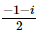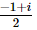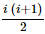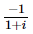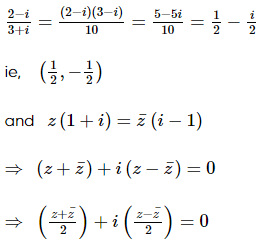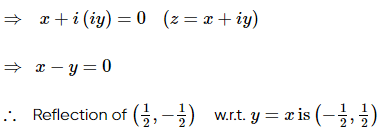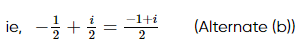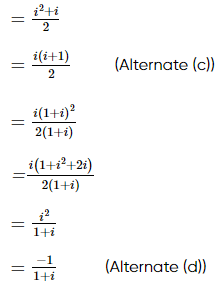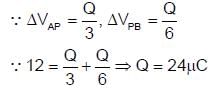All Exams >
JEE >
JEE Main & Advanced Mock Test Series 2025 >
All Questions
All questions of JEE Advanced Practice Tests for JEE Exam
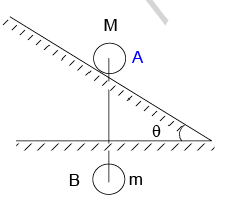
A disc ‘A’ of mass M is placed at rest on the smooth inclined surface of inclination θ. A ball B of mass m is suspended vertically from the centre of the disc A by a light inextensible string of light ℓ as shown in the figure. If the acceleration of the disc B immediately after the system is released from rest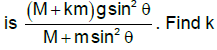
- a)2
- b)1
- c)5
- d)3
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
A disc ‘A’ of mass M is placed at rest on the smooth inclined surface of inclination θ. A ball B of mass m is suspended vertically from the centre of the disc A by a light inextensible string of light ℓ as shown in the figure. If the acceleration of the disc B immediately after the system is released from rest
a)
2
b)
1
c)
5
d)
3
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
apply newton’s laws of motion for the body A and body B
Consider the following cell reaction:2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H2O(l); E° = 1.67 VAt [Fe2+] = 10-3 M, P(O2) = 0.1 atom and pH = 3, the cell potential (in V) at 25°C is
Correct answer is '1.57'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following cell reaction:
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H2O(l); E° = 1.67 V
At [Fe2+] = 10-3 M, P(O2) = 0.1 atom and pH = 3, the cell potential (in V) at 25°C is
|
|
Lakshmi Roy answered |
The given cell reaction is as follows:
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) -> 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
To determine the cell potential, we need to use the Nernst equation, which is given by:
E = E° - (0.0592/n) log(Q)
where E is the cell potential, E° is the standard cell potential, n is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the balanced equation, and Q is the reaction quotient.
Given:
E° = 1.67 V
[Fe2+] = 10^-3 M
P(O2) = 0.1 atm
pH = 3
First, let's calculate the reaction quotient Q:
Q = [Fe2+]^2[H2O]/[O2][H+]^4
Since the coefficients in the balanced equation are all 1, we can simplify the expression to:
Q = [Fe2+]^2[H2O]/[O2][H+]^4
Substituting the given values:
Q = (10^-3)^2/(0.1)(10^-3)^4
Q = 10^-6/(10^-1)(10^-12)
Q = 10^-6/(10^-13)
Q = 10^7
Now we can plug the values into the Nernst equation to find the cell potential:
E = 1.67 V - (0.0592/2) log(10^7)
E = 1.67 V - (0.0296) log(10^7)
E = 1.67 V - (0.0296)(7)
E = 1.67 V - 0.2072
E = 1.4628 V
Therefore, the cell potential at 25°C is approximately 1.46 V.
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) -> 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
To determine the cell potential, we need to use the Nernst equation, which is given by:
E = E° - (0.0592/n) log(Q)
where E is the cell potential, E° is the standard cell potential, n is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the balanced equation, and Q is the reaction quotient.
Given:
E° = 1.67 V
[Fe2+] = 10^-3 M
P(O2) = 0.1 atm
pH = 3
First, let's calculate the reaction quotient Q:
Q = [Fe2+]^2[H2O]/[O2][H+]^4
Since the coefficients in the balanced equation are all 1, we can simplify the expression to:
Q = [Fe2+]^2[H2O]/[O2][H+]^4
Substituting the given values:
Q = (10^-3)^2/(0.1)(10^-3)^4
Q = 10^-6/(10^-1)(10^-12)
Q = 10^-6/(10^-13)
Q = 10^7
Now we can plug the values into the Nernst equation to find the cell potential:
E = 1.67 V - (0.0592/2) log(10^7)
E = 1.67 V - (0.0296) log(10^7)
E = 1.67 V - (0.0296)(7)
E = 1.67 V - 0.2072
E = 1.4628 V
Therefore, the cell potential at 25°C is approximately 1.46 V.
The number of bicarbonates that do not exist in solid form among the following is....................
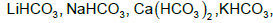
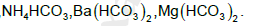
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of bicarbonates that do not exist in solid form among the following is....................
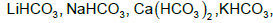
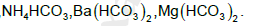
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
No bicarbonates exist in solid due to inefficient packing except Ammonium and Na+ to Cs+. Only NaHCO3 , KHCO3 , RbHCO3 , CsHCO3 and NH4HCO3 exist in solid.
So the correct answer is 4.
So the correct answer is 4.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect regarding chloride of iron?- a)Iron chloride is back at anhydrous condition.
- b)It sublimes at 300°C and forms a dimer.
- c)It is an oxidising agent.
- d)It is ether soluble but water insoluble.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect regarding chloride of iron?
a)
Iron chloride is back at anhydrous condition.
b)
It sublimes at 300°C and forms a dimer.
c)
It is an oxidising agent.
d)
It is ether soluble but water insoluble.
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
This problem is based on various properties of iron chlorides. To solve this problem, students must have the knowledge of solubility of iron chloride in aqueous solution, the existence of iron chloride in ether solution, oxidising properties of iron chloride.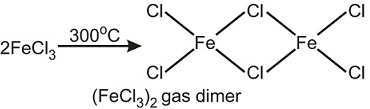
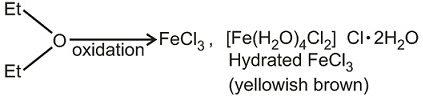
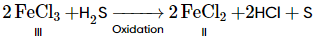
Properties of iron chloride
(i) FeCl3 (Iron chloride) is back coloured in anhydrous conditions. But its hydrated form is yellowish-brown.
(ii) FeCl3 sublimes at 300°C3 to give a dimer.

(iii) FeCl3 is water-soluble as well as ether soluble due to solvation.
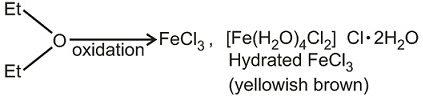
(iv) It is an oxidising agent, during oxidation. The yellow colour of aqueous Fe (III) changes to light green aqueous Fe (II).
Of the following amines how many can be separated by Hoffmann’s mustard oil reaction?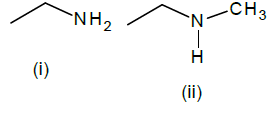
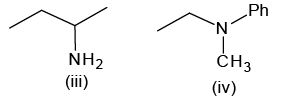
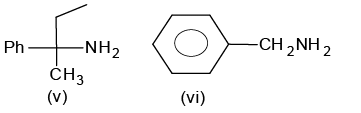
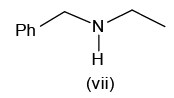
- a)2
- b)3
- c)5
- d)4
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the following amines how many can be separated by Hoffmann’s mustard oil reaction?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
5
d)
4

|
Manish Aggarwal answered |
Hoffmann’s mustard oil reaction is a test of 1o amine.
Let A and B be two fixed points and P, another point in the plane, move such that k1PA + k2PB = k3 where k1, k2 & k3 being real constants. The locus of P is- a)A circle if k1 = 0 and k2, k3 > 0
- b)A circle if k1 > 0, k2 < 0="" and="" />3 = 0
- c)An ellipse if k1 = k2 > 0 and k3 > 0
- d)A hyperbola if k2 = −1 and k1, k3 > 0
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Let A and B be two fixed points and P, another point in the plane, move such that k1PA + k2PB = k3 where k1, k2 & k3 being real constants. The locus of P is
a)
A circle if k1 = 0 and k2, k3 > 0
b)
A circle if k1 > 0, k2 < 0="" and="" />3 = 0
c)
An ellipse if k1 = k2 > 0 and k3 > 0
d)
A hyperbola if k2 = −1 and k1, k3 > 0
|
|
Sameer Saha answered |
, and k3 are constants.
