
1. DNA replication: The bacterial cell replicates its DNA.
2. Cell elongation: The bacterial cell elongates and increases in size.
3. Chromosome segregation: The replicated DNA moves to opposite ends of the cell.
4. Cell division: The cell membrane and cell wall grow inward and divide the cell into two identical daughter cells.
Advantages of asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction in bacteria has several advantages, including:
1. Rapid reproduction: Bacteria can reproduce quickly and produce large numbers of offspring.
2. Adaptability: Bacteria can adapt quickly to changing environments through mutations in their DNA.
3. Efficiency: Asexual reproduction is a very efficient way for bacteria to produce offspring, as there is no need for mating or the exchange of genetic material.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a bacterial cell produces two identical daughter cells when it reproduces asexually through binary fission. Asexual reproduction in bacteria has several advantages, including rapid reproduction, adaptability, and efficiency.
External fertilisation occurs in the majority of- a)Algae
- b)Fungi
- c)Mosses
- d)Liverworts
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
External fertilisation occurs in the majority of
a)
Algae
b)
Fungi
c)
Mosses
d)
Liverworts
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
External Fertilization. External fertilization usually occurs in aquatic environments where both eggs and sperm are released into the water. After the sperm reaches the egg, fertilization takes place.
Which of the following is developed by parthenogenesis:- a)Drones
- b)queen honey bee
- c)worker honey bee
- d)both b and c
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is developed by parthenogenesis:
a)
Drones
b)
queen honey bee
c)
worker honey bee
d)
both b and c
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Since drones are developed without fertilization of egg, they are developed by parthenogenesis. The male honey bees are called drones. Drones are produced through parthenogenesis, which occurs when an egg is not fertilised. Queen and worker honey bees are developed by fertilization of egg.
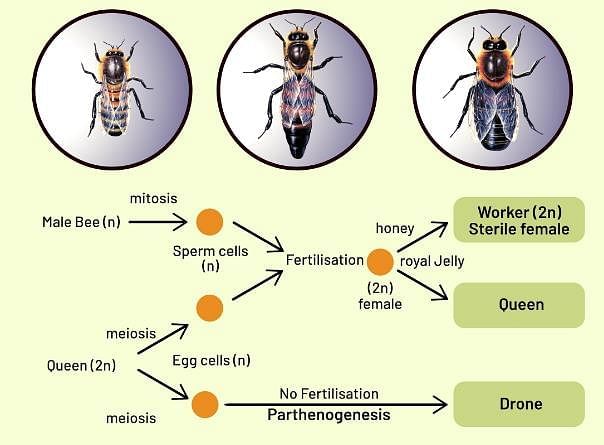
Fig: Parthenogenesis in Bees
The female gametophyte in angiosperm is also known as_______. - a)Egg
- b)Embryo sac
- c)Carpel
- d)Ovule
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The female gametophyte in angiosperm is also known as_______.
a)
Egg
b)
Embryo sac
c)
Carpel
d)
Ovule
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The female gametophyte is also commonly called the embryo sac or megagametophyte. The male gametophyte, also called the pollen grain or microgametophyte, develops within the anther and consists of two sperm cells encased within a vegetative cell (Gifford and Foster, 1989).
Hibiscus flower is ________.- a)Bisexual
- b)Unisexual
- c)Neuter
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hibiscus flower is ________.
a)
Bisexual
b)
Unisexual
c)
Neuter
d)
None of these
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The flowers that contain both male and female reproductive organs in same flower are called bisexual. In Hibiscus flower both stamen and carpel are present within same flower.
During oogenesis, each diploid oocyte produces _____.
- a)Two functional egg and two polar bodies
- b)Four functional polar bodies
- c)One functional egg and three polar bodies
- d)Four functional ova
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During oogenesis, each diploid oocyte produces _____.
a)
Two functional egg and two polar bodies
b)
Four functional polar bodies
c)
One functional egg and three polar bodies
d)
Four functional ova
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
In human females, the process that produces mature eggs is called oogenesis. Just one egg is produced from the four haploid cells that result from meiosis.
Three polar bodies may form during oogenesis. These polar bodies will not form mature gametes.
Oogenesis begins before birth and is not completed until after fertilization. Oogenesis begins when oogonia, which are the immature eggs that form in the ovaries before birth and have the diploid number of chromosomes, undergo mitosis to form primary oocytes, also with the diploid number. Oogenesis proceeds as a primary oocyte undergoes the first cell division of meiosis to form secondary oocytes with the haploid number of chromosomes. A secondary oocyte only undergoes the second meiotic cell division to form a haploid ovum if it is fertilized by a sperm.
