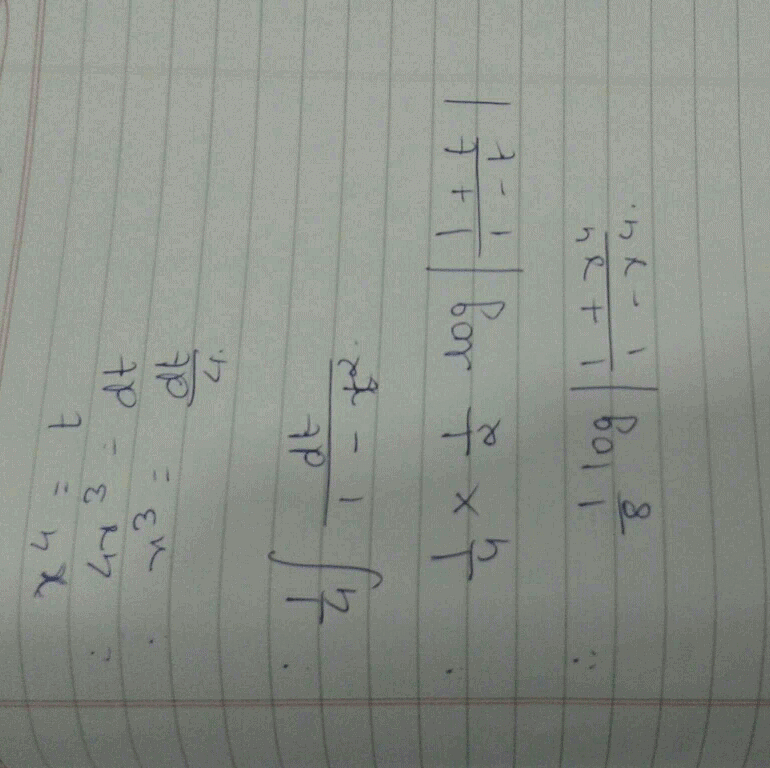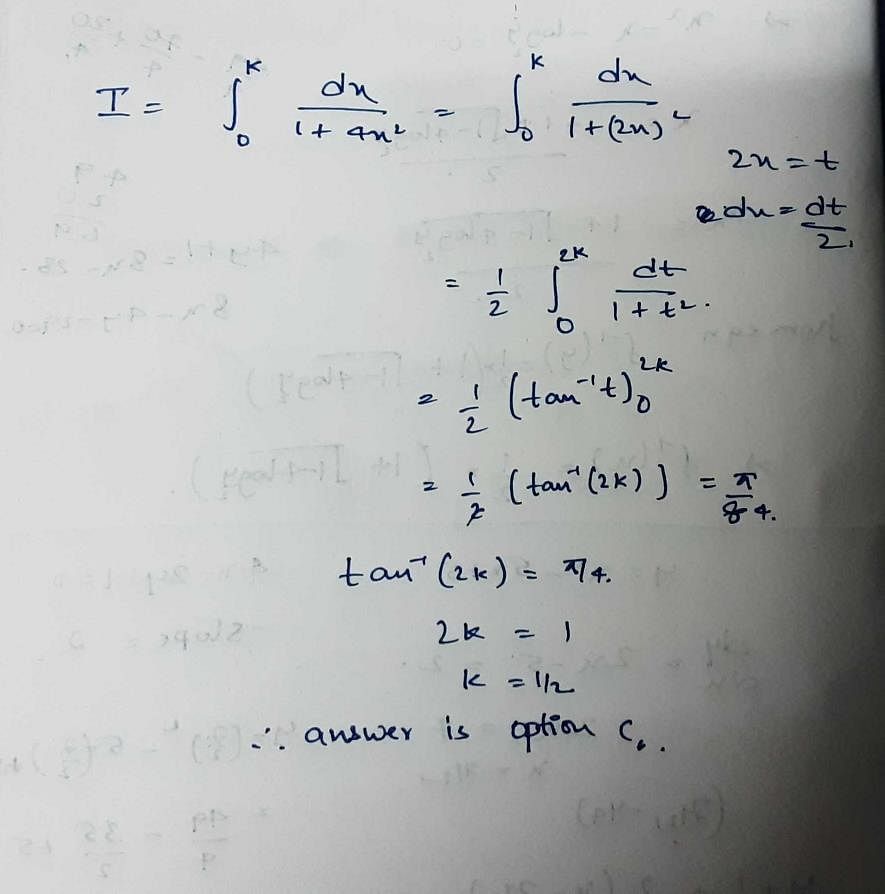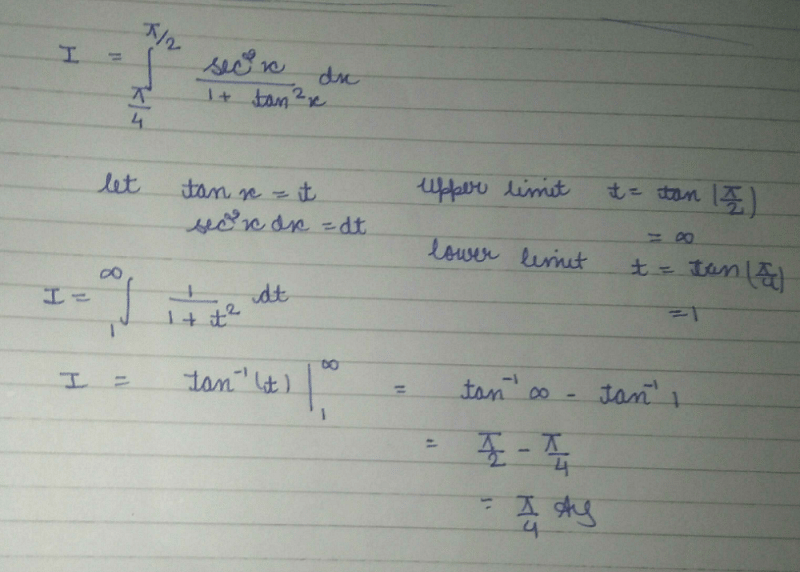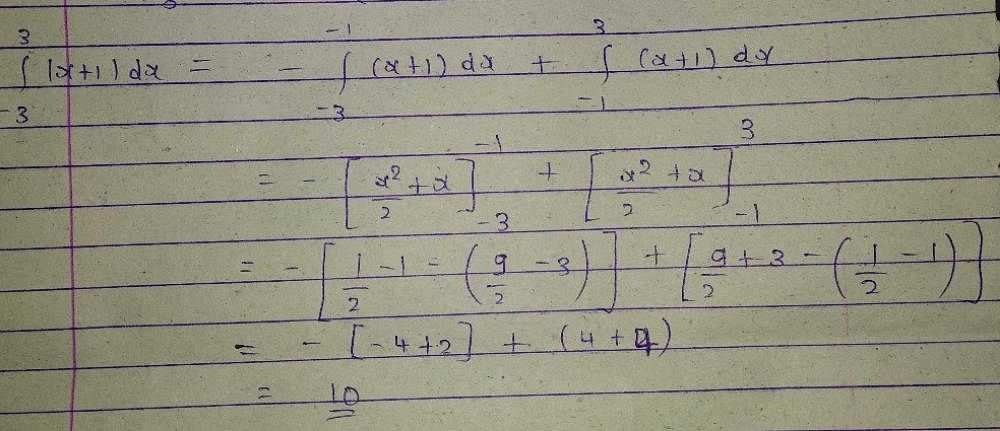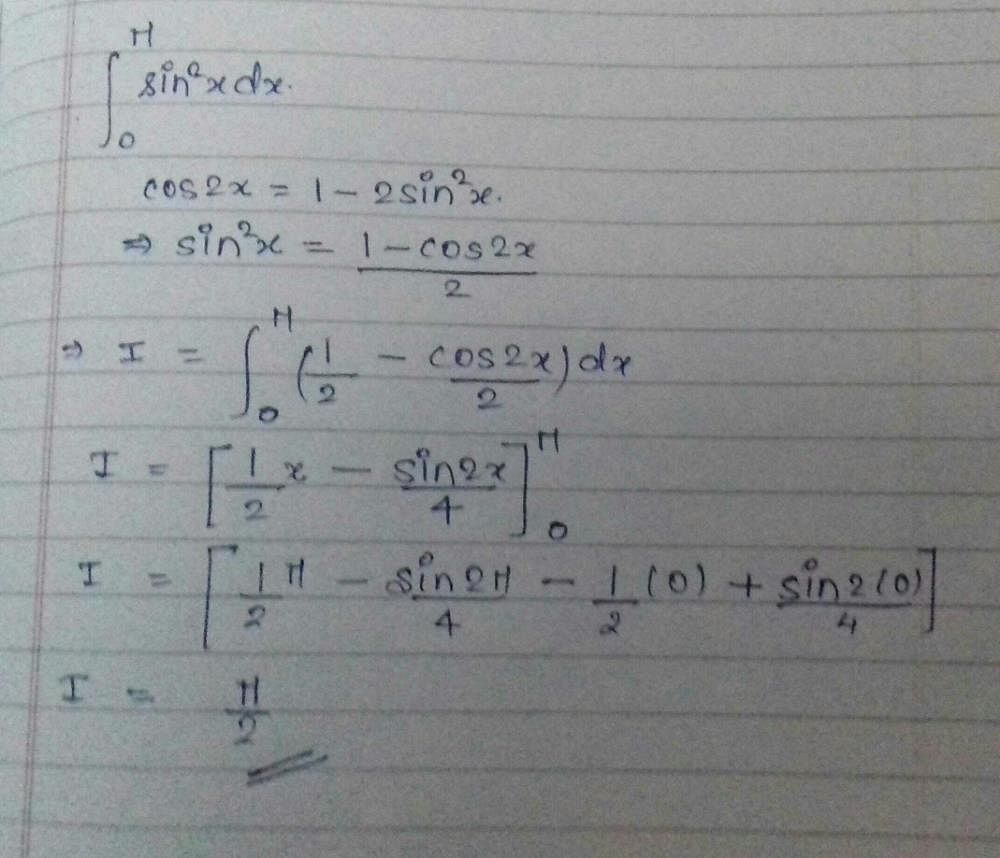All Exams >
Grade 9 >
Calculus AB >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 6: Integration for Grade 9 Exam
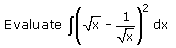
- a)
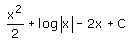
- b)
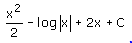
- c)
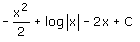
- d)
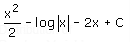
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Vishal Rahangdale answered |
Integration (x- 2 + 1/x)= x^2- 2x + log(x)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
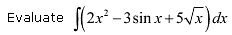
- a)
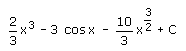
- b)
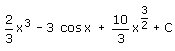
- c)
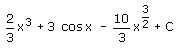
- d)
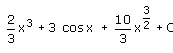
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Yogesh Singla answered |
D is right sinx= -cox and x*n=1/n x*n+1
Integral of sin5x.cos2x is: - a)

- b)
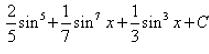
- c)
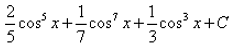
- d)

Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Integral of sin5x.cos2x is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
So Looking at this integral, we have
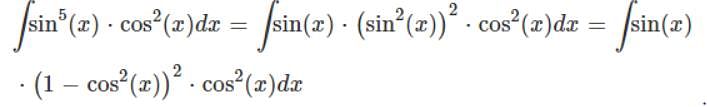

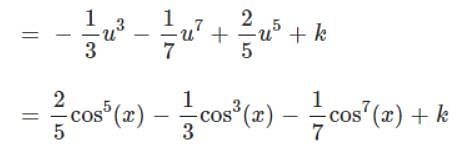
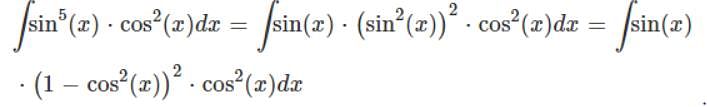

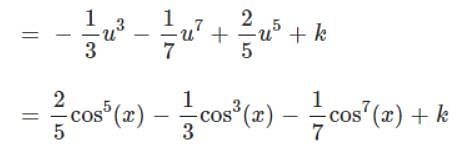

- a)cos(sin-1x) + c
- b)sin-1x + c
- c)sin(cos-1x) + c
- d)x + c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
cos(sin-1x) + c
b)
sin-1x + c
c)
sin(cos-1x) + c
d)
x + c

|
Patel Smit answered |
Take sin inverse x is equal to t and 1 upon under root 1 minas x square is equal to dt,then integration of cost is equal to sint plus c put t I equal to sin inverse x and got your answer.
Evaluate: 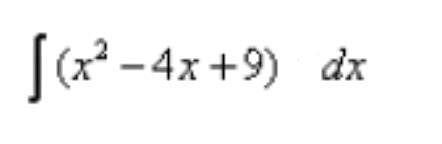
- a)

- b)1/√3 arc tan[(x-2)/√5] + C
- c)
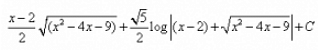
- d)
%7D%7D%7D%2B%7BC%7D)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 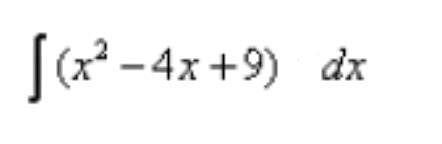
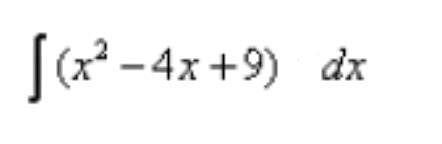
a)
b)
1/√3 arc tan[(x-2)/√5] + C
c)
d)
|
|
Deepak Kapoor answered |
Let's apply the integral substitution,
substitute 
Now use the standard integral :}}})
substitute back u=(x-2) and add a constant C to the solution,
Evaluate: 
- a)
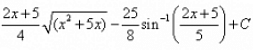
- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Leelu Bhai answered |
I = ∫√(x² + 5x)dx= ∫√(x² + 5x + 25/4 - 25/4)= ∫√{(x + 5/2)² - (5/2)²}={1/2(x+5/2)(√x² + 5x)} - {25/8 log{(x + 5/2)+√x²+ 5x}}= {(2x + 5)/4 (√x² + 5x)} - {25/8 log{(x + 5/2)+√x²+ 5x}}Thus, option D is correct...
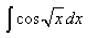
- a)
 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant - b)
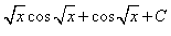 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant - c)
 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant - d)
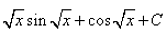 , where C is a constant
, where C is a constant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
q = √x, dq = dx/2√x
⇒ dx = 2q dq
so the integral is 2∫qcosqdq
integration by parts using form
∫uv' = uv − ∫u'v
here u = q, u'= 1 and v'= cosq, v=sinq
so we have 2(qsinq −∫sinqdq)
= 2(qsinq + cosq + C)
= 2(√xsin√x + cos√x + C)
⇒ dx = 2q dq
so the integral is 2∫qcosqdq
integration by parts using form
∫uv' = uv − ∫u'v
here u = q, u'= 1 and v'= cosq, v=sinq
so we have 2(qsinq −∫sinqdq)
= 2(qsinq + cosq + C)
= 2(√xsin√x + cos√x + C)
Evaluate: 
- a)
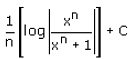
- b)
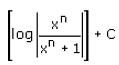
- c)
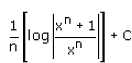
- d)
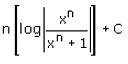
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
∫dx/x(xn + 1)..............(1)
∫dx/x(xn + 1) *(xn - 1)/(xn - 1)
Put xn = t
dt = nx(n-1)dx
dt/n = x(n-1)dx
Put the value of dt/n in eq(1)
= ∫(1/n)dt/t(t+1)
= 1/n ∫dt/(t+1)t
= 1/n{∫dt/t - ∫dt/t+1}
= 1/n {ln t - lnt + 1} + c
= 1/n {ln |t/(t + 1)|} + c
= 1/n {ln |xn/(xn + 1)|} + c
∫dx/x(xn + 1) *(xn - 1)/(xn - 1)
Put xn = t
dt = nx(n-1)dx
dt/n = x(n-1)dx
Put the value of dt/n in eq(1)
= ∫(1/n)dt/t(t+1)
= 1/n ∫dt/(t+1)t
= 1/n{∫dt/t - ∫dt/t+1}
= 1/n {ln t - lnt + 1} + c
= 1/n {ln |t/(t + 1)|} + c
= 1/n {ln |xn/(xn + 1)|} + c
Evaluate: 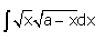
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)
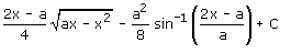
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 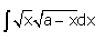
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
(x)½ (a - x)½ dx
= ∫(ax - x2)½ dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax)½} dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax + a2/4 - a2/4)½} dx
= ∫{-(x - a/2)2 - a2/4} dx
= ∫{(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} dx
= ½(x - a/2) {(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} + (a2/4) (½ sin-1(x - a)/a2)
= {(2x - a)/4 (ax - x2)½} + {a2/8 sin-1(2x - a)/a} + c
= ∫(ax - x2)½ dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax)½} dx
= ∫{-(x2 - ax + a2/4 - a2/4)½} dx
= ∫{-(x - a/2)2 - a2/4} dx
= ∫{(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} dx
= ½(x - a/2) {(a/2)2 - (x - a/2)2} + (a2/4) (½ sin-1(x - a)/a2)
= {(2x - a)/4 (ax - x2)½} + {a2/8 sin-1(2x - a)/a} + c
The integration of the function ex.cos3x is:- a)

- b)

- c)
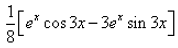
- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The integration of the function ex.cos3x is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Let I = ∫ex . cos 3x dx
⇒ I = cos 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫[d/dx(cos 3x) × ∫ex dx]dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x − ∫(− 3 sin 3x . ex)dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3∫sin 3x . ex dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫{ddx(sin 3x) × ∫ex dx}dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x . ex − ∫3 cos 3x . ex dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9∫ex . cos 3x dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9I
⇒ 10I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x
⇒ I = 1/10[ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x] + C
⇒ I = cos 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫[d/dx(cos 3x) × ∫ex dx]dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x − ∫(− 3 sin 3x . ex)dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3∫sin 3x . ex dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x × ∫ex dx − ∫{ddx(sin 3x) × ∫ex dx}dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3[sin 3x . ex − ∫3 cos 3x . ex dx]
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9∫ex . cos 3x dx
⇒ I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x − 9I
⇒ 10I = ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x
⇒ I = 1/10[ex cos 3x + 3 ex . sin 3x] + C
Evaluate: 
- a)1/2
- b)1/4
- c)1
- d)1/8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 
a)
1/2
b)
1/4
c)
1
d)
1/8

|
Sumair Sadiq answered |
This is maths questions I can explain it but you know it is not possible here because this app is not allow to take photo but try it ok let tan inverce 4x =t diff both side wrt x 4x³/1+x⁴ Ka square
x cube / 1+ x8 =dt/4 I = £ 0 se pie by 2 (because when x= 0 t = pie by 2and x = infinity then t = 0 )
I = 1/4 £ 0 se pie by 2 sin t l = 1/4 (- cos t limit 0 se pie by 2 )l = 1/4 ( - cos pie by 2 + cos 0) l = 1/4 ( 0+ 1) l= 1/4 × 1l= 1/4
use my WhatsApp number for further questions but only for study 7060398771
x cube / 1+ x8 =dt/4 I = £ 0 se pie by 2 (because when x= 0 t = pie by 2and x = infinity then t = 0 )
I = 1/4 £ 0 se pie by 2 sin t l = 1/4 (- cos t limit 0 se pie by 2 )l = 1/4 ( - cos pie by 2 + cos 0) l = 1/4 ( 0+ 1) l= 1/4 × 1l= 1/4
use my WhatsApp number for further questions but only for study 7060398771
Evaluate: 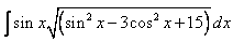
- a)
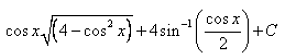
- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 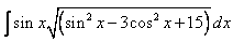
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
sin2x = 1 - cos2x
∫sinx(sin2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
Put cos2x = t
∫sinx(1 - cos2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
= ∫sinx (16 - 4cos2x)dx
Put t = cosx, differentiate with respect to x, we get
dt/dx = -sinx
= - ∫ [(16 - 4t2)]1/2dt
= -2 ∫ [(2)2 - (t)2]½
= -2{[(2)2 - (t)2]½ + 2sin-1(t/2)} + c
= - cosx {[4 - (cos)2x]½ - 4sin-1(cosx/2)} + c
∫sinx(sin2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
Put cos2x = t
∫sinx(1 - cos2x - 3cos2x + 15)dx
= ∫sinx (16 - 4cos2x)dx
Put t = cosx, differentiate with respect to x, we get
dt/dx = -sinx
= - ∫ [(16 - 4t2)]1/2dt
= -2 ∫ [(2)2 - (t)2]½
= -2{[(2)2 - (t)2]½ + 2sin-1(t/2)} + c
= - cosx {[4 - (cos)2x]½ - 4sin-1(cosx/2)} + c
The value of  is:
is:- a)
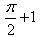
- b)
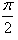
- c)
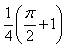
- d)
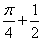
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of  is:
is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Samyak Jain answered |
1/2(cos π/2 + 1 -[cos(π/2-π/4)+1])=1/2+π/4
When do children go to school in Topsy-turvy Land?- a)Night
- b)Morning
- c)Afternoon
- d)Evening
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When do children go to school in Topsy-turvy Land?
a)
Night
b)
Morning
c)
Afternoon
d)
Evening
|
|
Aarushi gupta answered |
In Topsy-turvy Land children go to school at night.
So, correct answer is option (a).

- a)-1
- b)zero
- c)1
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
-1
b)
zero
c)
1
d)
2
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
∫(0 to 4)(x)1/2 - x2 dx
= [[(x)3/2]/(3/2) - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2x3/2]/3 - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2(0)3/2]/3 - (0)2]] - [[2(4)3/2]/3 - (4)2]]
= 0-0
= 0
= [[(x)3/2]/(3/2) - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2x3/2]/3 - x2](0 to 4)
= [[2(0)3/2]/3 - (0)2]] - [[2(4)3/2]/3 - (4)2]]
= 0-0
= 0
Evaluate:
- a)
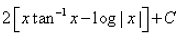
- b)
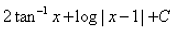
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Let x=tanθ , so that θ=tan−1x , dx=sec2θdθ
Then the given integral is equivalent to
∫tan−1(2x/(1−x2)dx
=∫tan−1 (2tanθ/(1−tan2θ))⋅sec2θdθ
=∫tan−1tan2θ⋅sec2θdθ
=2×∫θsec2θdθ
(integrate by parts)
=2θ⋅∫sec2θdθ −2⋅∫1⋅(∫sec2θdθ)dθ
=2θtanθ−2⋅∫tanθdθ
=2θtanθ−2loge secθ+c
=2xtan−1x−2loge√1+x2+c
=2xtan−1x−loge(1+x2)+c
Then the given integral is equivalent to
∫tan−1(2x/(1−x2)dx
=∫tan−1 (2tanθ/(1−tan2θ))⋅sec2θdθ
=∫tan−1tan2θ⋅sec2θdθ
=2×∫θsec2θdθ
(integrate by parts)
=2θ⋅∫sec2θdθ −2⋅∫1⋅(∫sec2θdθ)dθ
=2θtanθ−2⋅∫tanθdθ
=2θtanθ−2loge secθ+c
=2xtan−1x−2loge√1+x2+c
=2xtan−1x−loge(1+x2)+c
The integral of  is:
is:- a)
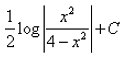
- b)
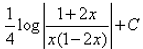
- c)
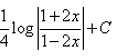
- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The integral of  is:
is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
∫dx/x3(x-2 -4).............(1)
= ∫x-3 dx/(x-2 - 4)
Let t = (x-2 - 4)
dt = -2x-3 dx
x-3 = -dt/2
Put the value of x-3 in eq(1)
= -½ ∫dt/t
= -½ log t + c
= -½ log(x-2 - 4) + c
= -½ log(1-4x2)/x2 + c
= ½ log(x2/(1 - 4x2)) + c
= ∫x-3 dx/(x-2 - 4)
Let t = (x-2 - 4)
dt = -2x-3 dx
x-3 = -dt/2
Put the value of x-3 in eq(1)
= -½ ∫dt/t
= -½ log t + c
= -½ log(x-2 - 4) + c
= -½ log(1-4x2)/x2 + c
= ½ log(x2/(1 - 4x2)) + c
Evaluate: 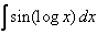
- a)

- b)

- c)
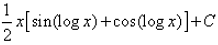
- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 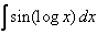
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
I=∫sin(logx)×1dx
= sin(logx) × x−∫cos(logx) × (1/x)×xdx
= xsin(logx)−∫cos(logx) × 1dx
= xsin(logx)−[cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx) × (1/x) × xdx]
∴ I=xsin(logx)−cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx)dx
2I=x[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
∴ I=(x/2)[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
= sin(logx) × x−∫cos(logx) × (1/x)×xdx
= xsin(logx)−∫cos(logx) × 1dx
= xsin(logx)−[cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx) × (1/x) × xdx]
∴ I=xsin(logx)−cos(logx) × x−∫sin(logx)dx
2I=x[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
∴ I=(x/2)[sin(logx)−cos(logx)]
If  is
is- a)2/3
- b)4/5
- c)1
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If  is
is
a)
2/3
b)
4/5
c)
1
d)
None of these
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In the question, it should be f’(2) instead of f”(2)
Explanation:- f(x) = ∫(0 to x) log(1+x2)
f’(x) = 2xdx/(1+x2)
f’(2) = 2(2)/(1+(2)2)
= 4/5
Explanation:- f(x) = ∫(0 to x) log(1+x2)
f’(x) = 2xdx/(1+x2)
f’(2) = 2(2)/(1+(2)2)
= 4/5

- a)

- b)
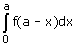
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Option d is correct, because it is the property of definite integral
∫02a f(x) dx = ∫0a f(x) dx + ∫0a f(2a – x) dx
∫02a f(x) dx = ∫0a f(x) dx + ∫0a f(2a – x) dx
Evaluate: 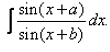
- a)(x + b) cos(a – b) – sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
- b)(x + b) cos(b – a) – sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
- c)(x + b) cos(b – a) + sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
- d)(x + b) cos(a – b) + sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 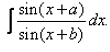
a)
(x + b) cos(a – b) – sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
b)
(x + b) cos(b – a) – sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
c)
(x + b) cos(b – a) + sin(b – a).log | sin(x + b) | + C
d)
(x + b) cos(a – b) + sin(a – b).log | sin(x + b) | + C
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Create ((X+B) + (A-B)) in numerator and then apply Sin(a+b) formula then you will be able to solve it.
The value of the integral 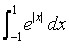 is:
is:- a)2e – 1
- b)2e + 1
- c)2e
- d)2(e – 1)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of the integral 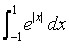 is:
is:
a)
2e – 1
b)
2e + 1
c)
2e
d)
2(e – 1)
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Correct Answer : d
Explanation : ∫(-1 to 1) e|x| dx
∫(-1 to 0) e|x|dx + ∫(0 to 1) e|x|dx
e1 -1 + e1 - 1
=> 2(e - 1)
The integral of tan4x is:- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The integral of tan4x is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Begin by rewriting ∫tan4xdx as ∫tan2xtan2xdx.
Now we can apply the Pythagorean Identity, tan2x+1=sec2x, or tan2x=sec2x−1
∫tan2x tan2x dx = ∫(sec2x−1)tan2xdx
Distributing the tan2x:
= ∫sec2xtan2x − tan2xdx
Applying the sum rule:
= ∫sec2xtan2xdx − ∫tan2xdx
We'll evaluate these integrals one by one.
First Integral
This one is solved using a
Let u = tanx
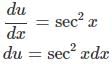
Applying the substitution,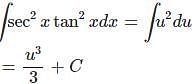
Because u = tanx,
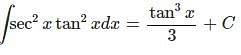
This one is solved using a

Let u = tanx
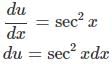
Applying the substitution,
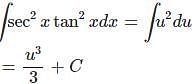
Because u = tanx,
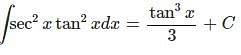
Second Integral
Since we don't really know what ∫tan2xdx is by just looking at it, try applying the tan2x = sec2x−1
Since we don't really know what ∫tan2xdx is by just looking at it, try applying the tan2x = sec2x−1
identity again:
∫tan2xdx = ∫(sec2x−1)dx
Using the sum rule, the integral boils down to:
∫sec2xdx − ∫1dx
∫sec2xdx − ∫1dx
The first of these, ∫sec2xdx, is just tanx + C.
The second one, the so-called "perfect integral", is simply x+C.
Putting it all together, we can say:
∫tan2xdx = tanx + C − x + C
∫tan2xdx = tanx + C − x + C
And because C+C is just another arbitrary constant, we can combine it into a general constant C:
∫tan2xdx = tanx − x + C
∫tan2xdx = tanx − x + C
Combining the two results, we have:
∫tan4xdx=∫sec2xtan2xdx−∫tan2xdx
∫tan4xdx=∫sec2xtan2xdx−∫tan2xdx
=(tan3x/3 + C) − (tanx − x + C)
=tan3x/3 − tanx + x + C
Again, because C+C is a constant, we can join them into one C.
Evaluate: 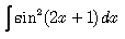
- a)
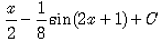
- b)
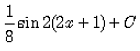
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate: 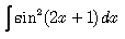
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∫sin2(2x+1) dx
Put t = 2x+1
dt = 2dx
dx= dt/2
= 1/2∫sin2 t dt
=1/2∫(1-cos2t)/2 dt
= 1/4∫(1-cos2t) dt
= ¼[(t - (sin2t)/2]dt
= t/4 - sin2t/8 + c
= (2x+1)/4 - ⅛(sin(4x+2)) + c
= x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + ¼ + c
As ¼ is also a constant, so eq is = x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + c
Put t = 2x+1
dt = 2dx
dx= dt/2
= 1/2∫sin2 t dt
=1/2∫(1-cos2t)/2 dt
= 1/4∫(1-cos2t) dt
= ¼[(t - (sin2t)/2]dt
= t/4 - sin2t/8 + c
= (2x+1)/4 - ⅛(sin(4x+2)) + c
= x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + ¼ + c
As ¼ is also a constant, so eq is = x/2 - 1/8sin(4x+2) + c
Integrate 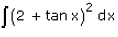
- a)3x – 4 log |sec x| + tan x + C
- b)3x + 4 log |sec x| + tan x
- c)3x + 4 log |sec X| + tan x + C
- d)3x + 4 log |sec x| – tan x + C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Integrate 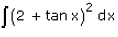
a)
3x – 4 log |sec x| + tan x + C
b)
3x + 4 log |sec x| + tan x
c)
3x + 4 log |sec X| + tan x + C
d)
3x + 4 log |sec x| – tan x + C
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
∫(2+tan x)2dx
= ∫(4 + tan2 x + 4tan x)dx
= ∫4 dx + ∫tan2 x dx + 4∫tan x dx
= 4x + ∫(sec2 x - 1)dx + 4(log|sec x|)
= 4x + tanx - x + 4(log|sec x|)
3x + tanx + 4(log|sec x|) + c
= ∫(4 + tan2 x + 4tan x)dx
= ∫4 dx + ∫tan2 x dx + 4∫tan x dx
= 4x + ∫(sec2 x - 1)dx + 4(log|sec x|)
= 4x + tanx - x + 4(log|sec x|)
3x + tanx + 4(log|sec x|) + c
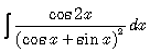
- a)log(sin x + cos x) +C
- b)sin 2x + cos 2x + C
- c)log(sin x - cos x) +C
- d)sin 2x - cos 2x + C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
log(sin x + cos x) +C
b)
sin 2x + cos 2x + C
c)
log(sin x - cos x) +C
d)
sin 2x - cos 2x + C
|
|
Om Desai answered |
I = ∫cos2x/(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫cos2x−sin2x(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫[(cosx+sinx)(cosx−sinx)]/(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫(cosx−sinx)/(sinx+cosx)dx
Let sinx+cosx = t
(cosx−sinx)dx = dt
Then, I = ∫dt/t
I = log|t|+c
I = log|sinx + cosx| + c
⇒I = ∫cos2x−sin2x(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫[(cosx+sinx)(cosx−sinx)]/(sinx+cosx)2dx
⇒I = ∫(cosx−sinx)/(sinx+cosx)dx
Let sinx+cosx = t
(cosx−sinx)dx = dt
Then, I = ∫dt/t
I = log|t|+c
I = log|sinx + cosx| + c
The value of 
- a)
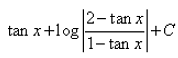
- b)

- c)

- d)
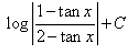
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of 
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Shubham Rajput answered |
I have got correct answer as d please confirm me anyone

- a)if f(2a – x) = – f(x)
- b)if f(2a – x) = f(x)
- c)if f(- x) = f(x)
- d)if f(- x) = – f(x)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
if f(2a – x) = – f(x)
b)
if f(2a – x) = f(x)
c)
if f(- x) = f(x)
d)
if f(- x) = – f(x)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∫(-a to a)f(x)dx
= ∫(0 to a) [f(x) + f(-x)] if f(x) is an odd function
⇒ f(-x) = -f(x)
= ∫(0 to a) [f(x) + f(-x)] if f(x) is an odd function
⇒ f(-x) = -f(x)

- a)g (x) h (s) = constant
- b)g (x) = h (x).
- c)g (x) - h (x) = constant
- d)h (x) + g (x) = constant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
g (x) h (s) = constant
b)
g (x) = h (x).
c)
g (x) - h (x) = constant
d)
h (x) + g (x) = constant
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Since g(x) and h(x) are integrals of the same function , therefore ; g(x) – h(x) is constant.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 6: Integration - Calculus AB 2024 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 6: Integration - Calculus AB in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Calculus AB
22 videos|44 docs|34 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup