All Exams >
Class 10 >
Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Carbon and Its Compounds for Class 10 Exam
A covalent bond is formed by- a)One sided sharing of electrons
- b)Mutual sharing of electrons
- c)Complete transfer of electrons
- d)Any of the three above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A covalent bond is formed by
a)
One sided sharing of electrons
b)
Mutual sharing of electrons
c)
Complete transfer of electrons
d)
Any of the three above
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Covalent bonding occurs when pairs of electrons are shared by atoms. Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms in order to gain more stability, which is gained by forming a full electron shell. By sharing their outermost (valence) electrons, atoms can fill up their outer electron shell and gain stability. Nonmetals will readily form covalent bonds with other nonmetals in order to obtain stability, and can form anywhere between one to three covalent bonds with other nonmetals depending on how many valence electrons they possess.
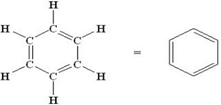
Which of the following is not a saturated hydrocarbon- a)Cyclohexane
- b)Butane
- c)Isobutane
- d)Benzene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a saturated hydrocarbon
a)
Cyclohexane
b)
Butane
c)
Isobutane
d)
Benzene
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Benzene- C6H6 has alternate carbon-carbon single and double bonds.

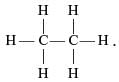
A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has- a)Two double bonds and one single bond
- b)Only double bonds
- c)Only triple bonds
- d)Only single bond
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has
a)
Two double bonds and one single bond
b)
Only double bonds
c)
Only triple bonds
d)
Only single bond
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Nitrogen has three electrons in its outermost shell and hydrogen has 1. 3 hydrogen atoms combine with 1 nitrogen atom to make ammonia. These bonds are single bonds.
Single bond: When two atoms share one electron pair between each other, then they are said to be bonded by single covalent bond, denoted by single dash joining the atoms.
Single bond: When two atoms share one electron pair between each other, then they are said to be bonded by single covalent bond, denoted by single dash joining the atoms.
Which one of the following is a denatured alcohol?- a)Ethanol
- b)Methanol
- c)Propanol
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a denatured alcohol?
a)
Ethanol
b)
Methanol
c)
Propanol
d)
Both (a) and (b)

|
Arnab Goyal answered |
Denatured Alcohol
Denatured alcohol refers to ethanol that has been rendered unfit for human consumption by the addition of certain chemicals. The purpose of denaturing alcohol is to discourage individuals from drinking it as a substitute for alcoholic beverages. It is commonly used in various industrial applications such as cleaning, disinfecting, and as a solvent.
Denatured Alcohol Options
The given options are:
a) Ethanol
b) Methanol
c) Propanol
Ethanol
Ethanol is a type of alcohol that is commonly found in alcoholic beverages. It is a clear, colorless liquid that is highly flammable and volatile. Ethanol is the primary ingredient in denatured alcohol. When ethanol is denatured, it undergoes a process in which chemicals are added to make it toxic or unpalatable.
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, is another type of alcohol that is highly toxic and unfit for human consumption. It is a clear, colorless liquid that is commonly used as an industrial solvent and fuel. Methanol is often used as an additive in denatured alcohol to make it undrinkable.
Propanol
Propanol is a type of alcohol that is commonly used as a solvent, disinfectant, and cleaning agent. It is less commonly used as a denaturant in alcohol. Propanol is not as toxic as methanol, but it can still cause harmful effects if ingested.
Correct Answer
The correct answer is option D - Both (a) and (b). Both ethanol and methanol can be used as denatured alcohol. Ethanol is the primary ingredient in denatured alcohol, while methanol is often added as a denaturant to make it toxic and undrinkable. Propanol, on the other hand, is less commonly used as a denaturant in alcohol.
Denatured alcohol refers to ethanol that has been rendered unfit for human consumption by the addition of certain chemicals. The purpose of denaturing alcohol is to discourage individuals from drinking it as a substitute for alcoholic beverages. It is commonly used in various industrial applications such as cleaning, disinfecting, and as a solvent.
Denatured Alcohol Options
The given options are:
a) Ethanol
b) Methanol
c) Propanol
Ethanol
Ethanol is a type of alcohol that is commonly found in alcoholic beverages. It is a clear, colorless liquid that is highly flammable and volatile. Ethanol is the primary ingredient in denatured alcohol. When ethanol is denatured, it undergoes a process in which chemicals are added to make it toxic or unpalatable.
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, is another type of alcohol that is highly toxic and unfit for human consumption. It is a clear, colorless liquid that is commonly used as an industrial solvent and fuel. Methanol is often used as an additive in denatured alcohol to make it undrinkable.
Propanol
Propanol is a type of alcohol that is commonly used as a solvent, disinfectant, and cleaning agent. It is less commonly used as a denaturant in alcohol. Propanol is not as toxic as methanol, but it can still cause harmful effects if ingested.
Correct Answer
The correct answer is option D - Both (a) and (b). Both ethanol and methanol can be used as denatured alcohol. Ethanol is the primary ingredient in denatured alcohol, while methanol is often added as a denaturant to make it toxic and undrinkable. Propanol, on the other hand, is less commonly used as a denaturant in alcohol.
Which of the following set of compounds have the same molecular formula?- a)Both (b) and (c)
- b)Cyclohexane and 1-hexen
- c)Butane and isobutane
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following set of compounds have the same molecular formula?
a)
Both (b) and (c)
b)
Cyclohexane and 1-hexen
c)
Butane and isobutane
d)
None of these
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
The molecular formula must be the same for both the molecules but the arrangement of atoms should be different. For example, look at the structure of n-butane and isobutane. Both of these molecules have the same molecular formula that is C4H10.
Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of- a)Carbon monoxide
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
- d)Coal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
a)
Carbon monoxide
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
d)
Coal
|
|
Anjali kumar answered |
Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
Explanation:
Carbon is one of the most abundant elements found on Earth and is an essential component of all living organisms. It is present in various forms in the atmosphere, one of which is carbon dioxide (CO2).
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Carbon dioxide is a compound composed of one carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- It is a greenhouse gas that plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's temperature by trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide is produced through natural processes such as respiration and volcanic activity, as well as human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- It is released into the atmosphere during the combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Carbon dioxide is an essential component of the carbon cycle, which involves the exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, and land.
2. Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Carbon monoxide is another compound that contains carbon and oxygen, but it is not as prevalent in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
- It is a colorless, odorless gas that is produced primarily through incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass.
- Carbon monoxide is toxic to humans and other animals when present in high concentrations.
- While carbon monoxide does exist in the atmosphere, it is typically found in trace amounts and is not a significant component compared to carbon dioxide.
3. Coal:
- Coal is a solid fossil fuel that is primarily composed of carbon.
- It is formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago.
- When coal is burned, it releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate change.
- While coal is a significant source of carbon emissions, it is not a direct form of carbon that exists in the atmosphere.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, carbon exists in the atmosphere primarily in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a greenhouse gas and plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate system. Carbon monoxide (CO) is also present but in trace amounts, and coal is a solid fossil fuel that releases carbon dioxide when burned.
Explanation:
Carbon is one of the most abundant elements found on Earth and is an essential component of all living organisms. It is present in various forms in the atmosphere, one of which is carbon dioxide (CO2).
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Carbon dioxide is a compound composed of one carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- It is a greenhouse gas that plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's temperature by trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide is produced through natural processes such as respiration and volcanic activity, as well as human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- It is released into the atmosphere during the combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Carbon dioxide is an essential component of the carbon cycle, which involves the exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, and land.
2. Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Carbon monoxide is another compound that contains carbon and oxygen, but it is not as prevalent in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
- It is a colorless, odorless gas that is produced primarily through incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass.
- Carbon monoxide is toxic to humans and other animals when present in high concentrations.
- While carbon monoxide does exist in the atmosphere, it is typically found in trace amounts and is not a significant component compared to carbon dioxide.
3. Coal:
- Coal is a solid fossil fuel that is primarily composed of carbon.
- It is formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago.
- When coal is burned, it releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate change.
- While coal is a significant source of carbon emissions, it is not a direct form of carbon that exists in the atmosphere.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, carbon exists in the atmosphere primarily in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a greenhouse gas and plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate system. Carbon monoxide (CO) is also present but in trace amounts, and coal is a solid fossil fuel that releases carbon dioxide when burned.
Vinegar is solution of- a)50%–60% acetic acid and in water
- b)50%–60% acetic acid in alcohol
- c)5%–8% acetic acid in water
- d)5%–8% acetic acid in alcohol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vinegar is solution of
a)
50%–60% acetic acid and in water
b)
50%–60% acetic acid in alcohol
c)
5%–8% acetic acid in water
d)
5%–8% acetic acid in alcohol
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Vinegar is a dilute aqueous solution of ethanoic acid. The main component of vinegar is acetic acid, which gives a sour taste and pungent aroma. Acetic acid (CH3COOH), also called ethanoic acid, is the most important of the carboxylic acids. Ethanoic acid is used as a solvent for the production of camphor and cooking material.
Which of the following substances is added to denature ethanol?- a)Methanol
- b)Copper sulphate
- c)Pyridine
- d)All the three above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following substances is added to denature ethanol?
a)
Methanol
b)
Copper sulphate
c)
Pyridine
d)
All the three above
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Denatured alcohol, also called methylated spirits has additives to make it poisonous, extremely bad tasting, foul smelling or nauseating. This is done in order to discourage its recreational consumption.
Which one of the following is a functional group of alcohol?- a)R — OH
- b)R — COOH
- c)R — CO — R
- d)R — CHO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a functional group of alcohol?
a)
R — OH
b)
R — COOH
c)
R — CO — R
d)
R — CHO
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- Alcohols contain a hydroxyl functional group (-OH). The general molecular formula for alcohol is CnH2n+1OH.
- In propanol (C3H7OH), the functional group present is an alcohol (−OH) group.
- In propanone((CH3)2CO), the functional group present is a ketone (−C=O) group.
- In propanoic acid (C2H5COOH), the functional group present is a carboxylic acid (COOH), group
- In ethanal (CH3CHO), the functional group present is an aldehyde(−CHO) group.
- In propanal (C2H5CHO), the functional group present is an aldehyde(−CHO) group.
Buckminster fullerene is an allotropic form of- a)Phosphorus
- b)Sulphur
- c)Carbon
- d)Tin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Buckminster fullerene is an allotropic form of
a)
Phosphorus
b)
Sulphur
c)
Carbon
d)
Tin
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Buckminsterfullerene (C60) or buckyball is one of the allotropes of carbon. The structure of fullerene is like in a cage shape due to which it looks like a football.
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g., hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of - a)Helium
- b)Neon
- c)Krypton
- d)Argon
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g., hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
a)
Helium
b)
Neon
c)
Krypton
d)
Argon
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
E.C. of Ne = 2, 8
Carbon forms a large member of organic compounds due to- a)Catenation
- b)Tendency to form multiple bonds
- c)Phenomenon of isomerism
- d)All the three above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon forms a large member of organic compounds due to
a)
Catenation
b)
Tendency to form multiple bonds
c)
Phenomenon of isomerism
d)
All the three above
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- Catenation: The unique property of the 'C' element to be able to form continuous links with other 'C' atoms through covalency called catenation, is one reason for the existence of a large number of organic compounds.
- Tetravalency: The carbon atom's four valence electrons can be shared by other atoms that have electrons to share, thus forming covalent (shared-electron) bonds. They can even be shared by other carbon atoms, which in turn can share electrons with other carbon atoms and so on, forming long strings of carbon atoms, bonded to each other like links in a chain.
- Isomerism: The same collection of atoms and bonds, but in a different geometrical arrangement within the molecule, makes a molecule with a different shape and hence different properties. These different molecules are called isomers.
- Multiple Bond: Carbon atoms can share not only a single electron with another atom to form a single bond, but it can also share two or three electrons, forming a double or triple bond.
Functional groups present in aspirin
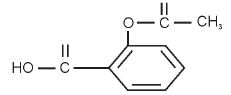
- a)Ester and aldehyde
- b)Ester and carboxylic acid
- c)Easter and ketone
- d)Carboxylic acid and ether
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Functional groups present in aspirin


a)
Ester and aldehyde
b)
Ester and carboxylic acid
c)
Easter and ketone
d)
Carboxylic acid and ether
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
An ester is an organic compound that is a derivative of a carboxylic acid in which the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group has been replaced with an alkyl group.
The soap molecule has a- a)Hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
- b)Hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
- c)Hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
- d)Hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The soap molecule has a
a)
Hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
b)
Hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
c)
Hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
d)
Hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
A soap molecule is a sodium or potassium salt of long-chain carboxylic acid. It is composed of two sections, i.e., a long hydrocarbon tail and a negatively charged head. The hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic, i.e., insoluble in water and repelled by water while the polar end is soluble in water and hydrophilic in nature. Because the hydrophobic tail oil and grease is trapped inside a micelle. The hydrophobic head makes the outer surface of the micelle. Hence micelle is easily washed by water.
The heteroatoms present in
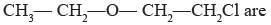
(i) Oxygen
(ii) Chlorine
(iii) Carbon
(iv) Hydrogen- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The heteroatoms present in
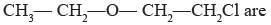
(i) Oxygen
(ii) Chlorine
(iii) Carbon
(iv) Hydrogen
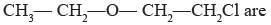
(i) Oxygen
(ii) Chlorine
(iii) Carbon
(iv) Hydrogen
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- In organic chemistry, heteroatoms are the ones that are not carbon or hydrogen.
- Molecules formed by only one type of atom are known as Homo-atomic molecules. For example, H2, N2, P4 etc.
- Molecules formed by different types of atoms are known as Heteroatomic molecules. For example, CO2, NO2, CH4, HCl etc.
Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structures of nitrogen?- a)
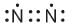
- b)
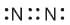
- c)
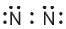
- d)
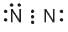
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structures of nitrogen?
a)
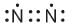
b)
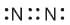
c)
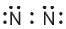
d)
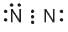
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
In Nitrogen molecule, each nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons and there is a triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms. Thus, the correct electron dot structure is; 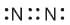
Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst from fats. This is an example of- a)Oxidation reaction
- b)Displacement reaction
- c)Addition reaction
- d)Substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst from fats. This is an example of
a)
Oxidation reaction
b)
Displacement reaction
c)
Addition reaction
d)
Substitution reaction
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Fats are formed when oils are treated with hydrogen in the presence of a palladium or nickel catalyst. Because hydrogen is added to oil by reducing agents palladium or nickel, this is an instance of an addition reaction.
Addition reaction: An addition reaction is a chemical reaction wherein two or more reactants come together to form a larger single product. Hydrochlorination of propane for which the equation is
CH3CH = CH2 + HCl → CH3C+HCH3 + Cl− → CH3CHClCH3
Addition reaction: An addition reaction is a chemical reaction wherein two or more reactants come together to form a larger single product. Hydrochlorination of propane for which the equation is
CH3CH = CH2 + HCl → CH3C+HCH3 + Cl− → CH3CHClCH3
The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is- a)
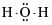
- b)
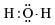
- c)
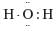
- d)
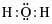
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is
a)
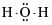
b)
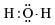
c)
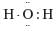
d)
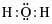
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
The electron dot structure of water is:
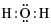
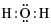
The first member of alkyne homologous series is- a)Ethyne
- b)Ethene
- c)methane
- d)ethane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The first member of alkyne homologous series is
a)
Ethyne
b)
Ethene
c)
methane
d)
ethane
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
In the alkyne series, there is a triple bond between the carbon atoms. The first member of the alkyne series is ethyne with two carbon atoms bonded by a triple bond as follow;
HC ≡ CH.
HC ≡ CH.
While cooking if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside. It means that- a)The food is not cooked completely
- b)The fuel is wet
- c)The fuel is burning completely
- d)The fuel is not burning completely
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
While cooking if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside. It means that
a)
The food is not cooked completely
b)
The fuel is wet
c)
The fuel is burning completely
d)
The fuel is not burning completely
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that the fuel is not burning completely.
- Sometimes, due to lack of oxygen, the fuel does not burn completely.
- When the fuel does not burn completely then a sooty flame appears which makes the bottom of the utensil black.
- At the point when fuel doesn't consume appropriately, it starts to form incomplete burning fumes or black fumes that store on the base surface of the pot.
Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are- a)Sodium ethoxide and oxygen.
- b)Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen.
- c)Sodium ethanoate and oxygen.
- d)Sodium ethanoate and hydrogen.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are
a)
Sodium ethoxide and oxygen.
b)
Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen.
c)
Sodium ethanoate and oxygen.
d)
Sodium ethanoate and hydrogen.
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
The equation for the reaction between sodium and ethanol can be written as:
2CH3CH2OH + 2Na → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
Therefore, the products formed are sodium ethoxide and hydrogen.
2CH3CH2OH + 2Na → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
Therefore, the products formed are sodium ethoxide and hydrogen.
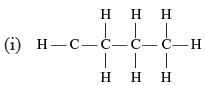
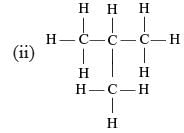
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
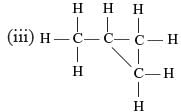
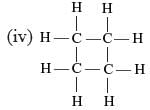
- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?








a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iv)
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Only (i) and (ii) has the same M.F. (C4H10) while (ii) and (iv) have C4H8 as the M.F.
Structural formula of alkene is- a)
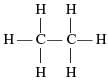
- b)
- c)
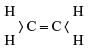
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Structural formula of alkene is
a)

b)
c)
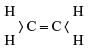
d)
All of these
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
General Molecular formula of alkene-CnH2n
For 5C the molecular formula of alkene is -C5H10
And the structural formula can be shown as below:
CH3 − CH = CH − CH2 − CH3
For 5C the molecular formula of alkene is -C5H10
And the structural formula can be shown as below:
CH3 − CH = CH − CH2 − CH3
Rubbing alcohol is- a)CH3OH
- b)C2H5OH
- c)C3H7OH
- d)C5H11OH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rubbing alcohol is
a)
CH3OH
b)
C2H5OH
c)
C3H7OH
d)
C5H11OH
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Rubbing alcohol is common name of isopropyl alcohol (C3H7OH).
Chapter doubts & questions for Carbon and Its Compounds - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Carbon and Its Compounds - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily