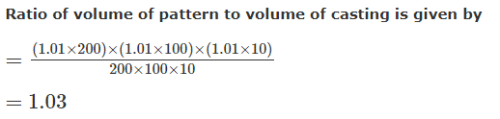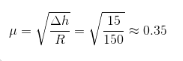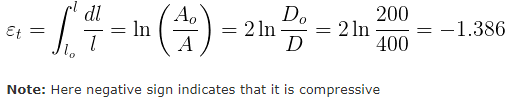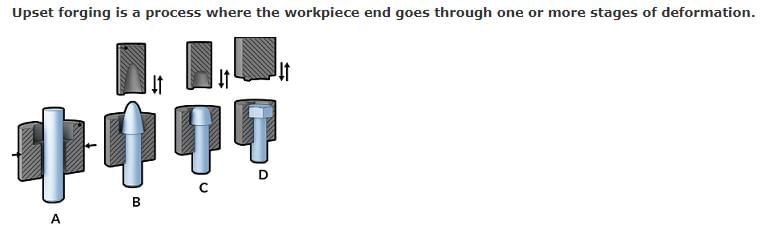All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Manufacturing Engineering for Mechanical Engineering Exam
Consider the following statements:
In comparison to hot working, in cold working,
1. higher forces are required
2. no heating is required
3. less ductility is required
4. better surface finish is obtainedQ.Which of the statements given above are correct? - a)1, 2 and 3
- b)2 and 4
- c)1 and 3
- d)2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
In comparison to hot working, in cold working,
1. higher forces are required
2. no heating is required
3. less ductility is required
4. better surface finish is obtained
In comparison to hot working, in cold working,
1. higher forces are required
2. no heating is required
3. less ductility is required
4. better surface finish is obtained
Q.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
2 and 4
c)
1 and 3
d)
2, 3 and 4
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Correct Answer :- b
Explanation : Although 1 is also correct but according to given option (b) is the most suitable. 3 is wrong because working more ductility is required.
For butt -welding 40 mm thick steel plates, when the expected quantity of such jobs is 5000 per month over a period of 10 year, choose the best suitable welding process out of the following available alternatives. - a)submerged arc welding
- b)Oxy-acetylene welding
- c)Electron beam welding
- d)MIC welding
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For butt -welding 40 mm thick steel plates, when the expected quantity of such jobs is 5000 per month over a period of 10 year, choose the best suitable welding process out of the following available alternatives.
a)
submerged arc welding
b)
Oxy-acetylene welding
c)
Electron beam welding
d)
MIC welding
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
We need maximum metal deposition rate so choice SAW.
Note: You know maximum metal deposition rate of all welding is SAW and it may joint 40 mm thick plates easily.
Note: You know maximum metal deposition rate of all welding is SAW and it may joint 40 mm thick plates easily.
During normalizing process of steel, the specimen is heated- a)Between the upper and lower critical temperature and cooled in still air.
- b)Above the upper critical temperature and cooled in furnace.
- c)Above the upper critical temperature and cooled in still air.
- d)Between the upper and lower critical temperature and cooled in furnace.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During normalizing process of steel, the specimen is heated
a)
Between the upper and lower critical temperature and cooled in still air.
b)
Above the upper critical temperature and cooled in furnace.
c)
Above the upper critical temperature and cooled in still air.
d)
Between the upper and lower critical temperature and cooled in furnace.
|
|
Aarav Singh answered |
Normalising involves prolonged heating just above the critical temperature to produce globular form of carbine and then cooling in air.
Which of the following is not improved by cold working of metals?- a)hardness
- b)toughness
- c)surface finish
- d)corrosion resistance
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not improved by cold working of metals?
a)
hardness
b)
toughness
c)
surface finish
d)
corrosion resistance

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
Corrosion resistance refers to the resistance a material offers against a reaction with adverse elements that can corrode the material. Various materials have this property intrinsically, depending upon their corrosion resistance rate. Alternatively, some methods or treatments can be used to resist corrosion such as painting or hot dip galvanizing, or a combination of these methods with coating.
Corrosion is a process in which a material is oxidized by substances in the environment that cause the material to lose electrons. Corrosion resistance is the capacity to hold the binding energy of a metal and withstand the deterioration and chemical breakdown that would otherwise occur when the material is exposed to such an environment.
Assertion (A): In case of hot working of metals, the temperature at which the process is finally stopped should not be above the recrystallisation temperature.
Reason (R): If the process is stopped above the recrystallisation temperature, grain growth will take place again and spoil the attained structure. - a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true hut R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): In case of hot working of metals, the temperature at which the process is finally stopped should not be above the recrystallisation temperature.
Reason (R): If the process is stopped above the recrystallisation temperature, grain growth will take place again and spoil the attained structure.
Reason (R): If the process is stopped above the recrystallisation temperature, grain growth will take place again and spoil the attained structure.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true hut R is false
d)
A is false but R is true

|
Vicky Sharma answered |
D
becoz hot working of metals takes place always above recrystllisation temp.
or agr process ko recrystllisation ke upr stop krte hai to to usme minor sa changes to hoga hi...
In the rolling process, roll separating force can be decreased by - a)reducing the roll diameter
- b)increasing the roll diameter
- c)providing back-up rolls
- d)increasing the friction between the rolls and the metal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the rolling process, roll separating force can be decreased by
a)
reducing the roll diameter
b)
increasing the roll diameter
c)
providing back-up rolls
d)
increasing the friction between the rolls and the metal

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
The answer is a.
Varies method to reduce the separating force are
1) Smaller roll diameter 2) Lower friction 3) High work piece temperature etc
Assertion (A): Aluminium alloys are cast in hot ch... moreamber die casting machine. Reason (R): Aluminium alloys require high melting when compared to zinc alloys.a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R arc true but R is NOTthe correct explanation of Ac)A is true hut R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The disadvantages of hot chamber die casting system is that it is limited to use with low-melting point metals and Aluminium alloys are not cast in hot chamber die casting machine because of high melting temperature.
While cooling, a cubical casting of side 40 mm undergoes 3%, 4% and 5% volume shrinkage during the liquid state, phase transition and solid state, respectively. The volume of metal compensated from the riser is - a)2%
- b)7%
- c)8%
- d)9%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
While cooling, a cubical casting of side 40 mm undergoes 3%, 4% and 5% volume shrinkage during the liquid state, phase transition and solid state, respectively. The volume of metal compensated from the riser is
a)
2%
b)
7%
c)
8%
d)
9%
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
The riser can compensate for volume shrinkage only in the liquid stage and transition stage and not in the solid state.