Which of the following is prevented by unisexuality? - a)Both xenogamy and geitonogamy
- b)Autogamy and geitonogamy
- c)Autogamy but not geitonogamy
- d)Geitonogamy but not xenogamy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is prevented by unisexuality?
a)
Both xenogamy and geitonogamy
b)
Autogamy and geitonogamy
c)
Autogamy but not geitonogamy
d)
Geitonogamy but not xenogamy
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Unisexuality promotes or favours the cross pollination (xenogamy) and prevent self pollination (Autogamy). Geitnogamy involve transfer of pollen grain between two flowers of the same plant so unisexuality will not prevent geitonogamy.
When offspring is produced by a single parent with or without the involvement of gametes formation, than the reproduction is ________?- a)Artificial propagation
- b)Vegetative propagation
- c)Sexual reproduction
- d)Asexual reproduction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When offspring is produced by a single parent with or without the involvement of gametes formation, than the reproduction is ________?
a)
Artificial propagation
b)
Vegetative propagation
c)
Sexual reproduction
d)
Asexual reproduction
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
When offspring is produced by a single parent with or without the involvement of gamete formation, the reproduction is asexual. When two parents (opposite sex) participate in the reproductive process and also involve fusion of male and female gametes, it is called sexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction do not involves: - a)Fusion of gametes
- b)Haploid gametes
- c)Generally two parents
- d)Faster mode of reproduction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sexual reproduction do not involves:
a)
Fusion of gametes
b)
Haploid gametes
c)
Generally two parents
d)
Faster mode of reproduction
|
|
Gopal Singh answered |
Sexual reproduction is slow and complex process because there is gametogenesis, gamete transfer, fertilisation, embryogenesis, parturition..... as these all processes are time consuming.
Ginger is vegetatively propagated through:- a)Rhizome
- b)Bulbil
- c)Leaf buds
- d)Offset
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ginger is vegetatively propagated through:
a)
Rhizome
b)
Bulbil
c)
Leaf buds
d)
Offset
|
|
Ankita Deshpande answered |
Propagation of Ginger through Rhizome:
Ginger is a tropical spice crop that is very popular for its medicinal and culinary properties. It is a perennial herb that reproduces vegetatively through rhizomes. Rhizomes are underground stems that produce roots and shoots from their nodes. The rhizomes of Ginger are fleshy, thick, and aromatic, and they are the most common method of propagation for this plant.
The following are the steps involved in propagating Ginger through rhizomes:
1. Selection of Rhizomes: The first step in propagating Ginger through rhizomes is to select healthy and disease-free rhizomes. The rhizomes should be firm, plump, and free from any signs of decay or damage.
2. Preparation of Rhizomes: Once the rhizomes have been selected, they should be cleaned and cut into pieces. Each piece should have at least one bud or eye, which will sprout into a new plant.
3. Soil Preparation: The soil should be well-drained, loose, and fertile. It should be enriched with organic matter such as compost or manure.
4. Planting of Rhizomes: The prepared rhizome pieces should be planted in the soil with the eye facing upwards. The planting depth should be around 2-3 cm.
5. Watering and Care: After planting, the soil should be watered thoroughly. The newly planted rhizomes should be kept moist, but not waterlogged. They should be protected from direct sunlight and strong winds until they have established.
6. Harvesting: Ginger plants take around 8-10 months to mature. The rhizomes can be harvested once the leaves turn yellow and start to wither. The harvested rhizomes can be used fresh or dried for storage.
In conclusion, Ginger is vegetatively propagated through rhizomes. This method is simple, reliable, and yields high-quality plants. By following the above steps, one can successfully propagate Ginger through rhizomes and enjoy the benefits of this versatile spice crop.
Ginger is a tropical spice crop that is very popular for its medicinal and culinary properties. It is a perennial herb that reproduces vegetatively through rhizomes. Rhizomes are underground stems that produce roots and shoots from their nodes. The rhizomes of Ginger are fleshy, thick, and aromatic, and they are the most common method of propagation for this plant.
The following are the steps involved in propagating Ginger through rhizomes:
1. Selection of Rhizomes: The first step in propagating Ginger through rhizomes is to select healthy and disease-free rhizomes. The rhizomes should be firm, plump, and free from any signs of decay or damage.
2. Preparation of Rhizomes: Once the rhizomes have been selected, they should be cleaned and cut into pieces. Each piece should have at least one bud or eye, which will sprout into a new plant.
3. Soil Preparation: The soil should be well-drained, loose, and fertile. It should be enriched with organic matter such as compost or manure.
4. Planting of Rhizomes: The prepared rhizome pieces should be planted in the soil with the eye facing upwards. The planting depth should be around 2-3 cm.
5. Watering and Care: After planting, the soil should be watered thoroughly. The newly planted rhizomes should be kept moist, but not waterlogged. They should be protected from direct sunlight and strong winds until they have established.
6. Harvesting: Ginger plants take around 8-10 months to mature. The rhizomes can be harvested once the leaves turn yellow and start to wither. The harvested rhizomes can be used fresh or dried for storage.
In conclusion, Ginger is vegetatively propagated through rhizomes. This method is simple, reliable, and yields high-quality plants. By following the above steps, one can successfully propagate Ginger through rhizomes and enjoy the benefits of this versatile spice crop.
Every sexually reproducing organism, including human being begin life as a single cell called? - a)Gamete
- b)Embryo
- c)Zygote
- d)Spore
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Every sexually reproducing organism, including human being begin life as a single cell called?
a)
Gamete
b)
Embryo
c)
Zygote
d)
Spore

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
All sexually reproducing organisms develops from single cell called zygote. Zygote is formed by fusion of male and female gametes. Traits from male and female are present in the zygote.
Apomixis means_____. - a)Formation of seeds without fusion of gamete
- b)Sexual reproduction
- c)Formation of seedless fruit
- d)Vegetative propagation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Apomixis means_____.
a)
Formation of seeds without fusion of gamete
b)
Sexual reproduction
c)
Formation of seedless fruit
d)
Vegetative propagation
|
|
Gayatri Chauhan answered |
Cucurbits and coconuts are examples of Monoecious plants.
Explanation:
Monoecious plants are those plants that have separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The term "monoecious" is derived from the Greek words "monos" meaning "single" and "oikos" meaning "house". In monoecious plants, the male flowers and female flowers are found on the same plant, but they are usually located in different parts of the plant.
Examples of monoecious plants:
1. Cucurbits: Cucurbits are a family of plants that includes cucumber, pumpkin, watermelon, and squash. They are monoecious plants, which means that they have separate male and female flowers on the same plant.
2. Coconuts: Coconuts are also monoecious plants. The male flowers are located at the top of the tree, while the female flowers are located at the base of the tree.
Advantages of monoecy:
1. Monoecy helps in self-pollination, which ensures the production of seeds and fruit.
2. It also reduces the need for cross-pollination, which can be beneficial in areas where pollinators are scarce.
3. Monoecy helps in the conservation of genetic diversity, as it allows for the formation of viable seeds without the need for genetic exchange between plants.
Explanation:
Monoecious plants are those plants that have separate male and female flowers on the same plant. The term "monoecious" is derived from the Greek words "monos" meaning "single" and "oikos" meaning "house". In monoecious plants, the male flowers and female flowers are found on the same plant, but they are usually located in different parts of the plant.
Examples of monoecious plants:
1. Cucurbits: Cucurbits are a family of plants that includes cucumber, pumpkin, watermelon, and squash. They are monoecious plants, which means that they have separate male and female flowers on the same plant.
2. Coconuts: Coconuts are also monoecious plants. The male flowers are located at the top of the tree, while the female flowers are located at the base of the tree.
Advantages of monoecy:
1. Monoecy helps in self-pollination, which ensures the production of seeds and fruit.
2. It also reduces the need for cross-pollination, which can be beneficial in areas where pollinators are scarce.
3. Monoecy helps in the conservation of genetic diversity, as it allows for the formation of viable seeds without the need for genetic exchange between plants.
A flower having both male and female reproductive parts are termed as______. - a)Heterolithic
- b)Monoecious
- c)Homolithic
- d)Dioecious
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A flower having both male and female reproductive parts are termed as______.
a)
Heterolithic
b)
Monoecious
c)
Homolithic
d)
Dioecious
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Monoecious: having both the male and female reproductive organs on the same plant
Dioecious: having the male and female reproductive organs on separate plants.
Hermaphrodite: having flowers containing both anther and stamen. It’s also known as bisexual plant.
Pollen grains are able to withstand extremes of temperature because there exine is composed of_____
- a)sporopollenin
- b)pectin
- c)cutin
- d)cellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pollen grains are able to withstand extremes of temperature because there exine is composed of_____
a)
sporopollenin
b)
pectin
c)
cutin
d)
cellulose
|
|
Mansi Nambiar answered |
Correct Option is : A
Solution :
The exine is composed of sporopollenin which is the polymer that is resistant to oxidation and leaching.
The development of root and shoot in tissue culture is determined by ______- a)Temperature
- b)Nutrients
- c)Auxin and cytokinin ratio
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The development of root and shoot in tissue culture is determined by ______
a)
Temperature
b)
Nutrients
c)
Auxin and cytokinin ratio
d)
None of the above
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Tissue culture involves the culture of totipotent cells in nutrient media under sterile conditions. The mass of the totipotent cell is known as a callus. It is unorganized actively dividing the mass of cells maintained in culture. It has the meristematic cell which has an ample amount of cytoplasm to trigger cell division. It is treated with growth hormones to allow cell division and differentiation. Callus when treated with nutrient media with a high percentage of auxin it promotes rooting and when it is treated with media with a high percentage of cytokinin it stimulates cell maturation, differentiation and finally, promotes the development of stem.
What is common between vegetative propagation and apomixes? - a)Both bypass the flowering plants
- b)Both are applicable to only dicots
- c)Both occurs throughout the year
- d)Both produce progeny identical to parents
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is common between vegetative propagation and apomixes?
a)
Both bypass the flowering plants
b)
Both are applicable to only dicots
c)
Both occurs throughout the year
d)
Both produce progeny identical to parents
|
|
Akshat Goyal answered |
Common Features of Vegetative Propagation and Apomixes
Both vegetative propagation and apomixes have the following common features:
1. Bypassing the Flowering Plants
Both methods do not require the involvement of flowers or sexual reproduction. They bypass the flowering plants that produce seeds and fruits through sexual reproduction.
2. Occurrence Throughout the Year
Both methods can occur at any time of the year, unlike sexual reproduction, which is season-dependent.
3. Production of Progeny Identical to Parents
Both methods produce progeny that are genetically identical to the parent plant. This is because there is no genetic recombination that occurs during sexual reproduction.
Conclusion
In summary, vegetative propagation and apomixes share common features such as bypassing flowering plants, occurring throughout the year, and producing progeny identical to parents. These methods are useful for plant propagation and have commercial applications in horticulture, agriculture, and forestry.
Both vegetative propagation and apomixes have the following common features:
1. Bypassing the Flowering Plants
Both methods do not require the involvement of flowers or sexual reproduction. They bypass the flowering plants that produce seeds and fruits through sexual reproduction.
2. Occurrence Throughout the Year
Both methods can occur at any time of the year, unlike sexual reproduction, which is season-dependent.
3. Production of Progeny Identical to Parents
Both methods produce progeny that are genetically identical to the parent plant. This is because there is no genetic recombination that occurs during sexual reproduction.
Conclusion
In summary, vegetative propagation and apomixes share common features such as bypassing flowering plants, occurring throughout the year, and producing progeny identical to parents. These methods are useful for plant propagation and have commercial applications in horticulture, agriculture, and forestry.
What are the 3 phases in a life cycle (in order)?- a)Reproductive, Senescence, Juvenile
- b)Juvenile, Senescence, Death
- c)Reproductive, Senescence, Death
- d)Juvenile, Reproductive, Senescence
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the 3 phases in a life cycle (in order)?
a)
Reproductive, Senescence, Juvenile
b)
Juvenile, Senescence, Death
c)
Reproductive, Senescence, Death
d)
Juvenile, Reproductive, Senescence
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
There are 3 phases in a life cycle:
- Juvenile phase/ vegetative phase: Period from birth to maturation of reproductive systems.
- Reproductive Phase: Period when the reproductive systems have matured and ready to produce offspring.
- Senescence: Period when the organism starts growing old and starts degrading.
The period from birth to death of an organism represents_________. - a)Juvenile period
- b)Adulthood
- c)Life span
- d)Reproductive life
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The period from birth to death of an organism represents_________.
a)
Juvenile period
b)
Adulthood
c)
Life span
d)
Reproductive life
|
|
Raghavendra Rane answered |
The period from Birth of an individual to its natural death is called life span. Different organisms have different life span starting from one day to hundreds of years.
Offset can also be described as a ______- a)Thin tuber
- b)Long rhizome
- c)Thick runner
- d)Short suckers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Offset can also be described as a ______
a)
Thin tuber
b)
Long rhizome
c)
Thick runner
d)
Short suckers
|
|
Alok Pillai answered |
Offset in plants
An offset is a type of vegetative propagation in plants, where a new plant is produced from a portion of the parent plant. This process is also known as stolon or runner formation.
Description of Offset
An offset can be described as a thick runner. A runner is a specialized stem that grows horizontally along the soil surface. It is also called a stolon or creeping stem. The runner produces adventitious roots and leaves at regular intervals, which eventually develop into a new plant. The offset is produced at the end of the runner and is a miniature replica of the parent plant.
Examples of plants that produce offsets
Many plants produce offsets as a means of reproduction. Some examples of plants that produce offsets are:
- Spider plant (Chlorophytum comosum)
- Strawberry (Fragaria spp.)
- Mother of thousands (Kalanchoe daigremontiana)
- Hen and chicks (Sempervivum tectorum)
- Spiderwort (Tradescantia spp.)
Benefits of offset propagation
Offset propagation has several benefits, such as:
- It is an easy and cost-effective way to propagate plants.
- The new plants produced from offsets are genetically identical to the parent plant.
- It is a natural way of multiplying plants without the use of seeds.
- It ensures that the desirable characteristics of the parent plant are preserved in the new plants.
Conclusion
Offset propagation is a common method of vegetative propagation in plants. It involves the production of new plants from a portion of the parent plant. The offset is produced at the end of a runner, which is a specialized stem that grows horizontally along the soil surface. The offset is a miniature replica of the parent plant and has several benefits, such as being genetically identical to the parent plant and preserving its desirable characteristics.
An offset is a type of vegetative propagation in plants, where a new plant is produced from a portion of the parent plant. This process is also known as stolon or runner formation.
Description of Offset
An offset can be described as a thick runner. A runner is a specialized stem that grows horizontally along the soil surface. It is also called a stolon or creeping stem. The runner produces adventitious roots and leaves at regular intervals, which eventually develop into a new plant. The offset is produced at the end of the runner and is a miniature replica of the parent plant.
Examples of plants that produce offsets
Many plants produce offsets as a means of reproduction. Some examples of plants that produce offsets are:
- Spider plant (Chlorophytum comosum)
- Strawberry (Fragaria spp.)
- Mother of thousands (Kalanchoe daigremontiana)
- Hen and chicks (Sempervivum tectorum)
- Spiderwort (Tradescantia spp.)
Benefits of offset propagation
Offset propagation has several benefits, such as:
- It is an easy and cost-effective way to propagate plants.
- The new plants produced from offsets are genetically identical to the parent plant.
- It is a natural way of multiplying plants without the use of seeds.
- It ensures that the desirable characteristics of the parent plant are preserved in the new plants.
Conclusion
Offset propagation is a common method of vegetative propagation in plants. It involves the production of new plants from a portion of the parent plant. The offset is produced at the end of a runner, which is a specialized stem that grows horizontally along the soil surface. The offset is a miniature replica of the parent plant and has several benefits, such as being genetically identical to the parent plant and preserving its desirable characteristics.
There is no natural death in single-celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because- a)They are microscopic.
- b)They cannot reproduce asexually.
- c)They reproduce by binary fission.
- d)The parental body is distributed among the offspring.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There is no natural death in single-celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because
a)
They are microscopic.
b)
They cannot reproduce asexually.
c)
They reproduce by binary fission.
d)
The parental body is distributed among the offspring.
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
(D) There is no natural death in single celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because the parental body is distributed among the offspring.
Hydra reproduces asexually through- a)Sporulation
- b)Budding
- c)Fragmentation
- d)Binary fission
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydra reproduces asexually through
a)
Sporulation
b)
Budding
c)
Fragmentation
d)
Binary fission
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
Budding: Hydra reproduce asexually through budding, where a bud forms that develops into an adult and breaks away from the main body.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Senescence in most of the animals is not caused by_____. - A:Wear and tear
- B:Genetic damage
- C:Lack of Nutrition
- D:Loss of metabolism
The answer is c.
Senescence in most of the animals is not caused by_____.
A:
Wear and tear
B:
Genetic damage
C:
Lack of Nutrition
D:
Loss of metabolism
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Senescence is a natural process followed by maturity of organism. The metabolic processes of organisms start slowing down in this process leading to wear and tear of vital body organ. Nutrition does not affect the process of senescence.
In non-primate mammals like cow, sheep, rats, dogs etc., such cyclical changes during reproduction are called?
- a)Oestrus cycle
- b)Gestation period
- c)Menstrual cycle
- d)Growth cycle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In non-primate mammals like cow, sheep, rats, dogs etc., such cyclical changes during reproduction are called?
a)
Oestrus cycle
b)
Gestation period
c)
Menstrual cycle
d)
Growth cycle
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
- Sexual reproduction in mammals involves cyclic changes in the ovaries, accessory glands and the reproductive hormones during which ovum is released.
- In non-primates animals, it is called oestrus cycle and in primates including human beings it is called menstrual cycle.
Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 9 of topic “1.2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION” of chapter 1
NCERT Reference: Page no. 9 of topic “1.2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION” of chapter 1
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The period of pregnancy is known as ________.
- A:
Blastulation
- B:
Gestation period
- C:
Menstruation
- D:
Incubation period
The answer is b.
The period of pregnancy is known as ________.
Blastulation
Gestation period
Menstruation
Incubation period

|
Arshiya Choudhury answered |
The duration from implantation of fertilised eggs to uterus till birth of well-developed baby is called gestation period. It is about nine months in human beings.
The eyes of potato are___________. - a)Root buds
- b)Axillary buds
- c)Shoot buds
- d)Flower bud
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The eyes of potato are___________.
a)
Root buds
b)
Axillary buds
c)
Shoot buds
d)
Flower bud

|
Juhi Deshpande answered |
The axillary buds of the potato tuber are called eyes in common language and they are found at the nodes of the stem tuber.
In grafting, scion forms?- a)Shoot system
- b)Root system
- c)Hybrid plant
- d)New plant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In grafting, scion forms?
a)
Shoot system
b)
Root system
c)
Hybrid plant
d)
New plant
|
|
Nisha Pillai answered |
Grafting (including budding) is a process by which a portion of the shoot system or root system of the same or different plants, brought into intimate contact, unite and grow together anatomically, and interact physiologically as a single functional unit (whole plant).
Reproduction is an essential life process, which help in _____?- a)Remain alive
- b)Continuity of race
- c)Change in size
- d)Change in habitat
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Reproduction is an essential life process, which help in _____?
a)
Remain alive
b)
Continuity of race
c)
Change in size
d)
Change in habitat
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Reproduction is a characteristic feature of all living organisms. It involves the creation of organelles, cells, or organisms of the same kind. Reproduction is necessary for the survival of a particular species. During reproduction, the information for inheritance of characteristics is passed on from the parents to the offsprings in the form of DNA.
The degenerative and irreversible changes in the organism is known as_______.- a)Degradation
- b)Ageing
- c)Senescence
- d)Maturation
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The degenerative and irreversible changes in the organism is known as_______.
a)
Degradation
b)
Ageing
c)
Senescence
d)
Maturation
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Ageing is the sum total of changes in total plant or its constituents while senescence represents the degenerative and irreversible changes in the organism. In annual and biennial plants, vegetative reproductive and senescent phases can be easily identified.
But to distinguish such phases in perennial plants seems to be little difficult. If lapse of time is a criterion for ageing, annual rings formation counting in such plants can tell the age of the plants. Trees do not show the process of physiological degeneration. In trees, some parts die and some new appear.
Water hyacinth is called as terror of Bengal due to_______. - a)Broads attractive leaves and showy flower
- b)Stem is spongy and inflated petiole
- c)The roots are pinkish or brownish in colour
- d)It makes water oxygen deficient
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Water hyacinth is called as terror of Bengal due to_______.
a)
Broads attractive leaves and showy flower
b)
Stem is spongy and inflated petiole
c)
The roots are pinkish or brownish in colour
d)
It makes water oxygen deficient
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Water hyacinth is water weeds which grows very fast and covers the whole ponds in few days. Weeds absorb oxygen from the water and make it oxygen deficient that kills the fish in ponds along with other aquatic organisms.
Sexual spores produced by Penicillium- a)Conidiospores
- b)Basidiospores
- c)Ascospores
- d)Zoospores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sexual spores produced by Penicillium
a)
Conidiospores
b)
Basidiospores
c)
Ascospores
d)
Zoospores
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Penicillium is a large and difficult genus encountered almost everywhere, and usually the most abundant genus of fungi in soils. Some species of Penicillium reproduce sexually by means of asci and ascospores produced within small stony stromata.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproduction in Organisms - Biology for Grade 12 2025 is part of Grade 12 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 12 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproduction in Organisms - Biology for Grade 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 12 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 12
124 videos|215 docs|236 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