Let's consider the triangle formed by points A, B, and P. The ratio k1PA/k2PB represents the ratio of the distances from P to A and P to B. This ratio is constant for all positions of P.
Now, let's consider a point Q that is also in the plane. The ratio k1QA/k2QB should also be equal to k3, according to the given condition.
So, we can say that for any two points P and Q in the plane, the ratio of their distances to A and B respectively will always be the same, equal to k3.
Therefore, the locus of points P that satisfy the given condition is a circle. The center of the circle is the midpoint of line segment AB, and the radius of the circle is given by k3 times the distance between A and B.
Let's consider the triangle formed by points A, B, and P. The ratio k1PA/k2PB represents the ratio of the distances from P to A and P to B. This ratio is constant for all positions of P.
Now, let's consider a point Q that is also in the plane. The ratio k1QA/k2QB should also be equal to k3, according to the given condition.
So, we can say that for any two points P and Q in the plane, the ratio of their distances to A and B respectively will always be the same, equal to k3.
Therefore, the locus of points P that satisfy the given condition is a circle. The center of the circle is the midpoint of line segment AB, and the radius of the circle is given by k3 times the distance between A and B.
An 820-turn wire coil of resistance 24 Ω is placed on a top of a-12,500 turn, 7 cm long solenoid as shown in the figure. Both coil and solenoid have a cross-section area of 10-4 m2. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid at the location of the coil is one half as strong as the field at the centre of the solenoid. The solenoid is connected to a battery of emf 60 V and resistance 14 Ω with the help of a switch. The switch is closed at t = 0.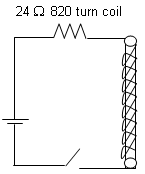 Determine the average emf (in V) induced in the circuit which opposes the current in the circuit to grow for a time interval 0 to t0.
Determine the average emf (in V) induced in the circuit which opposes the current in the circuit to grow for a time interval 0 to t0.
Correct answer is '37.9'. Can you explain this answer?
An 820-turn wire coil of resistance 24 Ω is placed on a top of a-12,500 turn, 7 cm long solenoid as shown in the figure. Both coil and solenoid have a cross-section area of 10-4 m2. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid at the location of the coil is one half as strong as the field at the centre of the solenoid. The solenoid is connected to a battery of emf 60 V and resistance 14 Ω with the help of a switch. The switch is closed at t = 0.

Determine the average emf (in V) induced in the circuit which opposes the current in the circuit to grow for a time interval 0 to t0.
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
Average emf induced in interval 0-t0 sec,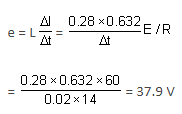
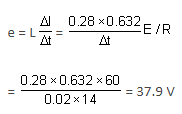
Therefore, the average emf induced in the circuit is 37.9 V.
A certain substance has a mass of 50g/mol. When 300J of heat is added to 25 gm of sample of this material, its temperature rises from 25 to 45oC.Q. The specific heat capacity of the substance is- a)300J / kgoC
- b)400J / KgoC
- c)500J / KgoC
- d)600J / kgoC
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A certain substance has a mass of 50g/mol. When 300J of heat is added to 25 gm of sample of this material, its temperature rises from 25 to 45oC.
Q. The specific heat capacity of the substance is
a)
300J / kgoC
b)
400J / KgoC
c)
500J / KgoC
d)
600J / kgoC
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
D
Specific heat capacity,
Specific heat capacity,
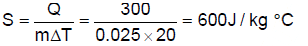
Two thin symmetrical lenses of different nature have equal radii of curvature R = 20 cm. The lenses are placed in contact and then immersed in water. The focal length of the system is found to be 24 cm. If the refractive indices of the two lenses are μ1 and μ2 respectively, then find the magnitude of 9(μ1 - μ2). Refractive index of water is 4/3.
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Two thin symmetrical lenses of different nature have equal radii of curvature R = 20 cm. The lenses are placed in contact and then immersed in water. The focal length of the system is found to be 24 cm. If the refractive indices of the two lenses are μ1 and μ2 respectively, then find the magnitude of 9(μ1 - μ2). Refractive index of water is 4/3.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
where
In YDSE, if incident light consists of two wavelengths λ1 = 4000 Å and λ2 = 5600 Å and is parallel to line SO. The minimum distance yy upon screen, measured from point O, will be where the bright fringe due to two wavelengths coincide is nλ1D/d. Find n.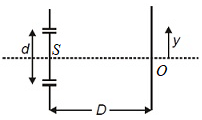
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
In YDSE, if incident light consists of two wavelengths λ1 = 4000 Å and λ2 = 5600 Å and is parallel to line SO. The minimum distance yy upon screen, measured from point O, will be where the bright fringe due to two wavelengths coincide is nλ1D/d. Find n.

|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
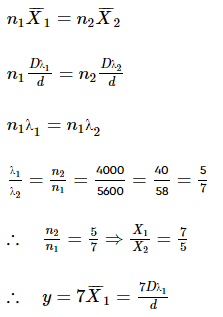
Can you explain the answer of this question below:On the basis of aromaticity, there are three types of compounds i.e. aromatic, non-aromatic and antiaromatic.
The increasing order of stability of these compounds are is under:
Anti-aromatic compound < non-aromatic compound < aromatic compounds. Compounds to be aromatic
follow the following conditions (according to valence bond theory)
(i) The compounds must be be cyclic in structure having (4n + 2)π e–, where n = Hückel’s number = 0, 1,
2, 3 et.c
(ii) The each atoms of the cyclic structure must have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. the atoms of the
compounds have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. usually have sp2 hybrid or planar.
(iii) There must be a ring current of π electrons in the ring or cyclic structure i.e. cyclic structure must
undergo resonance .
Compounds to be anti-aromatic, it must have 4nπe– where n = 1, 2… and it must be planar and undergo
resonance. Non-aromatic compounds the name itself spells that compounds must be non-planar
irrespective of number of π electrons. Either it has 4nπe– or (4n + 2) π electrons it does not matter.
The rate of reaction of any aromatic compounds depends upon the following factors:
(i) Electron density
(ii) stability of carbocation produced
Higher the amount of electron density of the ring, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic
substitution and vice-versa. Similarly, higher will be the stability of the produced carbocation after the
attack of electrophile, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution. There is a great
effect of kinetic labelling on the rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution. As we known that higher the
atomic weight or, molecualr weight, higher will be the van der Waal’s force of attraction or, bond energy.
Since there will be effect of kienetic labelling if the 2nd step of the reaction will be the slow step, (r.d.s.)
otherwise there will be no effect of kinetic labelling.
Q. Which of the following is correct order of the rate of reaction of C6H6, C6D6 and C6T6 towards
nitrations?- A:C6H6 >C6D6 > C6T6
- B:C6H6 = C6D6 = C6T6
- C:C6H6 > C6D6 = C6T6
- D:C6T6 >C6D6 >C6H6
The answer is b.
On the basis of aromaticity, there are three types of compounds i.e. aromatic, non-aromatic and antiaromatic.
The increasing order of stability of these compounds are is under:
Anti-aromatic compound < non-aromatic compound < aromatic compounds. Compounds to be aromatic
follow the following conditions (according to valence bond theory)
(i) The compounds must be be cyclic in structure having (4n + 2)π e–, where n = Hückel’s number = 0, 1,
2, 3 et.c
(ii) The each atoms of the cyclic structure must have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. the atoms of the
compounds have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. usually have sp2 hybrid or planar.
(iii) There must be a ring current of π electrons in the ring or cyclic structure i.e. cyclic structure must
undergo resonance .
Compounds to be anti-aromatic, it must have 4nπe– where n = 1, 2… and it must be planar and undergo
resonance. Non-aromatic compounds the name itself spells that compounds must be non-planar
irrespective of number of π electrons. Either it has 4nπe– or (4n + 2) π electrons it does not matter.
The rate of reaction of any aromatic compounds depends upon the following factors:
(i) Electron density
(ii) stability of carbocation produced
Higher the amount of electron density of the ring, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic
substitution and vice-versa. Similarly, higher will be the stability of the produced carbocation after the
attack of electrophile, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution. There is a great
effect of kinetic labelling on the rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution. As we known that higher the
atomic weight or, molecualr weight, higher will be the van der Waal’s force of attraction or, bond energy.
Since there will be effect of kienetic labelling if the 2nd step of the reaction will be the slow step, (r.d.s.)
otherwise there will be no effect of kinetic labelling.
Q. Which of the following is correct order of the rate of reaction of C6H6, C6D6 and C6T6 towards
nitrations?
The increasing order of stability of these compounds are is under:
Anti-aromatic compound < non-aromatic compound < aromatic compounds. Compounds to be aromatic
follow the following conditions (according to valence bond theory)
(i) The compounds must be be cyclic in structure having (4n + 2)π e–, where n = Hückel’s number = 0, 1,
2, 3 et.c
(ii) The each atoms of the cyclic structure must have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. the atoms of the
compounds have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. usually have sp2 hybrid or planar.
(iii) There must be a ring current of π electrons in the ring or cyclic structure i.e. cyclic structure must
undergo resonance .
Compounds to be anti-aromatic, it must have 4nπe– where n = 1, 2… and it must be planar and undergo
resonance. Non-aromatic compounds the name itself spells that compounds must be non-planar
irrespective of number of π electrons. Either it has 4nπe– or (4n + 2) π electrons it does not matter.
The rate of reaction of any aromatic compounds depends upon the following factors:
(i) Electron density
(ii) stability of carbocation produced
Higher the amount of electron density of the ring, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic
substitution and vice-versa. Similarly, higher will be the stability of the produced carbocation after the
attack of electrophile, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution. There is a great
effect of kinetic labelling on the rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution. As we known that higher the
atomic weight or, molecualr weight, higher will be the van der Waal’s force of attraction or, bond energy.
Since there will be effect of kienetic labelling if the 2nd step of the reaction will be the slow step, (r.d.s.)
otherwise there will be no effect of kinetic labelling.
Q. Which of the following is correct order of the rate of reaction of C6H6, C6D6 and C6T6 towards
nitrations?
A:
C6H6 >C6D6 > C6T6
B:
C6H6 = C6D6 = C6T6
C:
C6H6 > C6D6 = C6T6
D:
C6T6 >C6D6 >C6H6

|
Pranavi Chavan answered |
B
2nd step is fast step in nitration.
2nd step is fast step in nitration.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:In the circuit shown C1 = 2C2. Switch S is closed at time t = 0. Let i1 & i2 be the current flowing through C1 and C2 at any time t, then the ratio I1/I2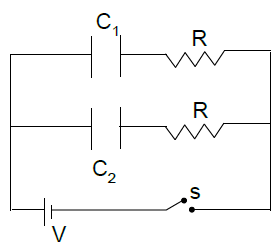
- A:is constant
- B:increases with increase in time t
- C:decreases with increase in time t
- D:first increases then decreases
The answer is b.
In the circuit shown C1 = 2C2. Switch S is closed at time t = 0. Let i1 & i2 be the current flowing through C1 and C2 at any time t, then the ratio I1/I2
A:
is constant
B:
increases with increase in time t
C:
decreases with increase in time t
D:
first increases then decreases
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The answer is a.
The voltage across both C1 and C2 will be same as they are parallel to each other.
For capacitor Q= CV, this means that the capacitor C1 will have greater charge as its capacitance is more.
But as the voltage is same the ratio of current i1/i2 will remain unchanged.
The oxidation state of molybdenum in [(η7-tropylium)Mo(CO)3]+ is - a)+2
- b)+1
- c)0
- d)-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation state of molybdenum in [(η7-tropylium)Mo(CO)3]+ is
a)
+2
b)
+1
c)
0
d)
-1
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Tropylim cation has one positive charges and CO is neutral ligand.
If the total number of faradays required to oxidize the following separately:a. one mole of S2O32- in acid mediumb. one Equivalent of S2O32- in neutral mediumc. one mole of S2O32- in basic medium.is 10 K. Then the value of 'K' is ____
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
If the total number of faradays required to oxidize the following separately:
a. one mole of S2O32- in acid medium
b. one Equivalent of S2O32- in neutral medium
c. one mole of S2O32- in basic medium.
is 10 K. Then the value of 'K' is ____
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
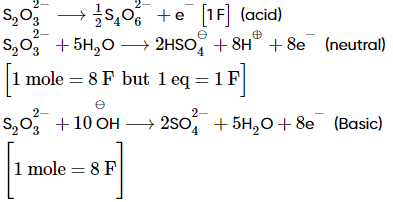
Total Faradays in (i), (ii) and (iii) = 1 + 1 + 8 = 10 F
What happens when a mixture of NaCl and K2Cr2O7 is gently warmed with conc. H2SO4?- a)A deep red vapour is evolved.
- b)The vapour when passed into NaOH solution gives a yellow solution of Na2CrO4.
- c)Chlorine gas is evolved.
- d)Chromyl chloride is formed.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when a mixture of NaCl and K2Cr2O7 is gently warmed with conc. H2SO4?
a)
A deep red vapour is evolved.
b)
The vapour when passed into NaOH solution gives a yellow solution of Na2CrO4.
c)
Chlorine gas is evolved.
d)
Chromyl chloride is formed.
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
During this process, chromyl chloride is formed which is deep red coloured fuming liquid.
4NaCl + K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 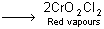 + 4NaHSO4 + 2KHSO4 + 3H2O
+ 4NaHSO4 + 2KHSO4 + 3H2O
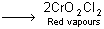 + 4NaHSO4 + 2KHSO4 + 3H2O
+ 4NaHSO4 + 2KHSO4 + 3H2OThe vapour of CrO2Cl2 when passed into NaOH solution gives a yellow solution of Na2CrO4.
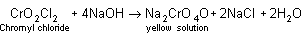
Directions: The following question has four choices, out of which ONE or MORE are correct.Cv and Cp denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. Then,- a)Cp + Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
- b)Cp / Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
- c)Cp . Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
- d)Cp - Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: The following question has four choices, out of which ONE or MORE are correct.
Cv and Cp denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. Then,
a)
Cp + Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
b)
Cp / Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
c)
Cp . Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
d)
Cp - Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas
|
|
Lekshmi Joshi answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
The molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp) are important thermodynamic properties that describe how the gas responds to changes in temperature. In this question, we are comparing the values of Cp and Cv for diatomic and monatomic ideal gases.
Cv and Cp for an ideal gas:
For an ideal gas, the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas by one degree Celsius while keeping the volume constant. On the other hand, the molar specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas by one degree Celsius while allowing the pressure to remain constant.
Comparison between diatomic and monatomic ideal gases:
To compare the values of Cp and Cv for diatomic and monatomic ideal gases, we need to consider the degrees of freedom of the gas molecules. The degrees of freedom represent the number of independent ways in which the gas molecules can store energy.
Monatomic ideal gas:
A monatomic ideal gas consists of single atoms, such as helium or argon. Since these atoms can only move in three dimensions (x, y, and z), they have three degrees of freedom. For a monatomic ideal gas, the molar specific heat capacities at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp) are related by the equation Cp/Cv = γ, where γ is the adiabatic index. For a monatomic ideal gas, γ is equal to 5/3 or approximately 1.67.
Diatomic ideal gas:
A diatomic ideal gas consists of molecules with two atoms, such as oxygen or nitrogen. In addition to the three translational degrees of freedom, diatomic molecules can also rotate about their center of mass. Since a diatomic molecule can rotate about two independent axes, it has a total of five degrees of freedom. For a diatomic ideal gas, the molar specific heat capacities at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp) are related by the equation Cp/Cv = γ, where γ is equal to 7/5 or approximately 1.4.
Comparison of Cp and Cv:
From the above information, we can conclude that Cp/Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas. This means that the molar specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) is larger than the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) for a diatomic ideal gas. Therefore, option B is incorrect.
Furthermore, the product Cp.Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas. This can be seen from the equation Cp/Cv = γ, where γ is greater for a monatomic ideal gas (5/3) compared to a diatomic ideal gas (7/5). Therefore, option C is correct.
In addition, Cp - Cv is also larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas. This can be seen from the difference in values of γ for the two types of gases. Therefore, option D is correct.
Summary:
In summary, for a diatomic ideal
Introduction:
The molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp) are important thermodynamic properties that describe how the gas responds to changes in temperature. In this question, we are comparing the values of Cp and Cv for diatomic and monatomic ideal gases.
Cv and Cp for an ideal gas:
For an ideal gas, the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas by one degree Celsius while keeping the volume constant. On the other hand, the molar specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas by one degree Celsius while allowing the pressure to remain constant.
Comparison between diatomic and monatomic ideal gases:
To compare the values of Cp and Cv for diatomic and monatomic ideal gases, we need to consider the degrees of freedom of the gas molecules. The degrees of freedom represent the number of independent ways in which the gas molecules can store energy.
Monatomic ideal gas:
A monatomic ideal gas consists of single atoms, such as helium or argon. Since these atoms can only move in three dimensions (x, y, and z), they have three degrees of freedom. For a monatomic ideal gas, the molar specific heat capacities at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp) are related by the equation Cp/Cv = γ, where γ is the adiabatic index. For a monatomic ideal gas, γ is equal to 5/3 or approximately 1.67.
Diatomic ideal gas:
A diatomic ideal gas consists of molecules with two atoms, such as oxygen or nitrogen. In addition to the three translational degrees of freedom, diatomic molecules can also rotate about their center of mass. Since a diatomic molecule can rotate about two independent axes, it has a total of five degrees of freedom. For a diatomic ideal gas, the molar specific heat capacities at constant volume (Cv) and constant pressure (Cp) are related by the equation Cp/Cv = γ, where γ is equal to 7/5 or approximately 1.4.
Comparison of Cp and Cv:
From the above information, we can conclude that Cp/Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas. This means that the molar specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) is larger than the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) for a diatomic ideal gas. Therefore, option B is incorrect.
Furthermore, the product Cp.Cv is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas. This can be seen from the equation Cp/Cv = γ, where γ is greater for a monatomic ideal gas (5/3) compared to a diatomic ideal gas (7/5). Therefore, option C is correct.
In addition, Cp - Cv is also larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monatomic ideal gas. This can be seen from the difference in values of γ for the two types of gases. Therefore, option D is correct.
Summary:
In summary, for a diatomic ideal
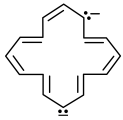
Select from following molecules or ions, which is/are aromatic.- a)
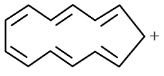
- b)
- c)
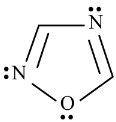
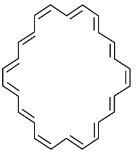
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select from following molecules or ions, which is/are aromatic.
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
For aromatic compounds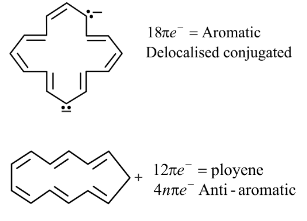
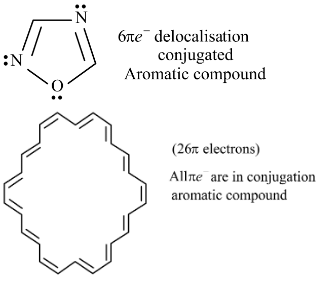
For a compound to be aromatic, it should follow Huckle's (4n + 2)πe− rule, i.e., 2, 6, 10, 14....πe−
They should show delocalised, conjugate π system with alternate single and double bonds. In addition to this, the compound should be cyclic and planar or almost planar.
The number of πe− is even, but not a multiple of 4.
For anti-aromatic compounds:
4nπe−, i.e., 4, 8, 12....πe− should be delocalized in a cyclic, planar, or almost planar system with alternate single and double bonds.
Planar conjugated carbocyclic polyene, carbocyclic polyene structure is less stable than its open structure.


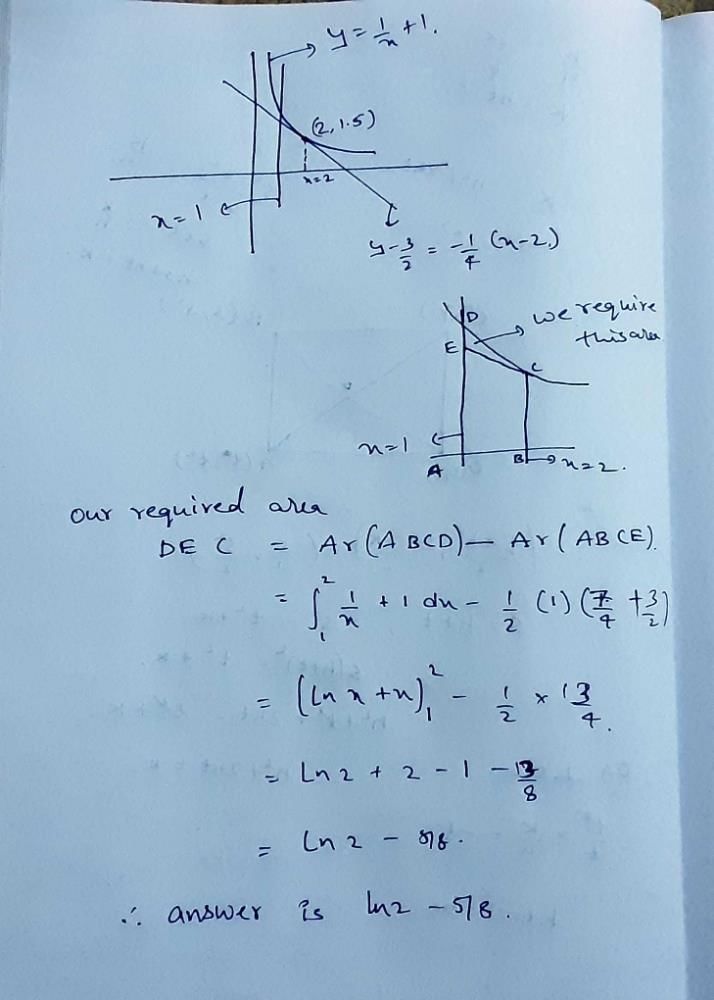
If range of the function f(x) = sin-1 x + 2 tan-1 x + x2 + 4x + 1 is [a, b], then the value of a + b is
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
If range of the function f(x) = sin-1 x + 2 tan-1 x + x2 + 4x + 1 is [a, b], then the value of a + b is
|
|
Avik Nambiar answered |
To find the range of the function f(x) = sin^{-1}x * 2tan^{-1}x * x^2 * 4x * 1, we need to consider the range of each individual term and then find the combined range.
1. Range of sin^{-1}x:
The range of the arcsine function is [-pi/2, pi/2]. This means that the function sin^{-1}x will give values between -pi/2 and pi/2 for all values of x.
2. Range of 2tan^{-1}x:
The range of the arctangent function is (-pi/2, pi/2). When multiplied by 2, the range becomes (-pi, pi). This means that the function 2tan^{-1}x will give values between -pi and pi for all values of x.
3. Range of x^2:
The range of x^2 is [0, infinity). This means that the function x^2 will give values greater than or equal to 0 for all values of x.
4. Range of 4x:
The range of 4x is (-infinity, infinity). This means that the function 4x will give all real values for all values of x.
5. Range of 1:
The range of a constant function is the single value that it represents. In this case, the function 1 will always give the value 1.
Now, to find the combined range, we need to consider the intersection of the ranges of the individual terms.
- The intersection of the ranges of sin^{-1}x and 2tan^{-1}x is (-pi/2, pi/2).
- The intersection of this range and the range of x^2 is [0, pi/2].
- The intersection of this range and the range of 4x is [0, pi/2].
- The intersection of this range and the range of 1 is [0, pi/2].
Therefore, the range of the function f(x) is [0, pi/2].
However, the question asks for the value of a + b. Since the range is [0, pi/2], a = 0 and b = pi/2. Therefore, a + b = 0 + pi/2 = pi/2.
Hence, the correct answer is 4.
1. Range of sin^{-1}x:
The range of the arcsine function is [-pi/2, pi/2]. This means that the function sin^{-1}x will give values between -pi/2 and pi/2 for all values of x.
2. Range of 2tan^{-1}x:
The range of the arctangent function is (-pi/2, pi/2). When multiplied by 2, the range becomes (-pi, pi). This means that the function 2tan^{-1}x will give values between -pi and pi for all values of x.
3. Range of x^2:
The range of x^2 is [0, infinity). This means that the function x^2 will give values greater than or equal to 0 for all values of x.
4. Range of 4x:
The range of 4x is (-infinity, infinity). This means that the function 4x will give all real values for all values of x.
5. Range of 1:
The range of a constant function is the single value that it represents. In this case, the function 1 will always give the value 1.
Now, to find the combined range, we need to consider the intersection of the ranges of the individual terms.
- The intersection of the ranges of sin^{-1}x and 2tan^{-1}x is (-pi/2, pi/2).
- The intersection of this range and the range of x^2 is [0, pi/2].
- The intersection of this range and the range of 4x is [0, pi/2].
- The intersection of this range and the range of 1 is [0, pi/2].
Therefore, the range of the function f(x) is [0, pi/2].
However, the question asks for the value of a + b. Since the range is [0, pi/2], a = 0 and b = pi/2. Therefore, a + b = 0 + pi/2 = pi/2.
Hence, the correct answer is 4.
Which of the following expression (s) represent the voltage of cell at 298 K:Ag+ | AgI (saturated solution)|Ag2C2O4(saturated solution)| Ag+- a)
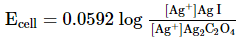
- b)
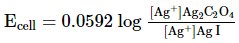
- c)
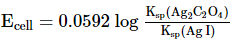
- d)
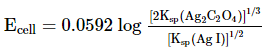
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expression (s) represent the voltage of cell at 298 K:
Ag+ | AgI (saturated solution)|Ag2C2O4(saturated solution)| Ag+
a)
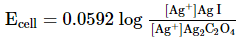
b)
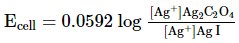
c)
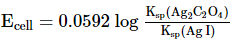
d)
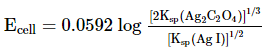
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The given cell is concentration cell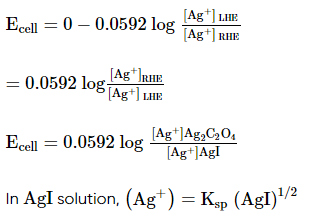
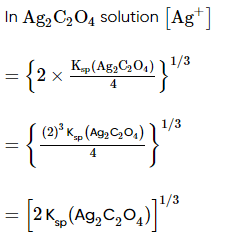
Ag ⟶(Ag+) LHE + e−
(Ag+)RHE+ e− ⟶ Ag
Net reaction:(Ag+)RHE ⟶ (Ag+)LHE
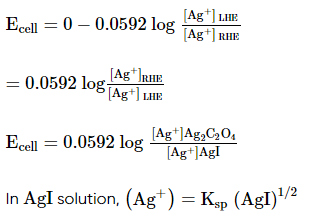
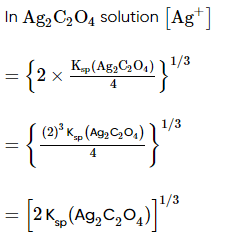
If a bag contains five balls. Two balls are drawn and are found to be white. What is the probabilitythat all the balls are white?- a)1/4
- b)1/3
- c)1/2
- d)2/3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a bag contains five balls. Two balls are drawn and are found to be white. What is the probabilitythat all the balls are white?
a)
1/4
b)
1/3
c)
1/2
d)
2/3
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
We don't know the number of white and black balls in the bag, but we know the number of white balls can't be less than 2.
Now, there are different cases, which are the number of white balls in the bag. The total cases are : 2c2+3c2+4c2+5c2 =20
The question is asking to find the probability of the case that there are 5 white balls, which 5c2 = 10 cases
So, probability =10/20=1/2
Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory predicts the shape of a molecule by considering the most stable configuration of the bond angles in the molecule. The main points of the theory are(i) Electron pairs in the valence shell of central atom of a molecule, whether bonding or lone pairs are regarded as occupying localised orbitals. These orbitals arrange themselves so as to minimize the mutual electronic repulsions.(ii) The magnitude of the different types of electronic repulsions follow the order given below:Lone pair-lone pair> lone pair-bonding pair > bonding pair-bonding pair. These repulsive forces alter the bond angles of the molecule or ion.(iii) The electron repulsion between two pairs of electrons will be minimum if they stay as far as possible. On this basis, several studied. have been doneWhich of the following statements is correct ?- a)The bond angle of NCl3 is greater than NH3 as Pπ − dπ back-bonding is present in NCl3.
- b)BF3 is more acidic than BCl3 due to presence of Pπ − dπ back bonding in BF3
- c)When the bond multiplicity is increased, bond angle is decreased.
- d)The bond angle of SiCl4 is greater than CCl4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory predicts the shape of a molecule by considering the most stable configuration of the bond angles in the molecule. The main points of the theory are
(i) Electron pairs in the valence shell of central atom of a molecule, whether bonding or lone pairs are regarded as occupying localised orbitals. These orbitals arrange themselves so as to minimize the mutual electronic repulsions.
(ii) The magnitude of the different types of electronic repulsions follow the order given below:
Lone pair-lone pair> lone pair-bonding pair > bonding pair-bonding pair. These repulsive forces alter the bond angles of the molecule or ion.
(iii) The electron repulsion between two pairs of electrons will be minimum if they stay as far as possible. On this basis, several studied. have been done
Which of the following statements is correct ?
a)
The bond angle of NCl3 is greater than NH3 as Pπ − dπ back-bonding is present in NCl3.
b)
BF3 is more acidic than BCl3 due to presence of Pπ − dπ back bonding in BF3
c)
When the bond multiplicity is increased, bond angle is decreased.
d)
The bond angle of SiCl4 is greater than CCl4
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
This problem includes the concept of bond angle the basis of Pπ − dπ back bonding and bond stifness, read all statements carefully and answer according to question using above concept.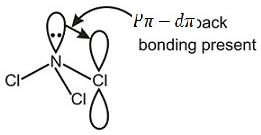

Due to presence of Pπ − dπ back bonding, NCl3 is sp2 hybridised but due to the absence of vacant d orbital in NH3 it can't form Pπ − dπ back bonding. So bond anlge of NCl3 is greater than NH3. Due to Pπ − dπ back bonding (d-orbitals available in Cl). The lone pair on N not available for exerting repulsion and hence bond angle in NCl3 > NH3.
In BF3 there is Pπ − dπ back bonding from filled orbitals of F creating a partial double bond character making it a poor Lewis acid than BCl3.
Bond multiplicity leads to more repulsion - double bond - lone pair repulsion is too high and hence bond angle increases.
SiCl4 and CCl4 bond angles are both tetrahedral (same).
In a head-on elastic collision of two bodies of equal masses- a)the velocities are interchanged
- b)the speeds are interchanged
- c)the momenta are interchanged
- d)the faster body slows down and the slower body speeds up
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a head-on elastic collision of two bodies of equal masses
a)
the velocities are interchanged
b)
the speeds are interchanged
c)
the momenta are interchanged
d)
the faster body slows down and the slower body speeds up
|
|
Hiral Rane answered |
Understanding Head-On Elastic Collisions
In a head-on elastic collision involving two bodies of equal masses, several important principles apply. Here’s a breakdown of the outcomes:
1. Velocities are Interchanged
- In an elastic collision, the law of conservation of momentum and kinetic energy applies.
- When two bodies of equal mass collide, their velocities effectively swap.
- If Body A moves towards Body B with velocity V1 and Body B moves towards Body A with velocity V2, after the collision, Body A will take on the velocity of Body B and vice versa.
2. Speeds are Interchanged
- Since the masses are equal, the speeds (magnitude of velocity) are also exchanged.
- This means if Body A was faster, it slows down while Body B speeds up to match the speed of Body A prior to the collision.
3. Momenta are Interchanged
- The momentum of a body is the product of its mass and velocity.
- In this case, because the masses are equal and velocities are interchanged, the momenta are also effectively swapped between the two bodies.
4. The Faster Body Slows Down and the Slower Body Speeds Up
- The kinetic energy, which is proportional to the square of the speed, is conserved in elastic collisions.
- As a result, the faster body loses some speed while the slower body gains speed, leading to an overall exchange of kinetic energy.
In summary, for two equal-mass bodies in a head-on elastic collision, the outcomes are interconnected: velocities, speeds, and momenta are interchanged, and each body adjusts its speed accordingly based on its initial conditions.
In a head-on elastic collision involving two bodies of equal masses, several important principles apply. Here’s a breakdown of the outcomes:
1. Velocities are Interchanged
- In an elastic collision, the law of conservation of momentum and kinetic energy applies.
- When two bodies of equal mass collide, their velocities effectively swap.
- If Body A moves towards Body B with velocity V1 and Body B moves towards Body A with velocity V2, after the collision, Body A will take on the velocity of Body B and vice versa.
2. Speeds are Interchanged
- Since the masses are equal, the speeds (magnitude of velocity) are also exchanged.
- This means if Body A was faster, it slows down while Body B speeds up to match the speed of Body A prior to the collision.
3. Momenta are Interchanged
- The momentum of a body is the product of its mass and velocity.
- In this case, because the masses are equal and velocities are interchanged, the momenta are also effectively swapped between the two bodies.
4. The Faster Body Slows Down and the Slower Body Speeds Up
- The kinetic energy, which is proportional to the square of the speed, is conserved in elastic collisions.
- As a result, the faster body loses some speed while the slower body gains speed, leading to an overall exchange of kinetic energy.
In summary, for two equal-mass bodies in a head-on elastic collision, the outcomes are interconnected: velocities, speeds, and momenta are interchanged, and each body adjusts its speed accordingly based on its initial conditions.
At STP, the volume of nitrogen gas required to cover a sample of silica gel, assuming langmuir monolayer adsorption, is found to be 1.30 cm3 g−1 of the gel. The area occupied by a nitrogen molecule is 0.16 nm2. What is the surface area per gram of silica gel? [Given NA = 6 × 1023]. The area may be 1.113 × A m2 g−1. The value of A is:
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
At STP, the volume of nitrogen gas required to cover a sample of silica gel, assuming langmuir monolayer adsorption, is found to be 1.30 cm3 g−1 of the gel. The area occupied by a nitrogen molecule is 0.16 nm2. What is the surface area per gram of silica gel? [Given NA = 6 × 1023]. The area may be 1.113 × A m2 g−1. The value of A is:
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
Number of molecules per gram of nitrogen in monolayer
= 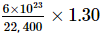
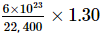
= 3.48 × 1019
Cross-sectional area of a molecule = 1.6 × 10−19m2
∴ Area covered by the molecules per gram = 3.48 × 1019 × 1.6 × 10−19 = 5.568 m2
∴ Surface area = 5.568 m2 g−1
= (1.113 × A) m2 g−1
A = 5
The minimum value of 3x + 4y, subject to the condition x2y3 = 6 and x > 0, y > 0, is
Correct answer is '10'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum value of 3x + 4y, subject to the condition x2y3 = 6 and x > 0, y > 0, is
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Break 3x as 3x/2 and 3x/2 and 4y as 4y/3, 4y/3 and 4y/3.
Now, we know that AM ≥ GM.
So, applying on numbers 3x/2, 3x/2 and 4y/3, 4y/3 and 4y/3,
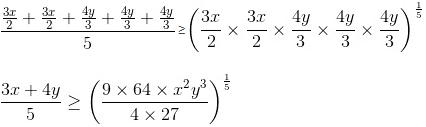
Putting the value of x2y3 = 6, we get
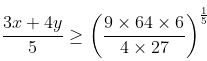
3x + 4y ≥ 10
Minimum value of 3x + 4y = 10
A convex lens forms a real image of an object kept at 15 cm from the lens on the screen. If the object is moved by 0.1 cm, the screen has to be moved by 0.4 cm to capture the image.The focal length of the lens is (in cm)
Correct answer is '10'. Can you explain this answer?
A convex lens forms a real image of an object kept at 15 cm from the lens on the screen. If the object is moved by 0.1 cm, the screen has to be moved by 0.4 cm to capture the image.
The focal length of the lens is (in cm)
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
Using 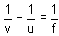
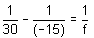
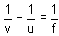
u = -15 m
v = mu
v = (-2) × (-15) = 30 cm
Hence,
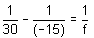
f = 10 cm
(I) Co(CO)6
(II) Co(CO)5NH3
(III) Co(CO)4(NH3)2
(IV) Co(CO)3(NH3)3
(V) Co(CO)2(NH3)4
(VI) Co(CO)(NH3)5
Which statement is correct for these compounds?- a)order of Co – C bond length in complexes is I > II > III > IV > V > VI
- b)order of Co – C bond length in complexes is VI > V > IV > III > II > I
- c)order of Co – C bond strength in complexes is I = II = III = IV = V = VI
- d)order of C – O bond length in complexes is I = II = III = IV = V = VI
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
(I) Co(CO)6
(II) Co(CO)5NH3
(III) Co(CO)4(NH3)2
(IV) Co(CO)3(NH3)3
(V) Co(CO)2(NH3)4
(VI) Co(CO)(NH3)5
Which statement is correct for these compounds?
(II) Co(CO)5NH3
(III) Co(CO)4(NH3)2
(IV) Co(CO)3(NH3)3
(V) Co(CO)2(NH3)4
(VI) Co(CO)(NH3)5
Which statement is correct for these compounds?
a)
order of Co – C bond length in complexes is I > II > III > IV > V > VI
b)
order of Co – C bond length in complexes is VI > V > IV > III > II > I
c)
order of Co – C bond strength in complexes is I = II = III = IV = V = VI
d)
order of C – O bond length in complexes is I = II = III = IV = V = VI

|
Avantika Saha answered |
A
Synergic bonding.
Synergic bonding.
An ellipse intersects the hyperbola 2x2 − 2y2 = 1 orthogonally. The eccentricity of the ellipse is reciprocal of that of the hyperbola. If the axes of the ellipse are along the coordinates axes, then- a)Equation of ellipse is x2 + 2y2 = 2
- b)The foci of ellipse are (±1, 0)
- c)Equation of ellipse is x2 + 2y2 = 4
- d)The foci of ellipse are (±√2, 0)
Correct answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer?
An ellipse intersects the hyperbola 2x2 − 2y2 = 1 orthogonally. The eccentricity of the ellipse is reciprocal of that of the hyperbola. If the axes of the ellipse are along the coordinates axes, then
a)
Equation of ellipse is x2 + 2y2 = 2
b)
The foci of ellipse are (±1, 0)
c)
Equation of ellipse is x2 + 2y2 = 4
d)
The foci of ellipse are (±√2, 0)
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Eccentricity of the hyperbola is 2√2 as it is a rectangular hyperbola so eccentricity ee of the ellipse is 1/√2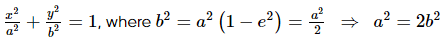
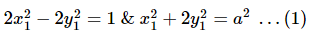
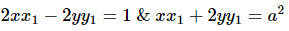
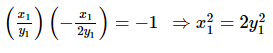
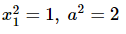
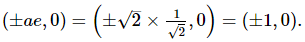
Let the equation of the ellipse be
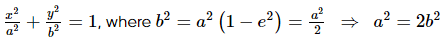
So, the equation of the ellipse is
x2 +2y2 = a2x2 + 2y2 = a2
Let (x1, y1) be a point of intersection of the ellipse and the hyperbola, then
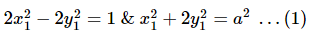
Equations of the tangents at (x1, y1) to the two conics are
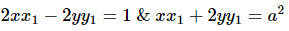
Since the two conics intersect orthogonally
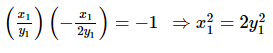
and from (1), we get
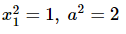
Hence, the equation of the ellipse is x2 + 2y2 = 2 and its focus is
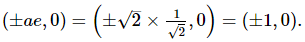
138 g of N2O4(g) is placed in 8.2 L container at 300 K. The equilibrium vapour density of mixture was found to be 30.67. Then (R = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1)- a)Total pressure at equilibrium = 6.75 atm
- b)Degree of dissociation of N2O4 = 0.25
- c)The density of equilibrium mixture = 16.83 g/L
- d)Kp of N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g) will be 9 atm
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
138 g of N2O4(g) is placed in 8.2 L container at 300 K. The equilibrium vapour density of mixture was found to be 30.67. Then (R = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1)
a)
Total pressure at equilibrium = 6.75 atm
b)
Degree of dissociation of N2O4 = 0.25
c)
The density of equilibrium mixture = 16.83 g/L
d)
Kp of N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g) will be 9 atm
|
|
Amrutha Iyer answered |
Given:
- Amount of N2O4 = 138 g
- Volume of container = 8.2 L
- Temperature = 300 K
- Equilibrium vapor density = 30.67
- Gas constant (R) = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1
To find:
a) Total pressure at equilibrium
b) Degree of dissociation of N2O4
c) Density of equilibrium mixture
d) Kp of N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g)
Let's solve each part one by one:
a) Total pressure at equilibrium:
The total pressure at equilibrium can be determined using the ideal gas law equation:
PV = nRT
Where:
P = Pressure
V = Volume
n = Number of moles
R = Gas constant
T = Temperature in Kelvin
First, we need to calculate the number of moles of N2O4 using its molar mass:
Molar mass of N2O4 = (2 × molar mass of N) + (4 × molar mass of O)
= (2 × 14 g/mol) + (4 × 16 g/mol)
= 92 g/mol
Number of moles of N2O4 = Mass of N2O4 / Molar mass of N2O4
= 138 g / 92 g/mol
= 1.5 mol
Substituting the values in the ideal gas law equation:
P × 8.2 L = 1.5 mol × 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1 × 300 K
P = (1.5 mol × 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1 × 300 K) / 8.2 L
P ≈ 6.75 atm
Therefore, the total pressure at equilibrium is approximately 6.75 atm.
b) Degree of dissociation of N2O4:
The degree of dissociation (α) of N2O4 can be calculated using the equation:
α = (1 - (density of equilibrium mixture / equilibrium vapor density))
Given that the equilibrium vapor density is 30.67, and the density of the equilibrium mixture is required.
Let's calculate the density of the equilibrium mixture:
Density = Mass / Volume
Using the given data:
Mass of N2O4 = 138 g
Volume of container = 8.2 L
Density of the equilibrium mixture = 138 g / 8.2 L
≈ 16.83 g/L
Substituting the values in the equation for α:
α = (1 - (16.83 g/L / 30.67 g/L))
α ≈ 0.45
Therefore, the degree of dissociation of N2O4 is approximately 0.45.
c) Density of equilibrium mixture:
As calculated earlier, the density of the equilibrium mixture is approximately 16.83 g/L.
Therefore, the option 'c' is correct.
d) Kp of N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g):
The equilibrium constant expression (Kp) for the reaction N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g) can be written as:
Kp = (PNO2)^2 / PN2O4
Since the total pressure at equilibrium (P) is approximately 6.75 atm
- Amount of N2O4 = 138 g
- Volume of container = 8.2 L
- Temperature = 300 K
- Equilibrium vapor density = 30.67
- Gas constant (R) = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1
To find:
a) Total pressure at equilibrium
b) Degree of dissociation of N2O4
c) Density of equilibrium mixture
d) Kp of N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g)
Let's solve each part one by one:
a) Total pressure at equilibrium:
The total pressure at equilibrium can be determined using the ideal gas law equation:
PV = nRT
Where:
P = Pressure
V = Volume
n = Number of moles
R = Gas constant
T = Temperature in Kelvin
First, we need to calculate the number of moles of N2O4 using its molar mass:
Molar mass of N2O4 = (2 × molar mass of N) + (4 × molar mass of O)
= (2 × 14 g/mol) + (4 × 16 g/mol)
= 92 g/mol
Number of moles of N2O4 = Mass of N2O4 / Molar mass of N2O4
= 138 g / 92 g/mol
= 1.5 mol
Substituting the values in the ideal gas law equation:
P × 8.2 L = 1.5 mol × 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1 × 300 K
P = (1.5 mol × 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1 × 300 K) / 8.2 L
P ≈ 6.75 atm
Therefore, the total pressure at equilibrium is approximately 6.75 atm.
b) Degree of dissociation of N2O4:
The degree of dissociation (α) of N2O4 can be calculated using the equation:
α = (1 - (density of equilibrium mixture / equilibrium vapor density))
Given that the equilibrium vapor density is 30.67, and the density of the equilibrium mixture is required.
Let's calculate the density of the equilibrium mixture:
Density = Mass / Volume
Using the given data:
Mass of N2O4 = 138 g
Volume of container = 8.2 L
Density of the equilibrium mixture = 138 g / 8.2 L
≈ 16.83 g/L
Substituting the values in the equation for α:
α = (1 - (16.83 g/L / 30.67 g/L))
α ≈ 0.45
Therefore, the degree of dissociation of N2O4 is approximately 0.45.
c) Density of equilibrium mixture:
As calculated earlier, the density of the equilibrium mixture is approximately 16.83 g/L.
Therefore, the option 'c' is correct.
d) Kp of N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g):
The equilibrium constant expression (Kp) for the reaction N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2(g) can be written as:
Kp = (PNO2)^2 / PN2O4
Since the total pressure at equilibrium (P) is approximately 6.75 atm
Refractive index of an equilateral prism is √2
- a)Minimum deviation from this prism can be 30o
- b)Minimum deviation from this prism can be 45o
- c)At angle of incidence = 60o, deviation is minimum
- d)At angle of incidence = 45o, deviation is minimum
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Refractive index of an equilateral prism is √2
a)
Minimum deviation from this prism can be 30o
b)
Minimum deviation from this prism can be 45o
c)
At angle of incidence = 60o, deviation is minimum
d)
At angle of incidence = 45o, deviation is minimum
|
|
Lekshmi Joshi answered |
Refractive index of an equilateral prism is √2
An equilateral prism is a prism with three equal sides and three equal angles. The refractive index of a material is a measure of how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through the material. In this case, the refractive index of the equilateral prism is given as √2.
Minimum deviation from this prism can be 30o
The minimum deviation of a prism occurs when the incident angle and the emergent angle are equal. In an equilateral prism, the incident angle and the emergent angle are equal when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence. In this case, the minimum deviation can be 30 degrees.
Minimum deviation from this prism can be 45o
The minimum deviation of a prism is also dependent on the refractive index of the material. The refractive index determines how much the light is bent as it passes through the prism. In this case, since the refractive index of the prism is √2, the minimum deviation can also be 45 degrees.
At angle of incidence = 45o, deviation is minimum
When the angle of incidence is equal to 45 degrees, the deviation is minimized. This is because at this angle, the incident ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. As a result, the deviation angle is minimized.
At angle of incidence = 60o, deviation is minimum
When the angle of incidence is equal to 60 degrees, the deviation is also minimized. This is because at this angle, the incident ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. As a result, the deviation angle is minimized.
Conclusion
From the given options, the correct answers are option 'A' and 'D'. The minimum deviation from the equilateral prism can be 30 degrees or 60 degrees when the angle of incidence is equal to 45 degrees or 60 degrees respectively. These values are determined by the refractive index of the prism, which is given as √2.
An equilateral prism is a prism with three equal sides and three equal angles. The refractive index of a material is a measure of how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through the material. In this case, the refractive index of the equilateral prism is given as √2.
Minimum deviation from this prism can be 30o
The minimum deviation of a prism occurs when the incident angle and the emergent angle are equal. In an equilateral prism, the incident angle and the emergent angle are equal when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence. In this case, the minimum deviation can be 30 degrees.
Minimum deviation from this prism can be 45o
The minimum deviation of a prism is also dependent on the refractive index of the material. The refractive index determines how much the light is bent as it passes through the prism. In this case, since the refractive index of the prism is √2, the minimum deviation can also be 45 degrees.
At angle of incidence = 45o, deviation is minimum
When the angle of incidence is equal to 45 degrees, the deviation is minimized. This is because at this angle, the incident ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. As a result, the deviation angle is minimized.
At angle of incidence = 60o, deviation is minimum
When the angle of incidence is equal to 60 degrees, the deviation is also minimized. This is because at this angle, the incident ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. As a result, the deviation angle is minimized.
Conclusion
From the given options, the correct answers are option 'A' and 'D'. The minimum deviation from the equilateral prism can be 30 degrees or 60 degrees when the angle of incidence is equal to 45 degrees or 60 degrees respectively. These values are determined by the refractive index of the prism, which is given as √2.
After electrolysis of a NaCl solution with inert electrodes for a certain period of time, 60 ml of the solution was left which was found to be 1 N in NaOH. During the same time 31.75 g of Cu was deposited in a Cu voltameter in series with the electrolytic cell. Calculate the percentage of the theoretical yield of the sodium hydroxide obtained.- a)3
- b)6
- c)5
- d)4
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
After electrolysis of a NaCl solution with inert electrodes for a certain period of time, 60 ml of the solution was left which was found to be 1 N in NaOH. During the same time 31.75 g of Cu was deposited in a Cu voltameter in series with the electrolytic cell. Calculate the percentage of the theoretical yield of the sodium hydroxide obtained.
a)
3
b)
6
c)
5
d)
4
|
|
Geetika Mehta answered |
No. of eq. of NaOH that can be produced theoretically for 100% current efficiency = no of equivalents of NaCl decomposed = no of eq. of Cu deposited
No. of eq. of NaOH produced experimentally = 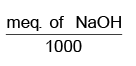
A point P moves such that the tangents PT1 and PT2 from it to the hyperbola 4x2 − 9y2 = 36 are mutually perpendicular. Then the equation of the locus of P is- a)x2 + y2 = 5
- b)x4 − y4 = 4
- c)x5 + y5 = 2
- d)x1 − y1 =4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A point P moves such that the tangents PT1 and PT2 from it to the hyperbola 4x2 − 9y2 = 36 are mutually perpendicular. Then the equation of the locus of P is
a)
x2 + y2 = 5
b)
x4 − y4 = 4
c)
x5 + y5 = 2
d)
x1 − y1 =4
|
|
Lekshmi Chopra answered |
Concept:
When the tangents from a moving point to a hyperbola are perpendicular, the locus of the moving point is a circle with the center at the center of the hyperbola.
Solution:
Given:
Equation of hyperbola: 4x^2 - 9y^2 = 36
Approach:
1. Find the center of the hyperbola.
2. Use the concept mentioned above to find the equation of the locus of point P.
Calculations:
1. The standard form of the hyperbola is (x^2/a^2) - (y^2/b^2) = 1.
Comparing this with the given equation, we get:
a^2 = 9, b^2 = 4
Center of the hyperbola is at (0, 0).
2. As mentioned earlier, the locus of the moving point P is a circle with the center at the center of the hyperbola.
Therefore, the equation of the locus is x^2 + y^2 = 5.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': x^2 + y^2 = 5.
When the tangents from a moving point to a hyperbola are perpendicular, the locus of the moving point is a circle with the center at the center of the hyperbola.
Solution:
Given:
Equation of hyperbola: 4x^2 - 9y^2 = 36
Approach:
1. Find the center of the hyperbola.
2. Use the concept mentioned above to find the equation of the locus of point P.
Calculations:
1. The standard form of the hyperbola is (x^2/a^2) - (y^2/b^2) = 1.
Comparing this with the given equation, we get:
a^2 = 9, b^2 = 4
Center of the hyperbola is at (0, 0).
2. As mentioned earlier, the locus of the moving point P is a circle with the center at the center of the hyperbola.
Therefore, the equation of the locus is x^2 + y^2 = 5.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': x^2 + y^2 = 5.
Consider n x n graph paper, where n is a natural number. Consider the right-angled isosceles triangles, whose vertices are integer points of this graph and whose sides forming right angle are parallel to x and y axes. If the number of such triangle is 2/kn(n + 1)(2n + 1), the numerical quantity k must be equal to
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider n x n graph paper, where n is a natural number. Consider the right-angled isosceles triangles, whose vertices are integer points of this graph and whose sides forming right angle are parallel to x and y axes. If the number of such triangle is 2/kn(n + 1)(2n + 1), the numerical quantity k must be equal to
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Let us first determine the number of possible squares on the graph.
The graph will have n × n squares of dimensions 1 x 1. (n - 1) × (n - 1) squares will rise to four isosceles right-angled triangles.
⇒ Required number of triangles
= 4.[n2 + (n - 1)2 + (n - 2)2 + ... + 12]
= 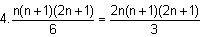
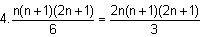
⇒ k must be equal to 3.
The arrangement of X– ions around A+ ion in solid AX is given in the figure (not drawn to scale). If the radius of X– is 250 pm, what is the radius (in pm) of A+? (Round off up to 1 decimal place)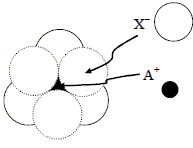
Correct answer is '103.5'. Can you explain this answer?
The arrangement of X– ions around A+ ion in solid AX is given in the figure (not drawn to scale). If the radius of X– is 250 pm, what is the radius (in pm) of A+? (Round off up to 1 decimal place)

|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
According to the given figure, A+ is present in the octahedral void of X–.
The limiting radius in octahedral void is related to the radius of sphere as:
rvoid = 0.414 rsphere
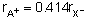
= 0.414 x 250 pm = 103.5 pm
Function x = A sin2 ωt + B cos2ωt + C sinωt cosωt represents SHM- a)for any value of A, B and C (except C = 0)
- b)if A = -B; C = 2B, amplitude = |B√2|
- c)if A = B; C = 0
- d)if A = B; C = 2B, amplitude = |B|
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Function x = A sin2 ωt + B cos2ωt + C sinωt cosωt represents SHM
a)
for any value of A, B and C (except C = 0)
b)
if A = -B; C = 2B, amplitude = |B√2|
c)
if A = B; C = 0
d)
if A = B; C = 2B, amplitude = |B|

|
Rhea Joshi answered |
Understanding the Function
The function x = A sin²(ωt) + B cos²(ωt) + C sin(ωt) cos(ωt) is a linear combination of sinusoidal functions, and we need to analyze when it represents Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM).
Criteria for SHM
- For a function to represent SHM, it must be expressible in the form x = R sin(ωt + φ).
Case Analysis
- Case A (Any A, B, C ≠ 0)
- The function can be rewritten using trigonometric identities:
- sin²(ωt) = (1 - cos(2ωt))/2
- cos²(ωt) = (1 + cos(2ωt))/2
- This transformation shows that the function represents a harmonic oscillation for any values of A, B, and C (except C = 0). Hence, it is valid.
- Case B (A = -B; C = 2B)
- Here, the function simplifies to a form that can be combined to yield a single sinusoidal function.
- The amplitude can be calculated as |B√2|, confirming it still represents SHM.
- Case C (A = B; C = 0)
- This leads to a simple form of the function that can still be expressed as a harmonic function, confirming it represents SHM.
- Case D (A = B; C = 2B)
- Similar to Case B, this forms a valid SHM where the amplitude is |B|, reaffirming it represents SHM.
Conclusion
The function represents SHM under the conditions outlined in options A, B, and D, confirming the versatility of the sine and cosine functions in describing harmonic motion.
The function x = A sin²(ωt) + B cos²(ωt) + C sin(ωt) cos(ωt) is a linear combination of sinusoidal functions, and we need to analyze when it represents Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM).
Criteria for SHM
- For a function to represent SHM, it must be expressible in the form x = R sin(ωt + φ).
Case Analysis
- Case A (Any A, B, C ≠ 0)
- The function can be rewritten using trigonometric identities:
- sin²(ωt) = (1 - cos(2ωt))/2
- cos²(ωt) = (1 + cos(2ωt))/2
- This transformation shows that the function represents a harmonic oscillation for any values of A, B, and C (except C = 0). Hence, it is valid.
- Case B (A = -B; C = 2B)
- Here, the function simplifies to a form that can be combined to yield a single sinusoidal function.
- The amplitude can be calculated as |B√2|, confirming it still represents SHM.
- Case C (A = B; C = 0)
- This leads to a simple form of the function that can still be expressed as a harmonic function, confirming it represents SHM.
- Case D (A = B; C = 2B)
- Similar to Case B, this forms a valid SHM where the amplitude is |B|, reaffirming it represents SHM.
Conclusion
The function represents SHM under the conditions outlined in options A, B, and D, confirming the versatility of the sine and cosine functions in describing harmonic motion.
Chapter doubts & questions for JEE Advanced Practice Tests - JEE Main & Advanced Mock Test Series 2025 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of JEE Advanced Practice Tests - JEE Main & Advanced Mock Test Series 2025 in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup



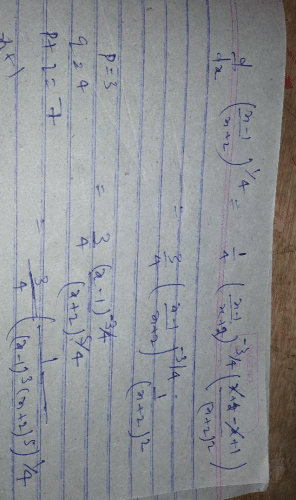
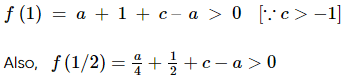

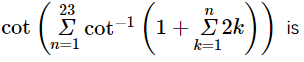
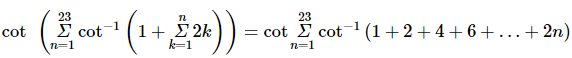
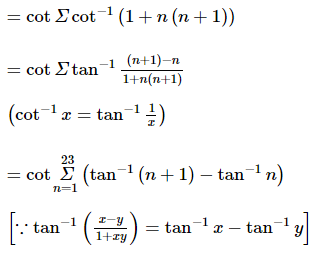
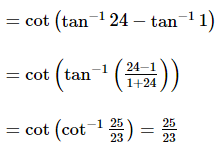
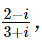 (where i = √−1) in the straight line z(1 + i) =
(where i = √−1) in the straight line z(1 + i) = 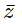 (i − 1)is
(i − 1)is