Hence volume of metal that needs to be compensated from the riser =3+4=7%
Assertion (A): Cold working of metals results in increase of strength and hardness
Reason (R): Cold working reduces the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material - a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true hut R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Cold working of metals results in increase of strength and hardness
Reason (R): Cold working reduces the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material
Reason (R): Cold working reduces the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true hut R is false
d)
A is false but R is true
|
|
Kajal Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
• Cold working of metals is a process of plastic deformation at temperatures below the recrystallization temperature of the metal.
• When the metal is subjected to cold working, its grain structure undergoes deformation and elongation due to the application of external forces.
• This results in an increase in the dislocation density of the metal, which in turn leads to an increase in its strength and hardness.
• The dislocations act as barriers to the movement of dislocation lines, which makes it harder for the metal to deform further under the application of external forces.
• The increase in the dislocation density also results in a decrease in the ductility of the metal, making it more brittle.
Assertion (A): Cold working of metals results in an increase in strength and hardness.
• This assertion is true as explained above.
Reason (R): Cold working reduces the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material.
• This reason is false as the cold working process increases the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material.
• This is because cold working creates more dislocations in the metal due to the plastic deformation and elongation of its grain structure.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer as both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
• Cold working of metals is a process of plastic deformation at temperatures below the recrystallization temperature of the metal.
• When the metal is subjected to cold working, its grain structure undergoes deformation and elongation due to the application of external forces.
• This results in an increase in the dislocation density of the metal, which in turn leads to an increase in its strength and hardness.
• The dislocations act as barriers to the movement of dislocation lines, which makes it harder for the metal to deform further under the application of external forces.
• The increase in the dislocation density also results in a decrease in the ductility of the metal, making it more brittle.
Assertion (A): Cold working of metals results in an increase in strength and hardness.
• This assertion is true as explained above.
Reason (R): Cold working reduces the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material.
• This reason is false as the cold working process increases the total number of dislocations per unit volume of the material.
• This is because cold working creates more dislocations in the metal due to the plastic deformation and elongation of its grain structure.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer as both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Consider the following steps involved in hammer forging a connecting rod from bar stock:
1. Blocking 2 . Trimming 3. Finishing 4. Fullering 5. Edging Q.Which of the following is the correct sequence of operations?- a)1, 4, 3, 2 and 5
- b)4, 5, 1, 3 and 2
- c)5, 4, 3, 2 and 1
- d)5, 1, 4, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following steps involved in hammer forging a connecting rod from bar stock:
1. Blocking 2 . Trimming 3. Finishing 4. Fullering 5. Edging
1. Blocking 2 . Trimming 3. Finishing 4. Fullering 5. Edging
Q.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of operations?
a)
1, 4, 3, 2 and 5
b)
4, 5, 1, 3 and 2
c)
5, 4, 3, 2 and 1
d)
5, 1, 4, 2 and 3
|
|
Meera Bose answered |
Sequence of Operations in Hammer Forging a Connecting Rod from Bar Stock
The process of hammer forging a connecting rod from bar stock involves several steps. The correct sequence of operations is:
4. Fullering: This is the first step in which the bar stock is heated and then forged into a rough shape with a fuller, which is a type of forging tool.
5. Edging: In this step, the rough shape formed in the previous step is further refined by using a forging tool to create edges on the connecting rod.
1. Blocking: Once the edges are formed, the connecting rod is blocked, which means it is shaped into a more recognizable form of a connecting rod.
3. Finishing: In this step, the connecting rod is further refined by using various forging tools to smooth out any rough edges or surfaces.
2. Trimming: Finally, the connecting rod is trimmed to its final shape and size, and any excess material is removed.
Therefore, the correct sequence of operations in hammer forging a connecting rod from bar stock is 4, 5, 1, 3, and 2, which is option B.
The process of hammer forging a connecting rod from bar stock involves several steps. The correct sequence of operations is:
4. Fullering: This is the first step in which the bar stock is heated and then forged into a rough shape with a fuller, which is a type of forging tool.
5. Edging: In this step, the rough shape formed in the previous step is further refined by using a forging tool to create edges on the connecting rod.
1. Blocking: Once the edges are formed, the connecting rod is blocked, which means it is shaped into a more recognizable form of a connecting rod.
3. Finishing: In this step, the connecting rod is further refined by using various forging tools to smooth out any rough edges or surfaces.
2. Trimming: Finally, the connecting rod is trimmed to its final shape and size, and any excess material is removed.
Therefore, the correct sequence of operations in hammer forging a connecting rod from bar stock is 4, 5, 1, 3, and 2, which is option B.
In a rolling process, sheet of 25 mm thickness is rolled to 20 mm thickness. Roll is of diameter 600 mm and it rotates at 100 rpm. The roll strip contact length will be - a)5 mm
- b)39 mm
- c)78 mm
- d)120 mm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a rolling process, sheet of 25 mm thickness is rolled to 20 mm thickness. Roll is of diameter 600 mm and it rotates at 100 rpm. The roll strip contact length will be
a)
5 mm
b)
39 mm
c)
78 mm
d)
120 mm
|
|
Debolina Menon answered |
The projected length of arc of contact, L = R sin α
And we know that
And we know that
Δh = 2R (1 -cos α) or cos α = 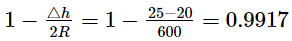
therefore sin α = 0.13
Therefore L= R sin α = 300 x .013 = 39 mm
A blank of 30 mm diameter is to be produced out of 10 mm thick sheet on a simple die. If 6%clearance is recommended, then the nominal diameters of pie and punch are respectively - a)30.6 mm and 29.4 mm
- b)30.6 mm and 30 mm
- c)30 mm and 29.4 mm
- d)30 mm and 28.8 mm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A blank of 30 mm diameter is to be produced out of 10 mm thick sheet on a simple die. If 6%clearance is recommended, then the nominal diameters of pie and punch are respectively
a)
30.6 mm and 29.4 mm
b)
30.6 mm and 30 mm
c)
30 mm and 29.4 mm
d)
30 mm and 28.8 mm

|
Devanshi Iyer answered |
It is blanking operation so clearance must be provided on punch.
Therefore, Die size = blank size = 30 mm
Punch size = blank size – 2C = 30 -2 x 0.06 x t = 30 – 2 x 0.06 x 10 = 28.8 mm
Therefore, Die size = blank size = 30 mm
Punch size = blank size – 2C = 30 -2 x 0.06 x t = 30 – 2 x 0.06 x 10 = 28.8 mm
In metals subjected to cold working, strain hardening effect is due to
- a)dislocation mechanism
- b)twining mechanism
- c)slip mechanism
- d)fracture mechanism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In metals subjected to cold working, strain hardening effect is due to
a)
dislocation mechanism
b)
twining mechanism
c)
slip mechanism
d)
fracture mechanism
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Correct answer is a)
Dislocation mechanism is responsible for strain hardening.
Which of the following materials requires the largest shrinkage allowance, while making a pattern for casting? - a)Brass
- b)Aluminium
- c)Cast Iron
- d)Plain Carbon Steel
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following materials requires the largest shrinkage allowance, while making a pattern for casting?
a)
Brass
b)
Aluminium
c)
Cast Iron
d)
Plain Carbon Steel
|
|
Hiral Jain answered |
Shrinkage allowance is given by,
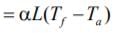
Where, α = Coefficient of thermal expansion.
So, Shrinkage ∝ α
Since, brass has the highest coefficient of
thermal expansion among the given materials
so, it will require largest shrinkage allowance.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
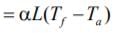
Where, α = Coefficient of thermal expansion.
So, Shrinkage ∝ α
Since, brass has the highest coefficient of
thermal expansion among the given materials
so, it will require largest shrinkage allowance.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Which of the following materials can be used for making patterns?
1. Aluminium
2. Wax
3. Stainless steel
4. Lead
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- a)1,3 and 4
- b)2,3 and 4
- c)1, 2 and 4
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following materials can be used for making patterns?
1. Aluminium
2. Wax
3. Stainless steel
4. Lead
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
1,3 and 4
b)
2,3 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 4
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
Stainless steel, wax and mercury can be used for making patterns
Assertion (A): Aluminium has poor weldability.
Reason (R): Aluminium has high thermal conductivity and high affinity to oxygen.
- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true hut R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Aluminium has poor weldability.
Reason (R): Aluminium has high thermal conductivity and high affinity to oxygen.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true hut R is false
d)
A is false but R is true
|
|
Niharika Iyer answered |
Explanation:
Aluminium is a widely used metal in industries due to its low density, high corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. However, it is not an easy metal to weld. The given assertion and reason can be explained as follows:
A. Poor Weldability of Aluminium:
Aluminium has poor weldability due to the following reasons:
R. High Thermal Conductivity and Affinity to Oxygen:
High thermal conductivity and high affinity to oxygen are the reasons for poor weldability of aluminium. The high thermal conductivity of aluminium makes it difficult to maintain a high-temperature gradient required for welding. The high affinity to oxygen results in the formation of an oxide layer on the surface of the metal, which can prevent proper fusion during welding.
Conclusion:
Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. While high thermal conductivity and high affinity to oxygen are the reasons for poor weldability of aluminium, other factors such as low melting point, coefficient of thermal expansion, and softness of the metal also contribute to the poor weldability. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Aluminium is a widely used metal in industries due to its low density, high corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. However, it is not an easy metal to weld. The given assertion and reason can be explained as follows:
A. Poor Weldability of Aluminium:
Aluminium has poor weldability due to the following reasons:
- Aluminium has a high thermal conductivity, which makes it difficult to maintain a high-temperature gradient required for welding.
- Aluminium has a high affinity to oxygen, which can result in the formation of an oxide layer on the surface of the metal and can prevent proper fusion during welding.
- Aluminium has a low melting point, which can result in burn-through during welding.
- Aluminium has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which can result in distortion and cracking of the welded joints.
- Aluminium is a soft metal, which can result in deformation during welding.
R. High Thermal Conductivity and Affinity to Oxygen:
High thermal conductivity and high affinity to oxygen are the reasons for poor weldability of aluminium. The high thermal conductivity of aluminium makes it difficult to maintain a high-temperature gradient required for welding. The high affinity to oxygen results in the formation of an oxide layer on the surface of the metal, which can prevent proper fusion during welding.
Conclusion:
Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. While high thermal conductivity and high affinity to oxygen are the reasons for poor weldability of aluminium, other factors such as low melting point, coefficient of thermal expansion, and softness of the metal also contribute to the poor weldability. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
In a blanking operation to produce steel washer, the maximum punch load used in 2 x 105 N.The plate thickness is 4 mm and percentage penetration is 25. The work done during this shearing operation is - a)200J
- b)400J
- c)600 J
- d)800 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a blanking operation to produce steel washer, the maximum punch load used in 2 x 105 N.The plate thickness is 4 mm and percentage penetration is 25. The work done during this shearing operation is
a)
200J
b)
400J
c)
600 J
d)
800 J
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
Which of the following are employed in shell moulding?1. Resin binder 2. Metal pattern 3. Heating coilsSelect the correct answer using the code given below: - a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 and 3 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are employed in shell moulding?
1. Resin binder 2. Metal pattern 3. Heating coils
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 and 3 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Shell moulding employed heated (1500) metal pattern with resin binder.
In deep drawing of sheets, the values of limiting draw ratio depends on- a)percentage elongation of sheet metal
- b)yield strength of sheet metal
- c)type of press used
- d)thickness of sheet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In deep drawing of sheets, the values of limiting draw ratio depends on
a)
percentage elongation of sheet metal
b)
yield strength of sheet metal
c)
type of press used
d)
thickness of sheet
|
|
Mahi Kaur answered |
The limit of deformation is reached when the load required deforming the flange becomes greater than the load-carrying capacity of the cup wall. Load carrying capacity of the wall = πDt x ft
The electrodes used in arc welding are coated. This coating is not expected to - a)provide protective atmosphere to weld
- b)stabilize the are
- c)add alloying elements
- d)prevents electrode from contamination,
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrodes used in arc welding are coated. This coating is not expected to
a)
provide protective atmosphere to weld
b)
stabilize the are
c)
add alloying elements
d)
prevents electrode from contamination,
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
-Electrode coatings should provide gas shielding for the arc, easy striking and arc stability, a protective slag, good weld shape, and most important of all a gas shield consuming the surrounding oxygen and protecting the molten weld metal.
-The electrodes used in arc welding are coated. This coating is not expected to prevents electrode from contamination.
Which one of the following is the process to refine the grains of metal after it has beendistorted by hammering or cold working? - a)Annealing
- b)Softening
- c)Re-crystallizing
- d)Normalizing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the process to refine the grains of metal after it has beendistorted by hammering or cold working?
a)
Annealing
b)
Softening
c)
Re-crystallizing
d)
Normalizing
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Recrystallization is a process by which deformed grains are replaced by a new set of defects-free grains that nucleate and grow until the original grains have been entirely consumed. Recrystallization is usually accompanied by a reduction in the strength and hardness of a material and a simultaneous increase in the ductility. Thus, the process may be introduced as a deliberate step in metals processing or may be an undesirable byproduct of another processing step. The most important industrial uses are the softening of metals previously hardened by cold work, which have lost their ductility, and the control of the grain structure in the final product.
Which of the following assumptions are correct for cold rolling?
1. The material is plastic.
2. The arc of contact is circular with a radius greater than the radius of the roll.
3. Coefficient of friction is constant over the arc of contact and acts in one direction
throughout the arc of contact.Q.Select the correct answer using the codes given below:Codes:- a)1 and 2
- b)1 and 3
- c)2 and 3
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following assumptions are correct for cold rolling?
1. The material is plastic.
2. The arc of contact is circular with a radius greater than the radius of the roll.
3. Coefficient of friction is constant over the arc of contact and acts in one direction
throughout the arc of contact.
1. The material is plastic.
2. The arc of contact is circular with a radius greater than the radius of the roll.
3. Coefficient of friction is constant over the arc of contact and acts in one direction
throughout the arc of contact.
Q.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:Codes:
a)
1 and 2
b)
1 and 3
c)
2 and 3
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Arnav Menon answered |
The correct assumptions for cold rolling are:
1. The material is plastic:
- This assumption is correct because cold rolling involves deforming the material by applying compressive forces. In order for the material to undergo plastic deformation, it must have a yield strength higher than the applied forces. Therefore, the material must be plastic in nature.
2. The arc of contact is circular with a radius greater than the radius of the roll:
- This assumption is correct because during cold rolling, the material is passed through a pair of rolls that have a cylindrical shape. The contact between the rolls and the material forms an arc, and this arc is assumed to be circular. Moreover, the radius of this circular arc is greater than the radius of the roll itself.
3. Coefficient of friction is constant over the arc of contact and acts in one direction throughout the arc of contact:
- This assumption is correct because the coefficient of friction plays a crucial role in determining the rolling process. It affects the amount of force required for rolling and the resulting surface finish of the material. In cold rolling, it is assumed that the coefficient of friction remains constant over the arc of contact between the rolls and the material. Additionally, it is assumed that the direction of frictional force remains the same throughout the arc of contact.
Explanation of the correct answer:
The correct answer is option 'D' because all of the given assumptions are correct for cold rolling. These assumptions are fundamental to the understanding and analysis of the cold rolling process. By assuming that the material is plastic, the arc of contact is circular with a greater radius than the roll, and the coefficient of friction is constant and acts in one direction throughout the arc of contact, engineers and researchers can develop models and equations to predict the behavior of the material during cold rolling. These assumptions allow for the calculation of forces, power requirements, and the prediction of the final shape and properties of the rolled material. Hence, option 'D' is the correct answer.
1. The material is plastic:
- This assumption is correct because cold rolling involves deforming the material by applying compressive forces. In order for the material to undergo plastic deformation, it must have a yield strength higher than the applied forces. Therefore, the material must be plastic in nature.
2. The arc of contact is circular with a radius greater than the radius of the roll:
- This assumption is correct because during cold rolling, the material is passed through a pair of rolls that have a cylindrical shape. The contact between the rolls and the material forms an arc, and this arc is assumed to be circular. Moreover, the radius of this circular arc is greater than the radius of the roll itself.
3. Coefficient of friction is constant over the arc of contact and acts in one direction throughout the arc of contact:
- This assumption is correct because the coefficient of friction plays a crucial role in determining the rolling process. It affects the amount of force required for rolling and the resulting surface finish of the material. In cold rolling, it is assumed that the coefficient of friction remains constant over the arc of contact between the rolls and the material. Additionally, it is assumed that the direction of frictional force remains the same throughout the arc of contact.
Explanation of the correct answer:
The correct answer is option 'D' because all of the given assumptions are correct for cold rolling. These assumptions are fundamental to the understanding and analysis of the cold rolling process. By assuming that the material is plastic, the arc of contact is circular with a greater radius than the roll, and the coefficient of friction is constant and acts in one direction throughout the arc of contact, engineers and researchers can develop models and equations to predict the behavior of the material during cold rolling. These assumptions allow for the calculation of forces, power requirements, and the prediction of the final shape and properties of the rolled material. Hence, option 'D' is the correct answer.
The force requirement in a blanking operation of low carbon steel sheet is 5.0 kN. The thickness of the sheet is ‘t’ and diameter of the blanked part is ‘d’. For the same work material, ifthe diameter of the blanked part is increased to 1.5 d and thickness is reduced to 0.4 t, the new blanking force in kN is - a)3.0
- b)4.5
- c)5.0
- d)8.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The force requirement in a blanking operation of low carbon steel sheet is 5.0 kN. The thickness of the sheet is ‘t’ and diameter of the blanked part is ‘d’. For the same work material, ifthe diameter of the blanked part is increased to 1.5 d and thickness is reduced to 0.4 t, the new blanking force in kN is
a)
3.0
b)
4.5
c)
5.0
d)
8.0
|
|
Nirala Raj answered |
A
Which one of the following is not a fusion welding process? - a)Gas welding
- b)Arc welding
- c)Brazing
- d)Resistance welding
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a fusion welding process?
a)
Gas welding
b)
Arc welding
c)
Brazing
d)
Resistance welding
|
|
Amrita Nambiar answered |
In Brazing base metal is not melted. And filler metal is not same or similar to that of base metal.
A strip with a cross-section 150 mm x 4.5 mm is being rolled with 20% reduction of areausing 450 mm diameter rolls. The angle subtended by the deformation zone at the roll centre is(in radian)- a)0.01
- b)0.02
- c)0.03
- d)0.06
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A strip with a cross-section 150 mm x 4.5 mm is being rolled with 20% reduction of areausing 450 mm diameter rolls. The angle subtended by the deformation zone at the roll centre is(in radian)
a)
0.01
b)
0.02
c)
0.03
d)
0.06
|
|
Ashutosh Sharma answered |
Initial thickness (h1) = 4.5 mm. As width constant therefore 20% reduction in area means 20% reduction in thickness also.
Final thickness (h12 = 0.8x4.5 = 3.6 mm
Tool material not suited to resistance welding is - a)Aluminium oxide
- b)Satellite
- c)High speed steel
- d)Masonite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Tool material not suited to resistance welding is
a)
Aluminium oxide
b)
Satellite
c)
High speed steel
d)
Masonite
|
|
Dipika Kulkarni answered |
Material suitability for Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a joining process that involves the application of heat and pressure to two or more metal surfaces to form a solid-state bond. The tool material used in resistance welding must be able to withstand high temperatures and pressures, as well as provide good electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity.
Unsuitable Tool Material for Resistance Welding
Among the given options, satellite is not suited for resistance welding. Satellite is an alloy that contains high amounts of cobalt, chromium, and tungsten. This material has excellent wear resistance and high-temperature strength, making it suitable for cutting tools, valves, and turbine blades. However, satellite has poor electrical conductivity, which makes it unsuitable for resistance welding.
Other Tool Materials for Resistance Welding
There are several other tool materials that are suitable for resistance welding, including:
- Copper: Copper is a common material used in resistance welding because it has high electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as good strength and wear resistance. Copper alloys such as beryllium copper and tungsten copper are also used in resistance welding.
- Molybdenum: Molybdenum has high-temperature strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for resistance welding.
- Refractory metals: Refractory metals such as tungsten, tantalum, and niobium have high melting points and excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making them suitable for resistance welding.
- Carbon: Carbon electrodes are used in resistance welding to provide a high current density and a stable arc.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resistance welding requires tool materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures, have good electrical and thermal conductivity, and provide a strong and durable bond. While satellite has excellent wear resistance and high-temperature strength, it is not suitable for resistance welding due to its poor electrical conductivity. Copper, molybdenum, refractory metals, and carbon are among the materials that are commonly used in resistance welding.
Resistance welding is a joining process that involves the application of heat and pressure to two or more metal surfaces to form a solid-state bond. The tool material used in resistance welding must be able to withstand high temperatures and pressures, as well as provide good electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity.
Unsuitable Tool Material for Resistance Welding
Among the given options, satellite is not suited for resistance welding. Satellite is an alloy that contains high amounts of cobalt, chromium, and tungsten. This material has excellent wear resistance and high-temperature strength, making it suitable for cutting tools, valves, and turbine blades. However, satellite has poor electrical conductivity, which makes it unsuitable for resistance welding.
Other Tool Materials for Resistance Welding
There are several other tool materials that are suitable for resistance welding, including:
- Copper: Copper is a common material used in resistance welding because it has high electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as good strength and wear resistance. Copper alloys such as beryllium copper and tungsten copper are also used in resistance welding.
- Molybdenum: Molybdenum has high-temperature strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for resistance welding.
- Refractory metals: Refractory metals such as tungsten, tantalum, and niobium have high melting points and excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making them suitable for resistance welding.
- Carbon: Carbon electrodes are used in resistance welding to provide a high current density and a stable arc.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resistance welding requires tool materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures, have good electrical and thermal conductivity, and provide a strong and durable bond. While satellite has excellent wear resistance and high-temperature strength, it is not suitable for resistance welding due to its poor electrical conductivity. Copper, molybdenum, refractory metals, and carbon are among the materials that are commonly used in resistance welding.
A 1.5 mm thick sheet is subject to unequal biaxial stretching and the true strains in the directions of stretching are 0.05 and 0.09. The fh'1al thickness of the sheet in mm is - a)1.414
- b)1.304
- c)1 362
- d)289
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 1.5 mm thick sheet is subject to unequal biaxial stretching and the true strains in the directions of stretching are 0.05 and 0.09. The fh'1al thickness of the sheet in mm is
a)
1.414
b)
1.304
c)
1 362
d)
289
|
|
Anmol Saini answered |
To find the final thickness of the sheet after unequal biaxial stretching, we can use the formula for true strain in the direction of stretching:
ε = ln(l_f/l_i)
Where ε is the true strain, l_f is the final length, and l_i is the initial length.
Given that the initial thickness of the sheet is 1.5 mm, we can find the final thickness by rearranging the formula:
l_f = l_i * e^ε
First, let's calculate the final length in the first direction of stretching:
l_f1 = 1.5 mm * e^0.05 = 1.577 mm
Now, let's calculate the final length in the second direction of stretching:
l_f2 = 1.5 mm * e^0.09 = 1.638 mm
Since the sheet is subject to unequal biaxial stretching, the final thickness will be the average of the final lengths in the two directions:
l_f_avg = (l_f1 + l_f2) / 2 = (1.577 mm + 1.638 mm) / 2 = 1.6075 mm
Therefore, the final thickness of the sheet is approximately 1.6075 mm.
However, none of the given answer options match this value exactly. The closest option is option 'B' with a value of 1.304 mm. It seems like there might be a mistake in the answer options provided, as option 'B' does not match the calculated value.
ε = ln(l_f/l_i)
Where ε is the true strain, l_f is the final length, and l_i is the initial length.
Given that the initial thickness of the sheet is 1.5 mm, we can find the final thickness by rearranging the formula:
l_f = l_i * e^ε
First, let's calculate the final length in the first direction of stretching:
l_f1 = 1.5 mm * e^0.05 = 1.577 mm
Now, let's calculate the final length in the second direction of stretching:
l_f2 = 1.5 mm * e^0.09 = 1.638 mm
Since the sheet is subject to unequal biaxial stretching, the final thickness will be the average of the final lengths in the two directions:
l_f_avg = (l_f1 + l_f2) / 2 = (1.577 mm + 1.638 mm) / 2 = 1.6075 mm
Therefore, the final thickness of the sheet is approximately 1.6075 mm.
However, none of the given answer options match this value exactly. The closest option is option 'B' with a value of 1.304 mm. It seems like there might be a mistake in the answer options provided, as option 'B' does not match the calculated value.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following are the cold working processes?
(1) Forging
(2) Bending
(3) Squeezing
(4) Pipe Welding
(5) Drawing
- A:
(1), (2) and (3)
- B:
(2), (3) and (5)
- C:
(2), (4) and (5)
- D:
(1), (2), (3) and (5)
The answer is b.
Which of the following are the cold working processes?
(1) Forging
(2) Bending
(3) Squeezing
(4) Pipe Welding
(5) Drawing
(1), (2) and (3)
(2), (3) and (5)
(2), (4) and (5)
(1), (2), (3) and (5)

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
1. Both the hot working process and cold working process are plastic deformation of metal but the cold working process is carried out at the temperature below recrystallisation temperature whereas hot working process is carried out at the temperature above recrystallisation temperature.
2. In above given processes, the bending, squeezing and drawing processes are carried out at the temperature below recrystallisation temperature.
3. Therefore, bending, squeezing and drawing are cold working processes; whereas forging and pipe welding are hot working processes.
Consider the following welding processes:1. TIG welding 2. Submerged arc welding3. Electro-slag welding 4. Thermit welding Which of these welding processes are used for welding thick pieces of metals? - a)1, 2 and 3
- b)1, 2 and 4
- c)1,3 and 4
- d)2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following welding processes:
1. TIG welding
2. Submerged arc welding
3. Electro-slag welding
4. Thermit welding
Which of these welding processes are used for welding thick pieces of metals?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
1, 2 and 4
c)
1,3 and 4
d)
2, 3 and 4
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : The three main welding techniques that are used in a shipyard are as follows:
Arc Welding
Gas Welding
Resistance Welding
Electro-slag welding is used for joining thick materials in the vertical plane. It is not an arc process, depending on the electrical resistivity of molten flux to produce the heat necessary to melt both filler and base metal. As the flux melts, a slag blanket (2.5–3.8 mm thick) is formed.
In a sand casting operation, the total liquid head... more is maintained constant such that it is equal to the mould height. The time taken to fill the mould with a top gate is tA. If the same mould is filled with a bottom gate, then the time taken is tB. Ignore the time required to fill the runner and frictional effects. Assume atmospheric pressure at the top molten metal surfaces. The relation between tA and tB is a)tB=√2tAb)tB=2tAc)tB=tA/√2d)tB= 2√2tACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aarav Unni answered |

For mild steel, the hot forging temperature range is - a)4000C to 6000C
- b)7000C to 9000C
- c)10000C to 12000C
- d)13000Cto 15000C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For mild steel, the hot forging temperature range is
a)
4000C to 6000C
b)
7000C to 9000C
c)
10000C to 12000C
d)
13000Cto 15000C
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
For Mild Steel, recrystallisation temp is of the order of 10000C
Assertion (A): The electrodes of ac arc welding are coated with sodium silicate, whereas electrodes used for dc arc welding are coated with potassium silicate binders.
Reason (R): Potassium has a lower ionization potential than sodium.
- a)A is true hut R is false
- b)Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The electrodes of ac arc welding are coated with sodium silicate, whereas electrodes used for dc arc welding are coated with potassium silicate binders.
Reason (R): Potassium has a lower ionization potential than sodium.
a)
A is true hut R is false
b)
Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
d)
A is false but R is true

|
Gate Funda answered |
Let's analyze the Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A):
"The electrodes of AC arc welding are coated with sodium silicate, whereas electrodes used for DC arc welding are coated with potassium silicate binders."
- This statement is true. In AC arc welding, electrodes are typically coated with sodium silicate because sodium helps stabilize the arc in alternating current. In DC arc welding, potassium silicate is preferred because potassium provides better arc stability with direct current due to its ionization properties.
Reason (R):
"Potassium has a lower ionization potential than sodium."
- This statement is false. In fact, potassium has a higher ionization potential than sodium. Sodium has a lower ionization potential, meaning it requires less energy to remove an electron from a sodium atom compared to potassium.
Conclusion:
- Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Thus, the correct answer is:
Option 1: A is true but R is false.
Consider the following processes: 1. Gas welding 2. Thermit welding 3. Arc welding 4. Resistance weldingThe correct sequence of these processes in increasing order of their welding temperatures is - a)1, 3, 4, 2
- b)1, 2, 3, 4
- c)4, 3, 1, 2
- d)4, 1, 3, 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following processes:
1. Gas welding
2. Thermit welding
3. Arc welding
4. Resistance welding
The correct sequence of these processes in increasing order of their welding temperatures is
a)
1, 3, 4, 2
b)
1, 2, 3, 4
c)
4, 3, 1, 2
d)
4, 1, 3, 2
|
|
Tarun Chatterjee answered |
Explanation:
Welding is a process in which two or more metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures and allowing them to cool and solidify.
The welding temperature depends on the type of welding process used. Some welding processes require very high temperatures while others can be performed at lower temperatures.
The given processes are gas welding, thermit welding, arc welding, and resistance welding. Let's discuss each of these processes and their welding temperatures.
1. Gas welding:
Gas welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures using a flame produced by burning a fuel gas such as acetylene. The welding temperature in gas welding is around 1500°C to 1600°C.
2. Thermit welding:
Thermit welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures using a chemical reaction between aluminum powder and iron oxide. The welding temperature in thermit welding is around 2500°C to 3000°C.
3. Arc welding:
Arc welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures using an electric arc produced between an electrode and the workpiece. The welding temperature in arc welding is around 6000°C to 7000°C.
4. Resistance welding:
Resistance welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by passing an electric current through them and heating them to their melting temperatures due to the resistance offered by the metal parts. The welding temperature in resistance welding is around 800°C to 1200°C.
Based on the above discussion, we can conclude that the correct sequence of these processes in increasing order of their welding temperatures is option 'B', i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, which means gas welding has the lowest welding temperature, followed by thermit welding, arc welding, and resistance welding.
Welding is a process in which two or more metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures and allowing them to cool and solidify.
The welding temperature depends on the type of welding process used. Some welding processes require very high temperatures while others can be performed at lower temperatures.
The given processes are gas welding, thermit welding, arc welding, and resistance welding. Let's discuss each of these processes and their welding temperatures.
1. Gas welding:
Gas welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures using a flame produced by burning a fuel gas such as acetylene. The welding temperature in gas welding is around 1500°C to 1600°C.
2. Thermit welding:
Thermit welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures using a chemical reaction between aluminum powder and iron oxide. The welding temperature in thermit welding is around 2500°C to 3000°C.
3. Arc welding:
Arc welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by heating them to their melting temperatures using an electric arc produced between an electrode and the workpiece. The welding temperature in arc welding is around 6000°C to 7000°C.
4. Resistance welding:
Resistance welding is a process in which two metal parts are joined together by passing an electric current through them and heating them to their melting temperatures due to the resistance offered by the metal parts. The welding temperature in resistance welding is around 800°C to 1200°C.
Based on the above discussion, we can conclude that the correct sequence of these processes in increasing order of their welding temperatures is option 'B', i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, which means gas welding has the lowest welding temperature, followed by thermit welding, arc welding, and resistance welding.
Assertion (A): If neutral flame is used in oxy-acetylene welding, both oxygen and acetylene cylinders of same capacity will be emptied at the same time. Reason (R): Neutral flame uses equal amounts of oxygen and acetylene. - a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true hut R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): If neutral flame is used in oxy-acetylene welding, both oxygen and acetylene cylinders of same capacity will be emptied at the same time.
Reason (R): Neutral flame uses equal amounts of oxygen and acetylene.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true hut R is false
d)
A is false but R is true
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
With a solidification factor of 0.97 x 102 s/m2, the solidification time (in seconds) for a spherical casting of 200 mm diameter is [GATE-2003]- a)539
- b)1078
- c)4311
- d)3233
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
With a solidification factor of 0.97 x 102 s/m2, the solidification time (in seconds) for a spherical casting of 200 mm diameter is
[GATE-2003]
a)
539
b)
1078
c)
4311
d)
3233
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Option (b) is correct
ts = K (V/SA)^2
K= Solidification factor
V=volume of casting
SA= surface area of casting
Assertion (A): A sound welded joint should not only be strong enough but should also exhibits a good amount of ductility Reason (R): Welding process is used for fabricating mild steel components only - a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true hut R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): A sound welded joint should not only be strong enough but should also exhibits a good amount of ductility
Reason (R): Welding process is used for fabricating mild steel components only
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R arc true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true hut R is false
d)
A is false but R is true

|
Kirti Sharma answered |
Assertion (A): A sound welded joint should not only be strong enough but should also exhibit a good amount of ductility.
Reason (R): Welding process is used for fabricating mild steel components only.
The correct answer is option 'C', which states that Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Explanation:
Understanding the Assertion:
A welded joint is formed by joining two or more metal components using the welding process. The primary purpose of welding is to create a strong and reliable joint between the components, ensuring that they remain securely connected even under external forces or loads. However, mere strength is not always sufficient for a welded joint. Ductility is also an essential characteristic that a sound welded joint should possess.
When a load is applied to a welded joint, the joint experiences stress. If the joint is only strong but lacks ductility, it may fail abruptly without any warning. On the other hand, if the joint has a good amount of ductility, it can deform plastically under stress, allowing it to redistribute the load and prevent sudden failure. Ductility provides the joint with the ability to absorb energy and withstand deformation without fracturing. Therefore, a sound welded joint should exhibit both strength and ductility.
Understanding the Reason:
The reason provided in the question states that the welding process is used for fabricating mild steel components only. However, this reason is incorrect. Welding is a versatile process that can be used to join various types of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, cast iron, etc. The choice of welding process and consumables may vary depending on the material being welded, but welding is not limited to mild steel components only.
Conclusion:
The assertion is true because a sound welded joint should indeed possess both strength and ductility. However, the reason provided is false because welding is not limited to mild steel components. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer.
Reason (R): Welding process is used for fabricating mild steel components only.
The correct answer is option 'C', which states that Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Explanation:
Understanding the Assertion:
A welded joint is formed by joining two or more metal components using the welding process. The primary purpose of welding is to create a strong and reliable joint between the components, ensuring that they remain securely connected even under external forces or loads. However, mere strength is not always sufficient for a welded joint. Ductility is also an essential characteristic that a sound welded joint should possess.
When a load is applied to a welded joint, the joint experiences stress. If the joint is only strong but lacks ductility, it may fail abruptly without any warning. On the other hand, if the joint has a good amount of ductility, it can deform plastically under stress, allowing it to redistribute the load and prevent sudden failure. Ductility provides the joint with the ability to absorb energy and withstand deformation without fracturing. Therefore, a sound welded joint should exhibit both strength and ductility.
Understanding the Reason:
The reason provided in the question states that the welding process is used for fabricating mild steel components only. However, this reason is incorrect. Welding is a versatile process that can be used to join various types of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, cast iron, etc. The choice of welding process and consumables may vary depending on the material being welded, but welding is not limited to mild steel components only.
Conclusion:
The assertion is true because a sound welded joint should indeed possess both strength and ductility. However, the reason provided is false because welding is not limited to mild steel components. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer.
Which one of the following processes is the wiredrawing process?
- a)Compressive
- b)Hydrostatic stress
- c)Shear
- d)Tensile
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following processes is the wiredrawing process?
a)
Compressive
b)
Hydrostatic stress
c)
Shear
d)
Tensile

|
Devika Tiwari answered |
Wire drawing is a cold working process to obtain wires from rods of bigger diameters through a die. The wire is subjected to tension only. Coining is essentially a cold‐forging operation except for the fact that the flow of the metal occurs only at the top layers and not the entire volume. In the coining process, compressive forces are there. In blanking, the piece being punched out becomes the work-piece and any major burrs or undesirable features should be left on the remaining strip. Blanking is a shearing operation. Drawing when cup height is more than half the diameter is termed deep drawing. During deep drawing, in the flange of blank, there is bi‐axial tension and compression stresses.
Which one of the following is not an electric resistance method of welding?
- a)Electro slag welding
- b)Percussion welding
- c)Seam welding
- d)Flash welding
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not an electric resistance method of welding?
a)
Electro slag welding
b)
Percussion welding
c)
Seam welding
d)
Flash welding
|
|
Aditya Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Electric resistance welding is a method of welding where heat is generated by passing an electric current through the workpieces to be joined. The resistance of the workpieces to the flow of electric current generates heat at the interface, which melts and fuses the workpieces together. There are several different methods of electric resistance welding, but one of the methods listed in the options is not an electric resistance welding method.
Options:
a) Electro slag welding
b) Percussion welding
c) Seam welding
d) Flash welding
Analysis of options:
a) Electro slag welding:
Electro slag welding is a welding method that uses a consumable electrode and a flux to create a molten slag pool between the workpieces. The heat generated by the resistance of the slag to the flow of electric current melts and fuses the workpieces together. Therefore, electro slag welding is indeed an electric resistance welding method.
b) Percussion welding:
Percussion welding, also known as impact welding, is a solid-state welding process in which two workpieces are forcefully brought together and welded by the heat generated from the impact. Percussion welding does not involve the use of electric current, so it is not an electric resistance welding method.
c) Seam welding:
Seam welding is a method of joining two metal sheets by passing an electric current through the workpieces and applying pressure to create a weld. The resistance of the workpieces to the flow of electric current generates heat and melts the metal at the interface, forming a continuous seam weld. Therefore, seam welding is an electric resistance welding method.
d) Flash welding:
Flash welding is a welding process in which two workpieces are brought into contact and then rapidly separated to create an arc. The heat generated by the arc melts the metal at the interface, and the workpieces are then pressed together to form a weld. Flash welding involves the use of electric current, so it is an electric resistance welding method.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Electro slag welding, as it is not an electric resistance welding method.
Electric resistance welding is a method of welding where heat is generated by passing an electric current through the workpieces to be joined. The resistance of the workpieces to the flow of electric current generates heat at the interface, which melts and fuses the workpieces together. There are several different methods of electric resistance welding, but one of the methods listed in the options is not an electric resistance welding method.
Options:
a) Electro slag welding
b) Percussion welding
c) Seam welding
d) Flash welding
Analysis of options:
a) Electro slag welding:
Electro slag welding is a welding method that uses a consumable electrode and a flux to create a molten slag pool between the workpieces. The heat generated by the resistance of the slag to the flow of electric current melts and fuses the workpieces together. Therefore, electro slag welding is indeed an electric resistance welding method.
b) Percussion welding:
Percussion welding, also known as impact welding, is a solid-state welding process in which two workpieces are forcefully brought together and welded by the heat generated from the impact. Percussion welding does not involve the use of electric current, so it is not an electric resistance welding method.
c) Seam welding:
Seam welding is a method of joining two metal sheets by passing an electric current through the workpieces and applying pressure to create a weld. The resistance of the workpieces to the flow of electric current generates heat and melts the metal at the interface, forming a continuous seam weld. Therefore, seam welding is an electric resistance welding method.
d) Flash welding:
Flash welding is a welding process in which two workpieces are brought into contact and then rapidly separated to create an arc. The heat generated by the arc melts the metal at the interface, and the workpieces are then pressed together to form a weld. Flash welding involves the use of electric current, so it is an electric resistance welding method.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Electro slag welding, as it is not an electric resistance welding method.
Consider the following statements in respect of investment castings: 1. The pattern or patterns is/are not joined to a stalk or sprue also of wax to form a tree of patterns. 2. The prepared moulds are placed in an oven and heated gently to dry off the invest and melt out the bulk of wax. 3. The moulds are usually poured by placing the moulds in a vacuum chamber. Which of the statements given above are correct? - a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 and 3 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements in respect of investment castings:
1. The pattern or patterns is/are not joined to a stalk or sprue also of wax to form a tree of patterns.
2. The prepared moulds are placed in an oven and heated gently to dry off the invest and melt out the bulk of wax.
3. The moulds are usually poured by placing the moulds in a vacuum chamber.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 and 3 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Devansh Nambiar answered |
The pattern or patterns is/are joined to a stalk or sprue also of wax to form a tree of patterns.
Which one of the following statements is correct? - a)No flux is used in gas welding of mild steel
- b)Borax is the commonly used flux coating on welding electrodes
- c)Laser beam welding employs a vacuum chamber and thus avoids use of a shielding method
- d)AC can be used for GTAW process
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct?
a)
No flux is used in gas welding of mild steel
b)
Borax is the commonly used flux coating on welding electrodes
c)
Laser beam welding employs a vacuum chamber and thus avoids use of a shielding method
d)
AC can be used for GTAW process
|
|
Ruchi Ahuja answered |
The correct statements are:
a) No flux is used in gas welding of mild steel.
b) Borax is the commonly used flux coating on welding electrodes.
Gas welding of mild steel:
Gas welding is a process that uses a flame produced by a mixture of fuel gas and oxygen to melt the base metal and filler rod in order to join two or more pieces of metal together. In the case of mild steel, no flux is used during the gas welding process. Flux is a substance that is used to prevent oxidation and contamination of the molten metal during welding. However, in gas welding of mild steel, the high temperature flame generated by the fuel gas and oxygen mixture provides sufficient protection against oxidation and contamination, eliminating the need for flux.
Flux coating on welding electrodes:
Welding electrodes are often coated with a flux material to enhance the welding process. Flux coating serves multiple purposes, such as removing impurities, improving the weld bead appearance, and protecting the molten weld pool from oxidation and atmospheric contamination. Borax, a compound containing boron, is commonly used as a flux coating on welding electrodes. Borax helps in removing oxides and other impurities from the surface of the base metal, allowing for a cleaner and stronger weld joint. It also helps in preventing the formation of porosity and other defects in the weld.
Explanation of incorrect options:
c) Laser beam welding and vacuum chamber:
Laser beam welding is a high-precision welding technique that uses a focused laser beam to melt and join the base metal. However, laser beam welding does not require a vacuum chamber. In fact, laser beam welding is often performed in ambient air or with the use of shielding gases to protect the molten metal from oxidation and contamination.
d) AC for GTAW process:
GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding), also known as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, is primarily performed using DC (Direct Current) power supply. The use of DC allows for better control of the welding process and improved stability of the arc. While AC (Alternating Current) can be used for certain applications in GTAW, such as welding aluminum, it is not the commonly used power supply for this process.
In summary, the correct statements are that no flux is used in gas welding of mild steel, and borax is the commonly used flux coating on welding electrodes.
a) No flux is used in gas welding of mild steel.
b) Borax is the commonly used flux coating on welding electrodes.
Gas welding of mild steel:
Gas welding is a process that uses a flame produced by a mixture of fuel gas and oxygen to melt the base metal and filler rod in order to join two or more pieces of metal together. In the case of mild steel, no flux is used during the gas welding process. Flux is a substance that is used to prevent oxidation and contamination of the molten metal during welding. However, in gas welding of mild steel, the high temperature flame generated by the fuel gas and oxygen mixture provides sufficient protection against oxidation and contamination, eliminating the need for flux.
Flux coating on welding electrodes:
Welding electrodes are often coated with a flux material to enhance the welding process. Flux coating serves multiple purposes, such as removing impurities, improving the weld bead appearance, and protecting the molten weld pool from oxidation and atmospheric contamination. Borax, a compound containing boron, is commonly used as a flux coating on welding electrodes. Borax helps in removing oxides and other impurities from the surface of the base metal, allowing for a cleaner and stronger weld joint. It also helps in preventing the formation of porosity and other defects in the weld.
Explanation of incorrect options:
c) Laser beam welding and vacuum chamber:
Laser beam welding is a high-precision welding technique that uses a focused laser beam to melt and join the base metal. However, laser beam welding does not require a vacuum chamber. In fact, laser beam welding is often performed in ambient air or with the use of shielding gases to protect the molten metal from oxidation and contamination.
d) AC for GTAW process:
GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding), also known as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, is primarily performed using DC (Direct Current) power supply. The use of DC allows for better control of the welding process and improved stability of the arc. While AC (Alternating Current) can be used for certain applications in GTAW, such as welding aluminum, it is not the commonly used power supply for this process.
In summary, the correct statements are that no flux is used in gas welding of mild steel, and borax is the commonly used flux coating on welding electrodes.
Spot welding of two 1 mm thick sheets of steel (density = 8000 kg/m3) is carried out successfully by passing a certain amount of current for 0.1 second through the electrodes. The resultant weld nugget formed is 5 mm in diameter and 1.5 mm thick. If the latent heat of fusion of steel is 1400 kJ/kg and the effective resistance in the welding operation in 200 Ω , the current passing through the electrodes is approximately - a)1480A
- b)3300 A
- c)4060 A
- d)9400 A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Spot welding of two 1 mm thick sheets of steel (density = 8000 kg/m3) is carried out successfully by passing a certain amount of current for 0.1 second through the electrodes. The resultant weld nugget formed is 5 mm in diameter and 1.5 mm thick. If the latent heat of fusion of steel is 1400 kJ/kg and the effective resistance in the welding operation in 200 Ω , the current passing through the electrodes is approximately
a)
1480A
b)
3300 A
c)
4060 A
d)
9400 A
|
|
Amrita Chauhan answered |
Heat required for melting = (mL) =
Chapter doubts & questions for Manufacturing Engineering - GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Manufacturing Engineering - GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2026
30 docs|220 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily