All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
Engineering Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Virtual Work for Mechanical Engineering Exam
If a system is in equilibrium and the position of the system depends upon many independent variables, the principle of virtual work states that the partial derivatives of its total potential energy with respect to each of the independent variable must be- a)-1.0
- b)0
- c)1.0
- d)∞
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a system is in equilibrium and the position of the system depends upon many independent variables, the principle of virtual work states that the partial derivatives of its total potential energy with respect to each of the independent variable must be
a)
-1.0
b)
0
c)
1.0
d)
∞
|
|
Ananya Kumari answered |
The system of construction and conductive here among the point and design and low of motion and give to tere ans all
and among this is is ans o
and among this is is ans o
Who founded the principle of virtual displacement?- a)Euler
- b)Pascal
- c)Castigliano
- d)Bernoulli
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who founded the principle of virtual displacement?
a)
Euler
b)
Pascal
c)
Castigliano
d)
Bernoulli
|
|
Ananya Kumari answered |
Who founded the principal of Theron and complain say and among all of these ans bout,
Bernoulli law ans
Bernoulli law ans
The principle of virtual work can be applied to elastic system by considering the virtual work of- a)internal forces only
- b)external forces only
- c)internal as well as external forces
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The principle of virtual work can be applied to elastic system by considering the virtual work of
a)
internal forces only
b)
external forces only
c)
internal as well as external forces
d)
none of the above
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Principle of virtual work: (unit-load Method)
Developed by Bernoulli:
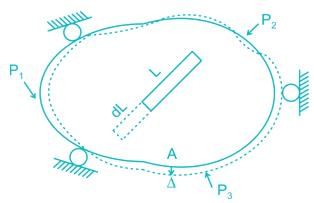
To find Δ at point A due to loads P1, P2, P3. Remove all loads, apply virtual load P’ on point A.
For simplicity P’ = 1
It creates internal load u on representative element.
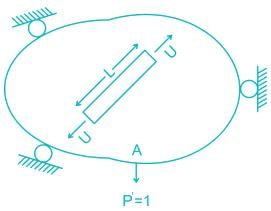
Now remove this load, apply P1, P2, P3 due to which pt. A will be displaced by Δ
∴ External virtual work = 1.Δ
Internal virtual work = u.dL
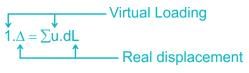
P' = 1 = external virtual unit load in direction of Δ.
u = internal virtual load acting on element in direction of a dL.
Δ = external displacement caused by real loads.
dL = internal deformation caused by real loads.
Developed by Bernoulli:

To find Δ at point A due to loads P1, P2, P3. Remove all loads, apply virtual load P’ on point A.
For simplicity P’ = 1
It creates internal load u on representative element.

Now remove this load, apply P1, P2, P3 due to which pt. A will be displaced by Δ
∴ External virtual work = 1.Δ
Internal virtual work = u.dL

P' = 1 = external virtual unit load in direction of Δ.
u = internal virtual load acting on element in direction of a dL.
Δ = external displacement caused by real loads.
dL = internal deformation caused by real loads.
Virtual work refers to- a)Virtual work done by Virtual forces
- b)Virtual work done by Actual forces
- c)Actual work done by Actual forces
- d)Actual work done by Virtual forces
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Virtual work refers to
a)
Virtual work done by Virtual forces
b)
Virtual work done by Actual forces
c)
Actual work done by Actual forces
d)
Actual work done by Virtual forces

|
Amar Desai answered |
Virtual work refers to the work done by virtual forces on a system. In order to understand this concept, it is important to first define what virtual forces are and how they differ from actual forces.
Virtual forces:
- Virtual forces are hypothetical forces that do not actually exist in the physical world.
- These forces are used in engineering and physics to analyze and understand the behavior of systems.
- Virtual forces are introduced mathematically to simplify the analysis of complex systems.
Actual forces:
- Actual forces are the real forces that act on a system and cause it to move or change its state.
- These forces can be applied externally or internally within the system.
- Actual forces are tangible and measurable.
Virtual work:
- Virtual work is a concept used in mechanics to analyze the equilibrium and motion of systems.
- It is defined as the work done by virtual forces on a system.
- Virtual work is a mathematical tool that allows engineers and physicists to analyze systems without explicitly considering the actual forces that are present.
Explanation of the answer:
The correct answer is option 'B', which states that virtual work refers to the work done by actual forces. This means that virtual forces, which are hypothetical forces, are used to calculate the work done by the actual forces acting on a system.
The concept of virtual work is based on the principle of virtual displacements, which states that the work done by the actual forces on a system is equal to zero for any virtual displacement. This principle allows engineers to simplify the analysis of systems by considering only the virtual forces and virtual displacements.
By using virtual forces, engineers can analyze the equilibrium and motion of complex systems without explicitly considering the actual forces that are present. This simplifies the analysis and allows for easier calculations and predictions.
In conclusion, virtual work refers to the work done by virtual forces on a system. These virtual forces are used to simplify the analysis of systems and calculate the work done by the actual forces. By using virtual forces, engineers and physicists can gain insights into the behavior of systems without explicitly considering the actual forces that are present.
Virtual forces:
- Virtual forces are hypothetical forces that do not actually exist in the physical world.
- These forces are used in engineering and physics to analyze and understand the behavior of systems.
- Virtual forces are introduced mathematically to simplify the analysis of complex systems.
Actual forces:
- Actual forces are the real forces that act on a system and cause it to move or change its state.
- These forces can be applied externally or internally within the system.
- Actual forces are tangible and measurable.
Virtual work:
- Virtual work is a concept used in mechanics to analyze the equilibrium and motion of systems.
- It is defined as the work done by virtual forces on a system.
- Virtual work is a mathematical tool that allows engineers and physicists to analyze systems without explicitly considering the actual forces that are present.
Explanation of the answer:
The correct answer is option 'B', which states that virtual work refers to the work done by actual forces. This means that virtual forces, which are hypothetical forces, are used to calculate the work done by the actual forces acting on a system.
The concept of virtual work is based on the principle of virtual displacements, which states that the work done by the actual forces on a system is equal to zero for any virtual displacement. This principle allows engineers to simplify the analysis of systems by considering only the virtual forces and virtual displacements.
By using virtual forces, engineers can analyze the equilibrium and motion of complex systems without explicitly considering the actual forces that are present. This simplifies the analysis and allows for easier calculations and predictions.
In conclusion, virtual work refers to the work done by virtual forces on a system. These virtual forces are used to simplify the analysis of systems and calculate the work done by the actual forces. By using virtual forces, engineers and physicists can gain insights into the behavior of systems without explicitly considering the actual forces that are present.
A system of connected rigid bodies is in equilibrium, provided the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system is _______ for each independent virtual displacement of the system.- a)One
- b)zero
- c)infinite
- d)twice the external force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A system of connected rigid bodies is in equilibrium, provided the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system is _______ for each independent virtual displacement of the system.
a)
One
b)
zero
c)
infinite
d)
twice the external force

|
Lekshmi Rane answered |
Equilibrium of a System of Connected Rigid Bodies
Introduction
When a system of connected rigid bodies is in equilibrium, it means that the system is not experiencing any net external forces or couples that would cause it to accelerate or rotate. In other words, the system is in a state of balance.
Virtual Work
Virtual work is a concept used to analyze the equilibrium of a system by considering the work done by external forces and couples. It involves considering virtual displacements, which are hypothetical, infinitesimally small displacements applied to the system.
Equilibrium Condition
For a system of connected rigid bodies to be in equilibrium, the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system must be zero for each independent virtual displacement of the system. This condition is based on the principle of virtual work, which states that the work done by external forces and couples during a virtual displacement is equal to zero in equilibrium.
Explanation
In the given question, the correct answer is option 'B', which states that the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system is zero for each independent virtual displacement of the system.
This means that in equilibrium, the work done by the external forces and couples is balanced and cancels out each other. The system remains at rest or in a state of uniform motion.
If the virtual work done by the external forces and couples was non-zero for a virtual displacement, it would imply that there is a net external force or couple acting on the system, causing it to accelerate or rotate. This would violate the condition of equilibrium.
Conclusion
In conclusion, for a system of connected rigid bodies to be in equilibrium, the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system must be zero for each independent virtual displacement of the system. This condition ensures that the system is balanced and not experiencing any net external forces or couples.
Introduction
When a system of connected rigid bodies is in equilibrium, it means that the system is not experiencing any net external forces or couples that would cause it to accelerate or rotate. In other words, the system is in a state of balance.
Virtual Work
Virtual work is a concept used to analyze the equilibrium of a system by considering the work done by external forces and couples. It involves considering virtual displacements, which are hypothetical, infinitesimally small displacements applied to the system.
Equilibrium Condition
For a system of connected rigid bodies to be in equilibrium, the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system must be zero for each independent virtual displacement of the system. This condition is based on the principle of virtual work, which states that the work done by external forces and couples during a virtual displacement is equal to zero in equilibrium.
Explanation
In the given question, the correct answer is option 'B', which states that the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system is zero for each independent virtual displacement of the system.
This means that in equilibrium, the work done by the external forces and couples is balanced and cancels out each other. The system remains at rest or in a state of uniform motion.
If the virtual work done by the external forces and couples was non-zero for a virtual displacement, it would imply that there is a net external force or couple acting on the system, causing it to accelerate or rotate. This would violate the condition of equilibrium.
Conclusion
In conclusion, for a system of connected rigid bodies to be in equilibrium, the virtual work done by all the external forces and couples acting on the system must be zero for each independent virtual displacement of the system. This condition ensures that the system is balanced and not experiencing any net external forces or couples.
In virtual work Principle, the work done by self weight of the body is taken into consideration, when- a)centre of gravity moves vertically
- b)centre of gravity moves horizantally
- c)shear centre moves horizantally
- d)shear centre moves vertically
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In virtual work Principle, the work done by self weight of the body is taken into consideration, when
a)
centre of gravity moves vertically
b)
centre of gravity moves horizantally
c)
shear centre moves horizantally
d)
shear centre moves vertically
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Virtual work principle states that “when a body is in equilibrium then for a small change in displacement, the total work done should be zero”.
The forces which are considered for virtual work is:
The forces which are considered for virtual work is:
- The tension in the body when displacement alters the length of the body.
- The thrust in the body when displacement alters the length of the body.
- Weight of the body.
If ‘w’ is the weight of the body and ‘h’ is the distance between the centre of gravity and the fixed plane, then the virtual work should be ‘wh’ when the centre of gravity is below the fixed plane. When the centre of gravity is above the fixed plane, the virtual work is ‘-wΔh’. If the centre of gravity is not moving in the upward or downward direction, then the weight of the body is not doing any work. Hence, the work done by the self-weight of the body is taken into consideration when the centre of gravity moves vertically.
Option ‘1’ is correct.
Option ‘1’ is correct.
The principle of virtual work states that, for a body to be in equilibrium, the virtual work should be:- a)Any value between zero and one
- b)Zero
- c)Maximum
- d)Minimum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The principle of virtual work states that, for a body to be in equilibrium, the virtual work should be:
a)
Any value between zero and one
b)
Zero
c)
Maximum
d)
Minimum
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Virtual work is the work done by a real force acting through a virtual displacement or a virtual force acting through a real displacement.
A virtual displacement is any displacement consistent with the constraints of the structure, i.e., that satisfy the boundary conditions at the supports.
A virtual force is any system of forces in equilibrium.
The principle of virtual work states, for bodies in equilibrium, for a small arbitrary displacement, the total work done by the system is zero.
In this method, the system is displaced through a small amount about a reference point and the work done by all the forces about the reference point is summed to zero to find the unknown reactions if any.
∴ The principle of virtual work states that, for a body to be in equilibrium, the virtual work should be zero.
A virtual displacement is any displacement consistent with the constraints of the structure, i.e., that satisfy the boundary conditions at the supports.
A virtual force is any system of forces in equilibrium.
The principle of virtual work states, for bodies in equilibrium, for a small arbitrary displacement, the total work done by the system is zero.
In this method, the system is displaced through a small amount about a reference point and the work done by all the forces about the reference point is summed to zero to find the unknown reactions if any.
∴ The principle of virtual work states that, for a body to be in equilibrium, the virtual work should be zero.
Who founded the principle of virtual displacement?- a)Euler
- b)Pascal
- c)Castigliano
- d)Bernoulli
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who founded the principle of virtual displacement?
a)
Euler
b)
Pascal
c)
Castigliano
d)
Bernoulli
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
- Virtual work is the work done by a real force acting through a virtual displacement i.e. Virtual work done by real forces.
- The initial formulation of the principle of virtual displacement was given by Bernoulli.
- A virtual displacement is any displacement consistent with the constraints of the structure, i.e., that satisfy the boundary conditions at the supports.
- A virtual force is any system of forces in equilibrium.
- The principle of virtual work states, for bodies in equilibrium, for a small arbitrary displacement, the total work done by the system is zero.
- In this method, the system is displaced through a small amount about a reference point and the work done by all the forces about the reference point is summed to zero to find the unknown reactions if any.
- The principle of virtual work states that, for a body to be in equilibrium, the virtual work should be zero.
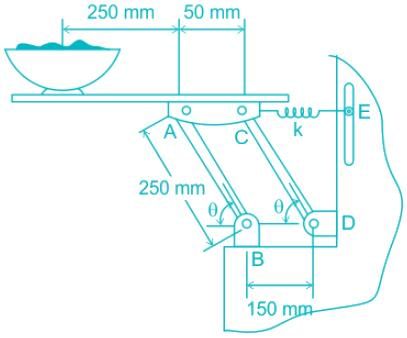
A 5 kg uniform serving table is supported on each side by two pairs of identical links, AB and CD, and springs CE. If the bowl has a mass of 1 kg and is in equilibrium when θ = 45°, determine the stiffness k of each spring. The springs are upstretched when θ = 90°. Neglect the mass of the links.
- a)138 N/m
- b)194 N/m
- c)166 N/m
- d)88 N/m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 5 kg uniform serving table is supported on each side by two pairs of identical links, AB and CD, and springs CE. If the bowl has a mass of 1 kg and is in equilibrium when θ = 45°, determine the stiffness k of each spring. The springs are upstretched when θ = 90°. Neglect the mass of the links.


a)
138 N/m
b)
194 N/m
c)
166 N/m
d)
88 N/m
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Virtual Work -
- Virtual Work is the work done by a real force acting through a virtual displacement.
- A virtual displacement is any displacement consistent with the constraints of the system/structure.
- Principle of Virtual Work states that "The principle of Virtual Work states that "Total work of external forces for small virtual displacement will be zero if the rigid body is in equilibrium."
Calculation:
Given:
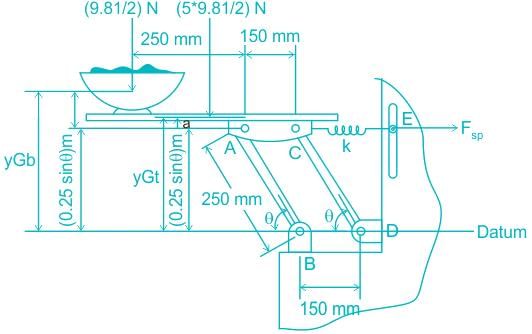
When θ undergoes a positive virtual displacement of δθ, the configuration given below is formed. In this figure only the spring force Fsp, the weight of table Wt and the weight of bowl Wb do work when the virtual displacement takes place.
The magnitude of Fsp can be given using the spring force formula,
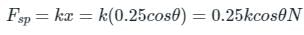
The position of the point of application of Wb, Wt and Fsp are denoted by yGp, yGt and xc respectively.

From the Concept of Virtual Work,
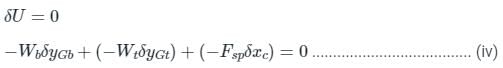
Since Wb, Wt, and Fsp act towards the negative sense of their corresponding virtual displacement, their work is negative.
Put the value of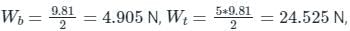 and Fsp = 0.25kcosθ N and all other values in equation (iv), then we have
and Fsp = 0.25kcosθ N and all other values in equation (iv), then we have
−4.905(0.25cosθδθ) − 24.525(0.25cosθδθ) − 0.25kcosθ(−0.25sinθδθ) = 0
δθ(−7.3575cosθ + 0.0625ksinθcosθ) = 0
Since δθ ≠ 0 then
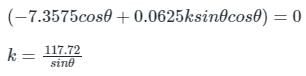
When θ = 45°, then
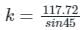
k = 166.48 N/m ≃ 166 N/m
Given:

When θ undergoes a positive virtual displacement of δθ, the configuration given below is formed. In this figure only the spring force Fsp, the weight of table Wt and the weight of bowl Wb do work when the virtual displacement takes place.
The magnitude of Fsp can be given using the spring force formula,
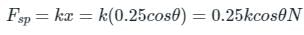
The position of the point of application of Wb, Wt and Fsp are denoted by yGp, yGt and xc respectively.

From the Concept of Virtual Work,
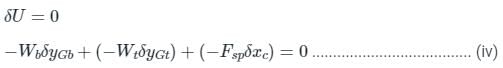
Since Wb, Wt, and Fsp act towards the negative sense of their corresponding virtual displacement, their work is negative.
Put the value of
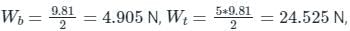 and Fsp = 0.25kcosθ N and all other values in equation (iv), then we have
and Fsp = 0.25kcosθ N and all other values in equation (iv), then we have−4.905(0.25cosθδθ) − 24.525(0.25cosθδθ) − 0.25kcosθ(−0.25sinθδθ) = 0
δθ(−7.3575cosθ + 0.0625ksinθcosθ) = 0
Since δθ ≠ 0 then
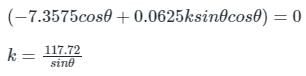
When θ = 45°, then
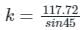
k = 166.48 N/m ≃ 166 N/m
Chapter doubts & questions for Virtual Work - Engineering Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Virtual Work - Engineering Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Engineering Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering
33 videos|78 docs|44 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









