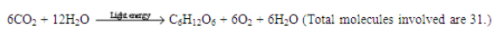All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Biology >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 3: Cellular Energetics for Grade 9 Exam
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles- a)a and b
- b)a and d
- c)b and d
- d)b and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a)
a and b
b)
a and d
c)
b and d
d)
b and c
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Plants unlike animals have no special systems for breathing or gaseous exchange. Stomata and lenticels allow gaseous exchange by diffusion.
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
- a)It starts with a six-carbon compound.
- b)It occurs in mitochondria.
- c)It is also called the citric acid cycle.
- d)The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
a)
It starts with a six-carbon compound.
b)
It occurs in mitochondria.
c)
It is also called the citric acid cycle.
d)
The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle because this reaction starts with the six-carbon compound which is citric acid. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs cycle is a closed-loop cycle. And each loop of the cycle generates a molecule of ATP. This cycle consists of eight steps which include redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. It is an aerobic pathway because NADH is produced and the electrons released are used up in the next cycle which uses oxygen.
- The process of the cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl- CoA with oxaloacetate.
- This reaction is controlled by the amount of ATP present.
- If the ATP level increases then the rate of the reaction decreases and vice versa. After glycolysis, the pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
- The Krebs cycle is the pathway that all organisms use to generate energy. The intermediate compound that links pyruvate to the Krebs cycle is Acetyl CoA.
- So, the answer is option (B) ‘the intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid’.
The first compound of TCA cycle is- a)Oxalo succinic acid
- b)Oxalo acetic acid
- c)Citric acid
- d)Cis aconitic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The first compound of TCA cycle is
a)
Oxalo succinic acid
b)
Oxalo acetic acid
c)
Citric acid
d)
Cis aconitic acid
|
|
Kaneez Fatima answered |
Citric acid is ist compound of TCA cycle ...
The splitting of water molecule is take place inside
a)Outer membraneb)Lumenc)Stromad)Inner membrane Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vibhor Goyal answered |
Splitting of water takes place near PS II, located in the inner side of the thylakoid membrane.
Splitting of water releases oxygen in the atmosphere and generates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
Autotrophic thallophytes are called as :-- a)Fungi
- b)Lichens
- c)Algae
- d)Microbes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Autotrophic thallophytes are called as :-
a)
Fungi
b)
Lichens
c)
Algae
d)
Microbes
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Plants that do not have well-differentiated body design fall in this group. They are commonly called algae. Algae are chlorophyll-bearing, simple, thalloid, autotrophic and largely aquatic (both fresh water and marine) organisms.
Thallus = a plant body not differentiated into stem, leaves, and roots and without a vascular system, typical of algae, fungi, lichens, and some liverworts.
The splitting of water molecules is associated with- a)PS II
- b)PS I
- c)Cyclic phosphorylation
- d)Non-cyclic phosphorylation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The splitting of water molecules is associated with
a)
PS II
b)
PS I
c)
Cyclic phosphorylation
d)
Non-cyclic phosphorylation
|
|
Swara Sarkar answered |
This is achieved by electrons available due to splitting of water. The splitting of water is associated with the PS II; water is split into H+, [O] and electrons.
How many netATP are produced in Glycolysis?- a)36 ATP
- b)8 ATP
- c)2 ATP
- d)16 ATP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many netATP are produced in Glycolysis?
a)
36 ATP
b)
8 ATP
c)
2 ATP
d)
16 ATP

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
At the end of glycolysis pathway, 2 net ATP molecules at step 6 and step 9 are produced.
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
- a)Respiratory products
- b)respiratory substrates
- c)ATP
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
a)
Respiratory products
b)
respiratory substrates
c)
ATP
d)
NADH

|
Shounak Nair answered |
The respiratory quotient depends upon the type of respiratory substrate used during respiration.
The colour of light not utilized during photosynthesis is :–- a)Violet
- b)Green
- c)Red
- d)Blue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The colour of light not utilized during photosynthesis is :–
a)
Violet
b)
Green
c)
Red
d)
Blue
|
|
Saranya Rane answered |
The Colour of Light Not Utilized During Photosynthesis is Green
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their food using light energy, water, and carbon dioxide. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of the plant cells. The chlorophyll pigments present in the chloroplasts absorb light energy, which is then used to produce food.
Different colors of light have different wavelengths, and the pigments in the chloroplasts absorb some colors of light more efficiently than others. The color of light not utilized during photosynthesis is green. This is because chlorophyll pigments, which are the main pigments involved in photosynthesis, absorb red and blue light efficiently but reflect green light. As a result, green light is not utilized during photosynthesis.
Factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis
Several factors affect the rate of photosynthesis, including:
Light intensity: Photosynthesis occurs at a faster rate when the light intensity is higher.
Temperature: Photosynthesis occurs at an optimum temperature, and the rate decreases at temperatures above or below this range.
Carbon dioxide concentration: The rate of photosynthesis increases with an increase in carbon dioxide concentration.
Water availability: Photosynthesis requires water, and a lack of water can reduce the rate of photosynthesis.
Conclusion
The color of light not utilized during photosynthesis is green. This is because chlorophyll pigments, which are the main pigments involved in photosynthesis, absorb red and blue light efficiently but reflect green light. The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by several factors, including light intensity, temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, and water availability.
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their food using light energy, water, and carbon dioxide. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of the plant cells. The chlorophyll pigments present in the chloroplasts absorb light energy, which is then used to produce food.
Different colors of light have different wavelengths, and the pigments in the chloroplasts absorb some colors of light more efficiently than others. The color of light not utilized during photosynthesis is green. This is because chlorophyll pigments, which are the main pigments involved in photosynthesis, absorb red and blue light efficiently but reflect green light. As a result, green light is not utilized during photosynthesis.
Factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis
Several factors affect the rate of photosynthesis, including:
Light intensity: Photosynthesis occurs at a faster rate when the light intensity is higher.
Temperature: Photosynthesis occurs at an optimum temperature, and the rate decreases at temperatures above or below this range.
Carbon dioxide concentration: The rate of photosynthesis increases with an increase in carbon dioxide concentration.
Water availability: Photosynthesis requires water, and a lack of water can reduce the rate of photosynthesis.
Conclusion
The color of light not utilized during photosynthesis is green. This is because chlorophyll pigments, which are the main pigments involved in photosynthesis, absorb red and blue light efficiently but reflect green light. The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by several factors, including light intensity, temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, and water availability.
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of- a)NADPH
- b)FADH2
- c)ADP
- d)ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of
a)
NADPH
b)
FADH2
c)
ADP
d)
ATP
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
- Oxysomes refer to small round structures present within the folds of the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is also known as F0-F1 particles.
- F0 and F1 particles are found in the inner mitochondrial region and are attached to the cristae and help in ATP production and oxidation.
Liverworts are closely related to- a)Lichen
- b)Mosses
- c)Algae
- d)Fungi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Liverworts are closely related to
a)
Lichen
b)
Mosses
c)
Algae
d)
Fungi

|
Prisha Singh answered |
The bryophytes are divided into liverworts and mosses. So they closely related to each other.
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by- a)GTP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)GDP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by
a)
GTP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
GDP

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
During conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesised.
In the half-leaf experiment of photosynthesis, KOH solution is used because- a)It provides O2 to the leaf.
- b)It provides moisture to the leaf.
- c)It helps in CO2 fixation.
- d)It absorbs CO2.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the half-leaf experiment of photosynthesis, KOH solution is used because
a)
It provides O2 to the leaf.
b)
It provides moisture to the leaf.
c)
It helps in CO2 fixation.
d)
It absorbs CO2.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
KOH (Potassium Hydroxide) absorbs carbon dioxide. The leaf inside the bottle containing KOH solution does not become blue-black when compared with the leaf which is exposed to atmospheric air. This shows that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
Which pigment is water soluble?- a)Chlorophyll
- b)Carotene
- c)Anthocyanin
- d)Xanthophyll
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pigment is water soluble?
a)
Chlorophyll
b)
Carotene
c)
Anthocyanin
d)
Xanthophyll

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Anthocyanins (literally "flower blue") are water-soluble flavonoid pigments that appear red to blue, according to pH. They occur in all tissues of higher plants, providing color in leaves, plant stem, roots, flowers, and fruits, though not always in sufficient quantities to be noticeable.
The TCA cycle is named after- a)Robert Emerson
- b)Melvin Calvin
- c)Embden
- d)Hans Krebs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle is named after
a)
Robert Emerson
b)
Melvin Calvin
c)
Embden
d)
Hans Krebs
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
*Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release the stored energy........ *It is a part of cellular respiration........ *It is also called as citric acid cycle or Krebs cycles which is named after it's discoverer Hans Krebs..... Thus, the correct answer is option 'D'.
R.Q. is less than one at the time of respiration of –- a)Starch
- b)Sugarcane
- c)Glucose
- d)Ground nut
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
R.Q. is less than one at the time of respiration of –
a)
Starch
b)
Sugarcane
c)
Glucose
d)
Ground nut
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
RQ value is less than 1 in case of ground nut
Cyanobacteria are classified under- a)Protista
- b)Plantae
- c)Monera
- d)Algae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cyanobacteria are classified under
a)
Protista
b)
Plantae
c)
Monera
d)
Algae
|
|
Bts My Life answered |
The sole member of kingdom monera is bacteria. Cyanobacteria have chlorophyll a similar to green plants and are photosynthetic autotrophs. The cyanobacteria are unicellular ,colonial,or filamentous fresh-water marine or terrestrial algae.
The dark reaction in photosynthesis is called so because- a)It does not depend on light energy.
- b)It can occur in dark also.
- c)It cannot occur during day light.
- d)It occurs more rapidly at night.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dark reaction in photosynthesis is called so because
a)
It does not depend on light energy.
b)
It can occur in dark also.
c)
It cannot occur during day light.
d)
It occurs more rapidly at night.
|
|
Mansi Ahuja answered |
Explanation:
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll pigment. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two parts - light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions.
The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light energy by the pigments like chlorophyll and the conversion of that energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions, on the other hand, occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and are also known as the Calvin cycle.
Dark reactions in photosynthesis:
The dark reactions or the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis are so called because they do not require the presence of light energy to occur. These reactions can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions, i.e., ATP and NADPH, to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules like glucose, which can be used as a source of energy by the plant.
The dark reactions also involve the enzyme RuBisCO, which is responsible for catalyzing the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). The reaction produces two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate, which is then converted into other organic molecules like glucose and other carbohydrates.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the dark reactions in photosynthesis are called so because they do not depend on light energy to occur. They can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules and are essential for the synthesis of glucose and other carbohydrates, which serve as a source of energy for the plant.
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll pigment. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two parts - light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions.
The light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light energy by the pigments like chlorophyll and the conversion of that energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions, on the other hand, occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and are also known as the Calvin cycle.
Dark reactions in photosynthesis:
The dark reactions or the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis are so called because they do not require the presence of light energy to occur. These reactions can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions, i.e., ATP and NADPH, to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules like glucose, which can be used as a source of energy by the plant.
The dark reactions also involve the enzyme RuBisCO, which is responsible for catalyzing the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). The reaction produces two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate, which is then converted into other organic molecules like glucose and other carbohydrates.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the dark reactions in photosynthesis are called so because they do not depend on light energy to occur. They can occur in the absence of light, but they do require the products of the light-dependent reactions to proceed. The dark reactions involve the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules and are essential for the synthesis of glucose and other carbohydrates, which serve as a source of energy for the plant.
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because- a)Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
- b)It takes place is micrograms
- c)It takes place in inert medium
- d)Glucose is not available
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because
a)
Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
b)
It takes place is micrograms
c)
It takes place in inert medium
d)
Glucose is not available
|
|
Kuldeep Kuldeep answered |
Option a is correct. Because, in Anaerobic Respiration, respiration takes place on the absence of oxygen. Iteans, the oxidation of pyruvate takes place in the absence of oxygen to release CO2, Ethanol along with the release of Energy. Here, in Anaerobic Respiration, Water is not yet released due to the absence of oxygen. So, there will be incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which range of wavelength (in nm) is called photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
- A:
400-700
- B:
760-10,000
- C:
100-390
- D:
390-430
The answer is a.
Which range of wavelength (in nm) is called photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
400-700
760-10,000
100-390
390-430
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Photosynthetically active radiation. Photosynthetically active radiation, often abbreviated PAR, designates the spectral range (wave band) of solar radiation from 400 to 700 nanometers that photosynthetic organisms are able to use in the process of photosynthesis.
The C4 plants show higher rate of photosynthesis in- a)Optimum temperature
- b)High temperature
- c)Absence of temperature
- d)Low temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The C4 plants show higher rate of photosynthesis in
a)
Optimum temperature
b)
High temperature
c)
Absence of temperature
d)
Low temperature

|
Shreya Saini answered |
C4 planets show higher rate of photosynthesis in higher temperatures because there is no energy loss in photorespiration in these plants, i.e.at high temperature they show full efficiency of production.
The end products of respiration in plants are- a)CO2, H2O and energy
- b)Starch and O2
- c)Sugar and oxygen
- d)H2O and energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The end products of respiration in plants are
a)
CO2, H2O and energy
b)
Starch and O2
c)
Sugar and oxygen
d)
H2O and energy
|
|
Siddheshwar Kale answered |
Glucose + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy ( 686 Kcal.)
"Red rust of tea" is caused by parasitic:-- a)Algae
- b)Fungi
- c)Bacteria
- d)Bryophyta
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
"Red rust of tea" is caused by parasitic:-
a)
Algae
b)
Fungi
c)
Bacteria
d)
Bryophyta
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Parasitic green alga which causes the disease 'red rust of tea' in tea plants and 'leaf spot disease of guava' in gauava plant. It also causes leaf spot diseases in other plants like mango, magnolia and coffee.
Energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reaction is stored immediately in the form of- a)Pyruvic acid
- b)Glucose
- c)ATP
- d)DNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reaction is stored immediately in the form of
a)
Pyruvic acid
b)
Glucose
c)
ATP
d)
DNA
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
The energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reactions is stored immediately in the form of ATP, as it is the energy currency of the cell.
Hence, option 'C' is correct.
Hence, option 'C' is correct.
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in- a)Intermembrane space of mitochondria
- b)Mitochondrial matrix
- c)Inner membrane of mitochondria
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in
a)
Intermembrane space of mitochondria
b)
Mitochondrial matrix
c)
Inner membrane of mitochondria
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Mitochondrial matrix.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
Carpogonia is the female sex organ in which of the algae?- a)Chlorophycophyta
- b)Xanthophycophyta
- c)Chrysophycophyta
- d)Rhodophycophyta
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Carpogonia is the female sex organ in which of the algae?
a)
Chlorophycophyta
b)
Xanthophycophyta
c)
Chrysophycophyta
d)
Rhodophycophyta
|
|
Akash Nair answered |
The correct answer is option D, Rhodophycophyta.
Rhodophycophyta, also known as red algae, is a diverse group of algae that includes thousands of species. They are primarily marine organisms and are found in a variety of habitats ranging from tropical to polar regions.
Female Sex Organ in Red Algae:
The female sex organ in red algae is called carpogonium. It is a specialized structure that is involved in sexual reproduction. The carpogonium is a multicellular structure that is found in the reproductive structures of red algae.
Structure of Carpogonium:
The carpogonium consists of a swollen base that contains a single nucleus and a long, hair-like projection called the trichogyne. The trichogyne is used to capture sperm cells during sexual reproduction.
Function of Carpogonium:
During sexual reproduction in red algae, the carpogonium acts as the female sex organ. It is the site of fertilization and the development of the zygote. The trichogyne of the carpogonium captures sperm cells released from the male sex organ, called spermatangia. The sperm cell then fuses with the nucleus of the carpogonium, leading to the formation of a zygote. The zygote develops into a diploid sporophyte, which produces spores that can germinate into new individuals.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the carpogonium is the female sex organ in red algae. It is a specialized structure that plays a key role in sexual reproduction by capturing sperm cells and facilitating the fusion of gametes.
Rhodophycophyta, also known as red algae, is a diverse group of algae that includes thousands of species. They are primarily marine organisms and are found in a variety of habitats ranging from tropical to polar regions.
Female Sex Organ in Red Algae:
The female sex organ in red algae is called carpogonium. It is a specialized structure that is involved in sexual reproduction. The carpogonium is a multicellular structure that is found in the reproductive structures of red algae.
Structure of Carpogonium:
The carpogonium consists of a swollen base that contains a single nucleus and a long, hair-like projection called the trichogyne. The trichogyne is used to capture sperm cells during sexual reproduction.
Function of Carpogonium:
During sexual reproduction in red algae, the carpogonium acts as the female sex organ. It is the site of fertilization and the development of the zygote. The trichogyne of the carpogonium captures sperm cells released from the male sex organ, called spermatangia. The sperm cell then fuses with the nucleus of the carpogonium, leading to the formation of a zygote. The zygote develops into a diploid sporophyte, which produces spores that can germinate into new individuals.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the carpogonium is the female sex organ in red algae. It is a specialized structure that plays a key role in sexual reproduction by capturing sperm cells and facilitating the fusion of gametes.
Stone wort is common name of :–- a)Chara
- b)Chlorella
- c)Laminaria
- d)Polysiphonia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stone wort is common name of :–
a)
Chara
b)
Chlorella
c)
Laminaria
d)
Polysiphonia
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Stonewort The common name for the brittle, calcified plants of the Charophyta; Chara and Nitella are the commonest British genera. The plant consists of a ‘stem’ or axis which bears whorls of branches at intervals (nodes) along its length. The axis is attached at its base to the substratum by means of branched rhizoids.
When fats are the respiratory substrate, the value of RQ would be- a)Approx. 0.7
- b)Approx. 1.0
- c)More than 1.0
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When fats are the respiratory substrate, the value of RQ would be
a)
Approx. 0.7
b)
Approx. 1.0
c)
More than 1.0
d)
None of the above

|
Surbhi Mishra answered |
Ans.
The respiratory quotient (or RQ or respiratory coefficient), is a dimensionless number used in calculations of basal metabolic rate (BMR) when estimated from carbon dioxide production. ... If metabolism consists solely of lipids, the Respiratory Quotient is 0.7, for proteins it is 0.8, and for carbohydrates it is 1.0.
During photochemical reaction of photosynthesis –- a)liberation of O2 takes place
- b)Formation of ATP and NADPH2 take place
- c)Liberation of O2, formation of ATP, and NADPH2 takes place
- d)Assimilation of CO2 takes place
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During photochemical reaction of photosynthesis –
a)
liberation of O2 takes place
b)
Formation of ATP and NADPH2 take place
c)
Liberation of O2, formation of ATP, and NADPH2 takes place
d)
Assimilation of CO2 takes place
|
|
Momin Anam answered |
C is correct
The by product of photosynthesis is- a)CO2
- b)Oxygen
- c)Energy
- d)Sugar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The by product of photosynthesis is
a)
CO2
b)
Oxygen
c)
Energy
d)
Sugar

|
Rajni Kokate answered |
6(CO2) + 12(H2O) ----------> C6H12O6 +6(O2) + 6H2O
In photosynthesis phototrophs synthesize glucose and water and evolve O2 as by product
In photosynthesis phototrophs synthesize glucose and water and evolve O2 as by product
In higher plants, the shape of the chloroplast is- a)Reticulate
- b)Girdle-shaped
- c)Discoid
- d)Cup-shaped
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In higher plants, the shape of the chloroplast is
a)
Reticulate
b)
Girdle-shaped
c)
Discoid
d)
Cup-shaped

|
EduRev JEE answered |
Chloroplasts are the green plastids which take part in photosynthesis and temporary or permanent storage of starch. These are discoid (disc-shaped) in higher plants with diameter of 4-6 μm and thickness of 2-4.μm.
Plants which are not differentiated into roots, stem and leaves are grouped under- a)Gymnosperms
- b)Pteridophytes
- c)Thallophytes
- d)Spermatophytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Plants which are not differentiated into roots, stem and leaves are grouped under
a)
Gymnosperms
b)
Pteridophytes
c)
Thallophytes
d)
Spermatophytes
|
|
Akshat Majumdar answered |
Thallophytes
Thallophytes are a group of plants that do not possess well-differentiated structures such as roots, stems, and leaves. They are characterized by their simple body structure and lack of specialized organs. Thallophytes include various types of algae, fungi, and lichens.
Algae:
Algae are photosynthetic organisms that can be found in aquatic environments such as freshwater, marine habitats, and even on damp surfaces. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have a simple body structure called a thallus, which can be unicellular or multicellular. Examples of algae include green algae, brown algae, and red algae.
Fungi:
Fungi are non-photosynthetic organisms that obtain nutrients by breaking down organic matter. They also have a thallus-like body structure, referred to as a mycelium, which consists of a network of hyphae. Fungi can be found in various habitats such as soil, decaying organic matter, and as symbiotic partners with other organisms. Examples of fungi include mushrooms, molds, and yeasts.
Lichens:
Lichens are unique organisms formed by a symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, usually an alga or a cyanobacterium. The fungal component provides a protected environment for the photosynthetic partner, while the photosynthetic partner provides nutrients through photosynthesis. Lichens can be found in diverse habitats such as rocks, tree trunks, and soil.
Significance of Thallophytes:
Thallophytes play important ecological roles in various ecosystems. Algae are primary producers and contribute to oxygen production and nutrient cycling in aquatic environments. Fungi are involved in the decomposition of organic matter and play a crucial role in nutrient recycling. Lichens are important pioneers in colonization of bare rocks and contribute to soil formation.
In conclusion, plants that do not have well-differentiated roots, stems, and leaves are grouped under thallophytes. Thallophytes include algae, fungi, and lichens, which have a simple body structure called a thallus. These organisms play significant roles in their respective ecosystems.
Thallophytes are a group of plants that do not possess well-differentiated structures such as roots, stems, and leaves. They are characterized by their simple body structure and lack of specialized organs. Thallophytes include various types of algae, fungi, and lichens.
Algae:
Algae are photosynthetic organisms that can be found in aquatic environments such as freshwater, marine habitats, and even on damp surfaces. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have a simple body structure called a thallus, which can be unicellular or multicellular. Examples of algae include green algae, brown algae, and red algae.
Fungi:
Fungi are non-photosynthetic organisms that obtain nutrients by breaking down organic matter. They also have a thallus-like body structure, referred to as a mycelium, which consists of a network of hyphae. Fungi can be found in various habitats such as soil, decaying organic matter, and as symbiotic partners with other organisms. Examples of fungi include mushrooms, molds, and yeasts.
Lichens:
Lichens are unique organisms formed by a symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, usually an alga or a cyanobacterium. The fungal component provides a protected environment for the photosynthetic partner, while the photosynthetic partner provides nutrients through photosynthesis. Lichens can be found in diverse habitats such as rocks, tree trunks, and soil.
Significance of Thallophytes:
Thallophytes play important ecological roles in various ecosystems. Algae are primary producers and contribute to oxygen production and nutrient cycling in aquatic environments. Fungi are involved in the decomposition of organic matter and play a crucial role in nutrient recycling. Lichens are important pioneers in colonization of bare rocks and contribute to soil formation.
In conclusion, plants that do not have well-differentiated roots, stems, and leaves are grouped under thallophytes. Thallophytes include algae, fungi, and lichens, which have a simple body structure called a thallus. These organisms play significant roles in their respective ecosystems.
Photophosphorylation means synthesis of- a)ATP from ADP
- b)NADP
- c)ADP from ATP
- d)PGA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Photophosphorylation means synthesis of
a)
ATP from ADP
b)
NADP
c)
ADP from ATP
d)
PGA
|
|
Ala Habibi answered |
Photophosphorylation is the process in which light energy is converted into chemical energy through the production of ATP. The process of reduction of NADP into NADP+H+ may be denoted as electron transport system (ETS). It is the process of formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (ip) utilizing light energy. The flow of electrons through ETS is linked to photophosphorylation. Electron transport chain is a series of electron carriers over which electrons pass in a downhill journey releasing energy at every step that is used in generating an electrochemical proton gradient which helps in synthesizing ATP. Based on the path of electrons, associated photophosphorylation can be identified as non-cyclic and cyclic phosphorylation.
The Calvin cycle leads to reduction of- a)RUBP
- b)RUMP
- c)O2
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Calvin cycle leads to reduction of
a)
RUBP
b)
RUMP
c)
O2
d)
CO2
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
In fixation, the first stage of the Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions are initiated; CO2 is fixed from an inorganic to an organic molecule. In the second stage, ATP and NADPH are used to reduce 3-PGA into G3P; then ATP and NADPH are converted to ADP and NADP+, respectively.
Who described the first action spectrum for photosynthesis?- a)T. W. Engelmann
- b)Cornelius van Niel
- c)Joseph Priestley
- d)Julius von Sachs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who described the first action spectrum for photosynthesis?
a)
T. W. Engelmann
b)
Cornelius van Niel
c)
Joseph Priestley
d)
Julius von Sachs
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Engelmann used a prism to split light into its spectral components, and then illuminated a green alga, Cladophora, placed in a suspension of aerobic bacteria. The bacteria were used to detect the sites of oxygen evolution.
He observed that bacteria mainly accumulated in the region of blue and red light of the split spectrum, thus giving the first action spectrum of photosynthesis.
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?- a)Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
- b)The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
- c)Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
- d)Mitochondria have a double membrane.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
a)
Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
b)
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
c)
Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
d)
Mitochondria have a double membrane.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mitochondria (singular - Mitochondrion) are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for the release of energy from food ,i.e, cellular respiration. This energy is released in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
While the cells release 2 ATP, mitochondria releases 34 ATP which adds up to 36 ATP. Since a major portion of the ATP is released by mitochondria, they are called the powerhouse of the cell.
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in- a)Grana
- b)Pyrenoid
- c)Stroma
- d)Both grana and stroma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in
a)
Grana
b)
Pyrenoid
c)
Stroma
d)
Both grana and stroma
|
|
Gulzar Ahmad answered |
Grana are the stakes of thylakoids which possess green pigment called chlorophyll...
Choose the odd one out among the following: Dryopteris, Pteris, Adiantum, Selaginella.- a)Pteris
- b)Adiantum
- c)Selaginella
- d)Dryopteris
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the odd one out among the following: Dryopteris, Pteris, Adiantum, Selaginella.
a)
Pteris
b)
Adiantum
c)
Selaginella
d)
Dryopteris
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Selaginella belong to Pteridophyta of class Lycopsida and other plants belong to class Pteropsida.
Which of the following is not a significance of photosynthesis ?- a)Glucose synthesis for most of consumer
- b)Increase in green house effect
- c)Provides O2 for synthesis of ozone umbrella
- d)Provides O2 for cell respiration.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a significance of photosynthesis ?
a)
Glucose synthesis for most of consumer
b)
Increase in green house effect
c)
Provides O2 for synthesis of ozone umbrella
d)
Provides O2 for cell respiration.

|
Lead Academy answered |
Photosynthesis is a crucial process on Earth, but not all its outcomes are universally positive. Here's why the "Increase in greenhouse effect" is not a significant of photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis reduces the greenhouse effect by absorbing CO2.
- It does not contribute to an increase in the greenhouse effect.
- The process actually helps to mitigate climate change by converting CO2 into oxygen and glucose.
- The other options listed (Glucose synthesis, O2 for ozone, O2 for respiration) highlight the vital roles of photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis reduces the greenhouse effect by absorbing CO2.
- It does not contribute to an increase in the greenhouse effect.
- The process actually helps to mitigate climate change by converting CO2 into oxygen and glucose.
- The other options listed (Glucose synthesis, O2 for ozone, O2 for respiration) highlight the vital roles of photosynthesis.
In which pteridophytes, hetersporous is produced?- a)Adiantum
- b)Equisetum
- c)Psilotum
- d)Salvinia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which pteridophytes, hetersporous is produced?
a)
Adiantum
b)
Equisetum
c)
Psilotum
d)
Salvinia

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Genera like Selaginellaand Salviniawhich produce two kinds of spores, macro (large) and micro (small) spores are known as heterosporous.
Element which helps in electron transport in the process of photosynthesis is- a)Zinc
- b)Molybdenum
- c)Boron
- d)Mangnese
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Element which helps in electron transport in the process of photosynthesis is
a)
Zinc
b)
Molybdenum
c)
Boron
d)
Mangnese
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
During noncyclic electron flow the electron hole in P-680 is filled by electrons obtained by photolysis of water. As a result, there is an evolution of oxygen and the electron move through Mn-protein bound to PS II. In this transport Mn++ is oxidised to Mn+++ and then reduced to Mn++ in a cyclic manner. The manganese thus transfers electrons from water to photosystem II and thus plays an important role in electron transport in the process of photosynthesis.
Select the incorrectly matched pair with regard to the C4 cycle.- a)Primary CO2 fixation product – PGA
- b)C4 plant – Maize
- c)Primary CO2 acceptor – PEP
- d)Site of initial carboxylation – Mesophyll cells
- e)Location of enzyme RuBisCO – Bundle sheath cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrectly matched pair with regard to the C4 cycle.
a)
Primary CO2 fixation product – PGA
b)
C4 plant – Maize
c)
Primary CO2 acceptor – PEP
d)
Site of initial carboxylation – Mesophyll cells
e)
Location of enzyme RuBisCO – Bundle sheath cells
|
|
Vignesh answered |
The primary CO
2
fixation product in C
4
plants is oxaloacetic acid, which is converted to malic acid or aspartic acid that is transported to the bundle sheath cells where the acid is decarboxylated and the CO
2
thus released enters the Calvin cycle.
Pteridophytes differ from mosses/ bryophytes in possessing- a) independent gametophyte
- b)archegonia
- c)well developed vascular system
- d)flagellate spermatozoids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pteridophytes differ from mosses/ bryophytes in possessing
a)
independent gametophyte
b)
archegonia
c)
well developed vascular system
d)
flagellate spermatozoids
|
|
Tanvi Dear answered |
Pteridophyte when compared to mosses / bryophytes have better way for zoidogamy . As bryophytes are known as amphibians of plant kingdom .
Pteridophyte have primitive type of vascular bundles with only tracheids which are not well designed .
Pteridophyte have primitive type of vascular bundles with only tracheids which are not well designed .
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 3: Cellular Energetics - AP Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 3: Cellular Energetics - AP Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Biology
130 videos|198 docs|114 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily