All Exams >
Class 10 >
Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Life Processes for Class 10 Exam
Which of the following has the longest small intestine?- a)Carnivore
- b)Omnivore
- c)Herbivore
- d)Autotroph
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has the longest small intestine?
a)
Carnivore
b)
Omnivore
c)
Herbivore
d)
Autotroph

|
Deepika Singh answered |
Herbivores have the longest small intestine because they digests cellulose
The two organism which breathe only through their moist skin are- a)Fish and frog
- b)Leech and earthworm
- c)Frog and earthworm
- d)Fish and earthworm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The two organism which breathe only through their moist skin are
a)
Fish and frog
b)
Leech and earthworm
c)
Frog and earthworm
d)
Fish and earthworm
|
|
Rajani dasgupta answered |
Leech and Earthworm
Leech and earthworm are the two organisms that breathe only through their moist skin. This unique respiratory system is known as cutaneous respiration.
Cutaneous Respiration
Cutaneous respiration is a form of respiration in which gas exchange occurs across the skin or outer integument of an organism. In leeches and earthworms, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged directly through their moist skin.
Mechanism in Leeches and Earthworms
- Leeches have a thin, permeable skin that allows for gas exchange. They absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide through their skin.
- Earthworms also have a moist skin that helps in the exchange of gases. They breathe through their skin by diffusion.
Importance of Moist Skin
- The presence of moisture on the skin is crucial for cutaneous respiration in leeches and earthworms. It helps in maintaining a suitable environment for gas exchange.
- Dry skin would impede the diffusion of gases, making it difficult for these organisms to breathe solely through their skin.
Adaptations for Cutaneous Respiration
- Both leeches and earthworms have evolved adaptations to facilitate cutaneous respiration. Their thin, moist skin is one such adaptation that allows for efficient gas exchange.
- The surface area of their skin is also maximized to enhance the exchange of gases with the environment.
In conclusion, leeches and earthworms are unique organisms that rely on cutaneous respiration for breathing, utilizing their moist skin to exchange gases with the environment.
Leech and earthworm are the two organisms that breathe only through their moist skin. This unique respiratory system is known as cutaneous respiration.
Cutaneous Respiration
Cutaneous respiration is a form of respiration in which gas exchange occurs across the skin or outer integument of an organism. In leeches and earthworms, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged directly through their moist skin.
Mechanism in Leeches and Earthworms
- Leeches have a thin, permeable skin that allows for gas exchange. They absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide through their skin.
- Earthworms also have a moist skin that helps in the exchange of gases. They breathe through their skin by diffusion.
Importance of Moist Skin
- The presence of moisture on the skin is crucial for cutaneous respiration in leeches and earthworms. It helps in maintaining a suitable environment for gas exchange.
- Dry skin would impede the diffusion of gases, making it difficult for these organisms to breathe solely through their skin.
Adaptations for Cutaneous Respiration
- Both leeches and earthworms have evolved adaptations to facilitate cutaneous respiration. Their thin, moist skin is one such adaptation that allows for efficient gas exchange.
- The surface area of their skin is also maximized to enhance the exchange of gases with the environment.
In conclusion, leeches and earthworms are unique organisms that rely on cutaneous respiration for breathing, utilizing their moist skin to exchange gases with the environment.
The end product of glycolysis is- a)Pyruvate
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)Lactic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The end product of glycolysis is
a)
Pyruvate
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
Lactic acid
|
|
Kirti verma answered |
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells convert glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen.
The End Product of Glycolysis:
The end product of glycolysis is pyruvate. During glycolysis, a molecule of glucose (a 6-carbon sugar) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon compound). This process occurs in a series of enzymatic reactions, which can be divided into two phases: the energy investment phase and the energy payoff phase.
Energy Investment Phase:
In the energy investment phase, two molecules of ATP are used to activate the glucose molecule. This requires the addition of two phosphate groups to the glucose molecule, forming fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. This step ensures that the glucose molecule is primed for further breakdown.
Energy Payoff Phase:
In the energy payoff phase, the fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is broken down into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a 3-carbon compound. Each G3P molecule is then converted into pyruvate through a series of reactions. In this process, several important events occur:
1. Oxidation: Each G3P molecule is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons. This oxidation reaction allows the transfer of high-energy electrons to carrier molecules, such as NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is reduced to NADH. This step is crucial for the production of ATP.
2. Substrate-level phosphorylation: During the conversion of G3P to pyruvate, each molecule of G3P produces 1 molecule of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation. This process involves the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), forming ATP.
3. Production of Pyruvate: Finally, each G3P molecule is converted into pyruvate, generating a total of 2 molecules of pyruvate from one glucose molecule.
Overall:
In summary, the end product of glycolysis is pyruvate. Glycolysis is an important metabolic pathway that provides cells with energy in the form of ATP. It is a central process in both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration.
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells convert glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen.
The End Product of Glycolysis:
The end product of glycolysis is pyruvate. During glycolysis, a molecule of glucose (a 6-carbon sugar) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (a 3-carbon compound). This process occurs in a series of enzymatic reactions, which can be divided into two phases: the energy investment phase and the energy payoff phase.
Energy Investment Phase:
In the energy investment phase, two molecules of ATP are used to activate the glucose molecule. This requires the addition of two phosphate groups to the glucose molecule, forming fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. This step ensures that the glucose molecule is primed for further breakdown.
Energy Payoff Phase:
In the energy payoff phase, the fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is broken down into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a 3-carbon compound. Each G3P molecule is then converted into pyruvate through a series of reactions. In this process, several important events occur:
1. Oxidation: Each G3P molecule is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons. This oxidation reaction allows the transfer of high-energy electrons to carrier molecules, such as NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is reduced to NADH. This step is crucial for the production of ATP.
2. Substrate-level phosphorylation: During the conversion of G3P to pyruvate, each molecule of G3P produces 1 molecule of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation. This process involves the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP (adenosine diphosphate), forming ATP.
3. Production of Pyruvate: Finally, each G3P molecule is converted into pyruvate, generating a total of 2 molecules of pyruvate from one glucose molecule.
Overall:
In summary, the end product of glycolysis is pyruvate. Glycolysis is an important metabolic pathway that provides cells with energy in the form of ATP. It is a central process in both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration.
Which of the following is the only conducting tissue is non-flowering plants?- a)Sieve tubes
- b)Tracheids
- c)Xylem vessels
- d)Companion cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the only conducting tissue is non-flowering plants?
a)
Sieve tubes
b)
Tracheids
c)
Xylem vessels
d)
Companion cells
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Innon-flowering plants tracheids are the only water conducting tissues Tracheids are dead cells with lignified walls with no open ends. They are long, thin and spindle shaped cells. They have pits in them and it is through pits only that water flows from one tracheid to another. All the plants have tracheid in them.
What prevents the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?- a)Thin wall of atria
- b)Thick muscular walls of ventricles
- c)Valves
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What prevents the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
a)
Thin wall of atria
b)
Thick muscular walls of ventricles
c)
Valves
d)
All of the above
|
|
Pranjal Mehta answered |
Valves prevent the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction:
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is made up of four chambers - two atria and two ventricles. During the cardiac cycle, the heart undergoes a series of contractions and relaxations that allow for the efficient circulation of blood.
One of the key functions of the heart is to ensure that blood flows in a unidirectional manner, preventing any backflow. This is achieved through the presence of valves within the heart.
Types of valves:
There are two main types of valves in the heart:
1. Atrioventricular (AV) valves: These valves separate the atria from the ventricles and prevent backflow from the ventricles into the atria. The AV valves consist of the tricuspid valve, which is located between the right atrium and right ventricle, and the mitral valve, which is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
2. Semilunar valves: These valves separate the ventricles from the major arteries leaving the heart and prevent backflow from the arteries into the ventricles. The semilunar valves consist of the pulmonic valve, which is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and the aortic valve, which is located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
How the valves work:
The valves in the heart are flaps of tissue that open and close in response to pressure changes within the heart chambers. When the heart muscle contracts, the pressure within the ventricles increases, causing the AV valves to close. This prevents blood from flowing back into the atria.
At the same time, the increased pressure within the ventricles forces the semilunar valves to open, allowing blood to be pumped out of the heart and into the major arteries. When the heart relaxes, the pressure within the ventricles decreases, causing the semilunar valves to close and prevent backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles.
The coordinated opening and closing of the valves ensure that blood flows in a unidirectional manner, from the atria to the ventricles and from the ventricles to the arteries. This mechanism effectively prevents the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is made up of four chambers - two atria and two ventricles. During the cardiac cycle, the heart undergoes a series of contractions and relaxations that allow for the efficient circulation of blood.
One of the key functions of the heart is to ensure that blood flows in a unidirectional manner, preventing any backflow. This is achieved through the presence of valves within the heart.
Types of valves:
There are two main types of valves in the heart:
1. Atrioventricular (AV) valves: These valves separate the atria from the ventricles and prevent backflow from the ventricles into the atria. The AV valves consist of the tricuspid valve, which is located between the right atrium and right ventricle, and the mitral valve, which is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
2. Semilunar valves: These valves separate the ventricles from the major arteries leaving the heart and prevent backflow from the arteries into the ventricles. The semilunar valves consist of the pulmonic valve, which is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and the aortic valve, which is located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
How the valves work:
The valves in the heart are flaps of tissue that open and close in response to pressure changes within the heart chambers. When the heart muscle contracts, the pressure within the ventricles increases, causing the AV valves to close. This prevents blood from flowing back into the atria.
At the same time, the increased pressure within the ventricles forces the semilunar valves to open, allowing blood to be pumped out of the heart and into the major arteries. When the heart relaxes, the pressure within the ventricles decreases, causing the semilunar valves to close and prevent backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles.
The coordinated opening and closing of the valves ensure that blood flows in a unidirectional manner, from the atria to the ventricles and from the ventricles to the arteries. This mechanism effectively prevents the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction.
The photosynthesis in a plant is not taking place during the daytime if the plant is releasing:- a)Water vapour
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Oxygen
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The photosynthesis in a plant is not taking place during the daytime if the plant is releasing:
a)
Water vapour
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Oxygen
d)
All the above
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
In photosynthesis, an enzyme called RuBP carboxylase absorbs CO2 in the first steps of photosynthesis. This works because there is plenty of carbon dioxide than oxygen. If there is too much oxygen, RuBP carboxylase will absorb oxygen instead of the CO2 and photorespiration will occur. Photorespiration does not help build up any sugars, so if photorespiration occurs, growth stops. Normally, oxygen (produced in photosynthesis) is passed through the stomata; however, if there isn't enough water available (as would happen under bright, hot, sunny conditions), excess oxygen may build up and trigger photorespiration and CO2 will be released out through the stomata.
If a patient is put on dialysis, he is most likely suffering from a severe ailment of the - a)Circulatory system
- b)Excretory system
- c)Digestive system
- d)Respiratory system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a patient is put on dialysis, he is most likely suffering from a severe ailment of the
a)
Circulatory system
b)
Excretory system
c)
Digestive system
d)
Respiratory system
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Dialysis is the procedure used for cleaning the blood of a person by reparating the waste substance (urea) from it.
The opening and closing of the stomatal pores depends upon- a)Oxygen
- b)Temperature
- c)Water in guard cell
- d)Concentration of CO2 in stomata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The opening and closing of the stomatal pores depends upon
a)
Oxygen
b)
Temperature
c)
Water in guard cell
d)
Concentration of CO2 in stomata
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
The opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This makes the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
- The opening and closing of stomata depend on the turgor pressure, caused by the osmotic flow of water in the guard cells.
- When the guard cells are turgid, they expand resulting in the opening of stomata.
- When the guard cells lose water, they become flaccid leading to stomatal closure.
- Stomata normally open when the light strikes the leaf and close during the night.
The instrument for measuring blood pressure is called- a)Manometer
- b)Barometer
- c)Potentiometer
- d)Sphygmomano meter
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The instrument for measuring blood pressure is called
a)
Manometer
b)
Barometer
c)
Potentiometer
d)
Sphygmomano meter
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
A sphygmomanometer also known as a blood pressure metre, blood pressure gauge, or blood pressure monitor, is a device that monitors blood pressure.
- The sphygmomanometer instrument consists of an inflatable rubber cuff which is applied to the arm.
- This is connected to the mercury column which helps to determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- It is composes of an inflatable rubber cuff, which is wrapped around the arm.
- A measuring device indicates the cuff’s pressure.
- A bulb inflates the cuff and a valve releases pressure.
- A stethoscope is used to listen to arterial blood flow sounds.
The wave of expansion of an artery when blood is forced into it is called- a)Heart beat
- b)Pulse
- c)Flow
- d)Ticking
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The wave of expansion of an artery when blood is forced into it is called
a)
Heart beat
b)
Pulse
c)
Flow
d)
Ticking
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- Pulse is the regular, recurrent expansion and contraction of an artery, produced by waves of pressure, caused by the ejection of blood from the left ventricle of the heart as it contracts.
- This pulse can be easily felt by pressing your finger gently over an artery on the wrist along the side of the thumb.
The process of carrying food from the leaves to other parts of a plant is called- a)Transportation
- b)Translocation
- c)Transpiration
- d)Transformation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of carrying food from the leaves to other parts of a plant is called
a)
Transportation
b)
Translocation
c)
Transpiration
d)
Transformation
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- The process of movement of food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant is called translocation.
- Translocation of food takes place through the phloem which carries the food produced through photosynthesis in the leaves to the other plant parts.
One of the following does not have a nucleus. This one is - a)Red blood cell
- b)White blood cell
- c)Guard cell
- d)Epidermal cell
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following does not have a nucleus. This one is
a)
Red blood cell
b)
White blood cell
c)
Guard cell
d)
Epidermal cell
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Mature RBC goes through a process called enucleation just before it enters the blood flow.
Enucleation is an adaptation of the red blood cell which enables it to attain a biconcave structure, increasing room for accomodating more of the haemoglobin leading to greater capacity to carry oxygen molecules. Biconcavity further helps in increasing the surface area for diffusion and agility to squeeze itself through the thin pores of the capillaries to reach oxygen to the tissues.
Enucleation is an adaptation of the red blood cell which enables it to attain a biconcave structure, increasing room for accomodating more of the haemoglobin leading to greater capacity to carry oxygen molecules. Biconcavity further helps in increasing the surface area for diffusion and agility to squeeze itself through the thin pores of the capillaries to reach oxygen to the tissues.
One of the following is not a constituent of blood. This one is - a)Platelets
- b)Sieve plates
- c)Red blood cells
- d)White blood cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following is not a constituent of blood. This one is
a)
Platelets
b)
Sieve plates
c)
Red blood cells
d)
White blood cells
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
A sieve plate is a perforated wall between the sieve elements in vascular plants. They are the outer end wall of a sieve-tube element and contain many pores.
In human digestive system, the enzymes pepsin and trypsin are secreted respectively by- a)Pancreas and gall bladder
- b)Stomach and pancreas
- c)Stomach and salivary glands
- d)Pancreas and liver
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In human digestive system, the enzymes pepsin and trypsin are secreted respectively by
a)
Pancreas and gall bladder
b)
Stomach and pancreas
c)
Stomach and salivary glands
d)
Pancreas and liver
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Stomach and pancreas both protein-digesting enzymes. Pepsin is secreted in the stomach by peptic cells in its inactive form- pepsinogen. Pepsinogen gets activated by the hydrochloric acid present in the stomach. Similarly, Trypsin is secreted by the pancreas in its inactive form- Trysogen.
The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires- a)Sunlight
- b)Chlorophyll
- c)Carbon dioxide and water
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
a)
Sunlight
b)
Chlorophyll
c)
Carbon dioxide and water
d)
All of the above
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Autotrophic nutrition is a process where an organism prepares its own food from simple inorganic material like water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight. It is found in plants. The process by which food is prepared is known as photosynthesis which requires carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight.
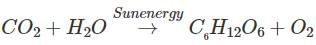
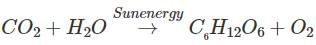
Ultrafiltration occurs in- a)Henle’s loop
- b)Proximal convoluted tubule
- c)Distal convoluted tubule
- d)Bowman’s capsule
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ultrafiltration occurs in
a)
Henle’s loop
b)
Proximal convoluted tubule
c)
Distal convoluted tubule
d)
Bowman’s capsule
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Bowman's capsule: It is a capsule structure. it has single layer of epithelial cells. It receives the products of glomerular filtration which is known as ultrafiltration.
An animal having double circulation in three-chambered heart is- a)Snake
- b)Deer
- c)Sparrow
- d)Fish
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An animal having double circulation in three-chambered heart is
a)
Snake
b)
Deer
c)
Sparrow
d)
Fish
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
The snake heart has 3 chambers - right and left atria and one ventricle. Hence, the correct choice is (a).
During marathon, we sometimes get painful contractions of leg muscles due to the accumulation of one of the following in leg muscles. This is- a)Alcohol
- b)Lactose
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During marathon, we sometimes get painful contractions of leg muscles due to the accumulation of one of the following in leg muscles. This is
a)
Alcohol
b)
Lactose
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Carbon dioxide
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
- During heavy exercise, the demand for energy is high but the supply of oxygen to produce energy is limited. Therefore, anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscles cells to fulfil the demand for energy. This anaerobic breakdown of glucose leads to the formation of lactic acid in muscles. The accumulation of lactic acid in muscles leads to muscle cramps.
- Hence, during heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of Lactic acid.
So, the correct answer is 'Lactic acid'.
Coagulation of blood in a cut or wound is brought about by- a)RBC
- b)WBC
- c)Platelets
- d)Plasma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Coagulation of blood in a cut or wound is brought about by
a)
RBC
b)
WBC
c)
Platelets
d)
Plasma
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
When a blood vessel wall is damaged, collagen fibers from within the wall are exposed. These exposed fibers become a place for platelets to cling to. Platelets are irregular-shaped bodies that help the clotting process by sticking to the lining of the blood vessels. These odd-shaped fragments of cells are normally found floating around your blood along with your red blood cells, kind of minding their own business. But when the cells that line the blood vessels get injured, they release chemicals that cause the platelets to kick into action and become sticky. What we see is layer upon layer of platelets laying down over the wound, somewhat like dirty 'plates' piling up in a sink.
Platelets are like the first responder to a site of an emergency, but platelets can't plug the hole alone. They need some help. This is where we start to see some of the clotting factors that we talked about earlier. One in particular, called fibrinogen, is an inactive clotting factor that helps bind the platelets to form a clot. These inactive clotting factors act as little cross-links, attaching the adjacent platelets to each other. So, in wound healing, platelets take a lot of the glory for being the first ones to the scene, but without their support team, fibrinogen, they would not be able to properly hold together.
Platelets are like the first responder to a site of an emergency, but platelets can't plug the hole alone. They need some help. This is where we start to see some of the clotting factors that we talked about earlier. One in particular, called fibrinogen, is an inactive clotting factor that helps bind the platelets to form a clot. These inactive clotting factors act as little cross-links, attaching the adjacent platelets to each other. So, in wound healing, platelets take a lot of the glory for being the first ones to the scene, but without their support team, fibrinogen, they would not be able to properly hold together.
Which of the following events does not occur in photosynthesis?- a)Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
- b)Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
- c)Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
- d)Absorption of light energy of chlorophyll
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following events does not occur in photosynthesis?
a)
Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
b)
Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
c)
Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
d)
Absorption of light energy of chlorophyll
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy as sugar.
- Photosynthesis is the process of preparing food in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
- In this process, the plant uses water from the soil, carbon dioxide from the air, and energy from sunlight to prepare glucose.
Carbon dioxide + Water + light energy → Glucose + Oxygen
- During the initial phase of photosynthesis, light energy is harvested to produce ATP and NADPH where water is oxidized to provide electrons and protons.
- After the formation of ATP and NADPH, carbon dioxide is reduced to carbohydrates (glucose)
- The reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates doesn’t directly depend on the presence of sunlight but on the supply of ATP and NADPH that were formed during the initial phase.
Which blood vessel does not carry any carbon dioxide?- a)Pulmonary artery
- b)Pulmonary vein
- c)Vena cava
- d)Hepatic vein
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which blood vessel does not carry any carbon dioxide?
a)
Pulmonary artery
b)
Pulmonary vein
c)
Vena cava
d)
Hepatic vein
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Pulmonary veins are responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. Humans have four of these veins in total, two from each lung.
Which type of respiration takes place in mitochondria?- a)Aerobic
- b)Anaerobic
- c)Reduction
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of respiration takes place in mitochondria?
a)
Aerobic
b)
Anaerobic
c)
Reduction
d)
All of these
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
In eukaryotes, aerobic stages of cell respiration occur in mitochondria which is a type of cell organelle. These aerobic phases are the Krebs cycle and the transport chain of electrons. The mitochondria, therefore, have aerobic respiration.
In cockroaches, air enters the body through- a)Lungs
- b)Gills
- c)Skin
- d)Spiracles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In cockroaches, air enters the body through
a)
Lungs
b)
Gills
c)
Skin
d)
Spiracles
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
- The respiratory system of cockroach consists of a network of the trachea, that open through 10 pairs of small holes called spiracles present on the lateral side of the body. Thin branching tubes (tracheal tubes subdivided into tracheoles) carry oxygen from the air to all the parts. air enters the body through spiracles.
- Tracheae are known to balance the pressure inside the system.
- When oxygen-rich air enters into the body of the cockroach via spiracles into the tracheal tubes, it diffuses into various tissues and cells of the body. Here, oxygen is used up to liberate energy.
- Likewise, carbon-dioxide rich air passes into the trachea and moves to the outwards through the spiracles. Carbon dioxide is given out as a result of the respiratory process.
The xylem in plants are responsible for - a)Transport of oxygen
- b)Transport of water
- c)Transport of food
- d)Transport of amino acids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The xylem in plants are responsible for
a)
Transport of oxygen
b)
Transport of water
c)
Transport of food
d)
Transport of amino acids
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Xylem tissues include tracheids, vessels, fibres and parenchyma and serve in the ascent of sap/water and minerals. Phloem tissues is a composed of four elements namely, sieve elements, companion cell, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma and serve in translocation of organic nutrients. Transfer RNA (tRNA) serve as carrier RNA and transports amino acids from cell pool to the mRNA bound to the ribosome where the protein is being synthesized. Haemoglobin molecule contains four polypeptide chains and four heme prosthetic groups. It serves as a carrier of oxygen gas.
Chapter doubts & questions for Life Processes - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Life Processes - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









