All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Animal Kingdom for NEET Exam
The cross-section of the body of an invertebrate is given below. Identify the animal which has this body plan.
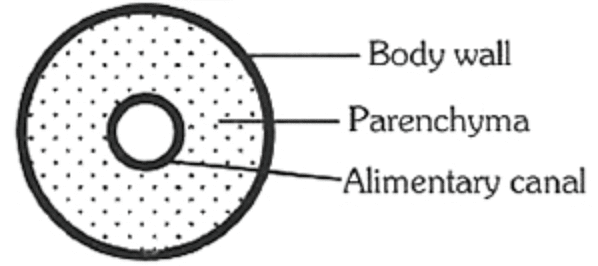
- a)Cockroach
- b)Earthworm
- c)Roundworm
- d)Planaria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cross-section of the body of an invertebrate is given below. Identify the animal which has this body plan.

a)
Cockroach
b)
Earthworm
c)
Roundworm
d)
Planaria

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- It has three-layered body wall which includes ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- Acoelomates lack a body cavity, and instead the space between the body wall and the digestive tract is filled with muscle fibres and loose tissue called parenchyma.
- It acts as a skeletal support, nutrient storage, motility, reserves of regenerative cells and transporting materials.
- Planaria belongs to phylum Platyhelminthes.
- These are flatworms and has acoelomate body plan.
Hence, the correct option is D.
NCERT Reference: Topic Phylum – Platyhelminthes” of chapter Animal Kingdom
Which is the second largest phylum?- a)Phylum Mollusca
- b)Phylum Arthropoda
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Echinodermata
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the second largest phylum?
a)
Phylum Mollusca
b)
Phylum Arthropoda
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Echinodermata

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
Phylum Mollusca is the second largest phylum.
Which phylum is a coelom and triploblastic animals?- a)Phylum Ctenophora
- b)Phylum Annelida
- c)Phylum Coelenterata
- d)Phylum Porifera
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum is a coelom and triploblastic animals?
a)
Phylum Ctenophora
b)
Phylum Annelida
c)
Phylum Coelenterata
d)
Phylum Porifera
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Annelida are aquatic (marine and freshwater) or terrestrial, free-living, and sometimes parasitic. They are bilateral symmetric and triploblastic.
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
- a) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- b)A is true, but R is false.
- c)A is false, but R is true.
- d)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
a)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
b)
A is true, but R is false.
c)
A is false, but R is true.
d)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Nematodes, or roundworms, are indeed classified as pseudocoelomates because they possess a body cavity, known as a pseudocoel, which is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm.
Which among the following is a gregarious pest?- a)Locusta
- b)Apis
- c)Laccifer
- d)Bombyx
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a gregarious pest?
a)
Locusta
b)
Apis
c)
Laccifer
d)
Bombyx
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Locust (Locusta) is a gregarious pest belonging to phylum Arthropoda.

Fig: Image of Locust
Which one of the following categories of animals, is correctly described with no single exception in it?
- a)All bony fishes have four pairs of gills and an operculum on each side.
- b)All mammals are viviparous and possess diaphragm for breathing.
- c)All sponges are marine and have collared cells.
- d)All reptiles possess scales, have a three chambered heart and are cold blooded (poikilothermal).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following categories of animals, is correctly described with no single exception in it?
a)
All bony fishes have four pairs of gills and an operculum on each side.
b)
All mammals are viviparous and possess diaphragm for breathing.
c)
All sponges are marine and have collared cells.
d)
All reptiles possess scales, have a three chambered heart and are cold blooded (poikilothermal).

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |

A reptile having four chambered heart isa)Snakeb)Salamanderc)Crocodiled)LizardsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prakhar Maheshwari answered |
Except for crocodilians, which have a four-chambered heart, all reptiles have a three-chambered heart consisting of two atria and one ventricle.
Which one of the following characteristics is not shared by birds and mammals ? [2016]- a)Ossified endoskeleton
- b)Breathing using lungs
- c)Viviparity
- d)Warm blooded nature
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following characteristics is not shared by birds and mammals ? [2016]
a)
Ossified endoskeleton
b)
Breathing using lungs
c)
Viviparity
d)
Warm blooded nature

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
(c) Giving birth to living young that develop within the mother's body rather than hatching from eggs. All mammals except the monotremes are viviparous.
What is the main excretory organ in insects?- a)Proboscis gland
- b)Malphighian tubules
- c)Gills
- d)Excretory pore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main excretory organ in insects?
a)
Proboscis gland
b)
Malphighian tubules
c)
Gills
d)
Excretory pore
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Malpighian tubule
The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids, and tardigrades. The system consists of branching tubules extending from the alimentary canal that absorbs solutes, water, and wastes from the surrounding hemolymph.
Which among the following is oviparous?- a)Platypus
- b)Flying fox
- c)Common dolphin
- d)lephant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is oviparous?
a)
Platypus
b)
Flying fox
c)
Common dolphin
d)
lephant
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Platypus is oviparous as it is an egg-laying mammal
Rest three are viviparous mammals.
Species going to extinct due to low reproductive rate is- a)Island sps
- b)Bald eagle
- c)Lion
- d)Giant panda
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Species going to extinct due to low reproductive rate is
a)
Island sps
b)
Bald eagle
c)
Lion
d)
Giant panda

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Giant panda is going to extinct due to low reproductively rate. They live in mountain ranges in central china. There reproductively rate is varyless due to climatic conditions.
Which of the following represents the correct combination without any exception? [2015 RS]
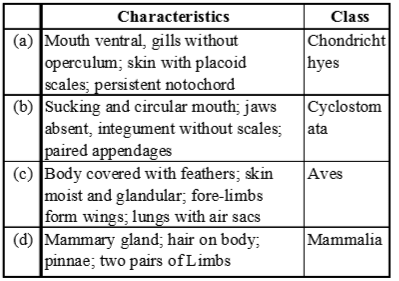
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the correct combination without any exception? [2015 RS]


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
(a) (i) Aves possess dry skin, without glands except oil gland near the base of tail. (ii) Pinnae are not found in aquatic animals and egg laying mammals. (iii) In cyclostomes, unpaired appendages (joints) are found.
Planaria possesses high capacity of: [2014]- a)Metamorphosis
- b)Regeneration
- c)Alternation of generation
- d)Bioluminescence
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Planaria possesses high capacity of: [2014]
a)
Metamorphosis
b)
Regeneration
c)
Alternation of generation
d)
Bioluminescence

|
Krish Khanna answered |
(b) Planaria is a flatworm which possesses a high power of regeneration.
In which one of the folllowing, the genus name, its two characters and its class/phylum are correctly matched? [2011]
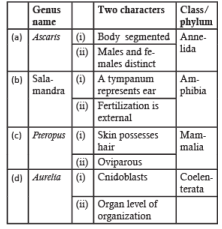
a)ab)bc)cd)dCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?


|
Surbhi Das answered |
The characteristics and phylum of Pteropus is correct.
The presence of milk producing glands is a unique characteristic feature of class- a)Reptilia
- b)Mammalia
- c)Amphibia
- d)Aves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The presence of milk producing glands is a unique characteristic feature of class
a)
Reptilia
b)
Mammalia
c)
Amphibia
d)
Aves

|
Krish Chakraborty answered |
The presence of mammary gland is a unique feature of class mammalia.
Which of the following featrues is not present in the Phylum - Arthropoda ? [2016]- a)Chitinous exoskeleton
- b)Metameric segmentation
- c)Parapodia
- d)Jointed appendages
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following featrues is not present in the Phylum - Arthropoda ? [2016]
a)
Chitinous exoskeleton
b)
Metameric segmentation
c)
Parapodia
d)
Jointed appendages

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
(c) All arthropods possess a stiff exoskeleton (external skeleton) composed primarily of chitin. Arthropod bodies are divided into segments. Parapodia are paired, lateral appendages extending from the body segments. Arthropod appendages may be either biramous (branched) or uniramous (unbranched). They do not possess jointed appendages.
Which one of the following group of animals is correctly matched with its characteristics without any exception?- a)Reptila possess 3-chambered heart with incompletely divided ventricle
- b)Mammalia give birth to young ones
- c)Chordates possess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw
- d)Chondrichthyes possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following group of animals is correctly matched with its characteristics without any exception?
a)
Reptila possess 3-chambered heart with incompletely divided ventricle
b)
Mammalia give birth to young ones
c)
Chordates possess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw
d)
Chondrichthyes possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The members of the class - Chondrichthyes are marine animals with a streamlined body and have a cartilaginous endoskeleton.
A marine cartilaginous fish that can produce electric current is: [2014]- a)Pristis
- b)Torpedo
- c)Trygon
- d)Scoliodon
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A marine cartilaginous fish that can produce electric current is: [2014]
a)
Pristis
b)
Torpedo
c)
Trygon
d)
Scoliodon

|
Gowri Nair answered |
(b) Torpedo is a sluggish fish. It is carnivorous. The prey is first killed by electric shock. The shock can also be harmful for human beings.
Which of the following animals is not viviparous? [2015 RS]- a)Elephant
- b)Platypus
- c)Whale
- d)Flying fox (Bat)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following animals is not viviparous? [2015 RS]
a)
Elephant
b)
Platypus
c)
Whale
d)
Flying fox (Bat)

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
(b) Platypus is oviparous (egg laying animal). It belongs to class-mammalia.
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called- a)Segmentation
- b)Metagenesis
- c)Metamerism
- d)Metamorphosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called
a)
Segmentation
b)
Metagenesis
c)
Metamerism
d)
Metamorphosis
|
|
Santunu Pradhan answered |
Metamerism
The excretory organ of Saccoglossus is- a)Malphighian tubules
- b)Proboscis gland
- c)Gills
- d)Excretory pore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The excretory organ of Saccoglossus is
a)
Malphighian tubules
b)
Proboscis gland
c)
Gills
d)
Excretory pore
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A proboscis is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouth parts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout.
How many chambers are there in camel’s stomach?Identify the animal given below. Mention its phylum.
- a)1 chamber, Ascidia and phylum Chordata
- b)3 Chamber, Spongilla and phylum Porifera
- c)3 chambers, Euspongia and phylum Porifera
- d)4 chamber, Aurelia and phylum Coelenterata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many chambers are there in camel’s stomach?Identify the animal given below. Mention its phylum.
a)
1 chamber, Ascidia and phylum Chordata
b)
3 Chamber, Spongilla and phylum Porifera
c)
3 chambers, Euspongia and phylum Porifera
d)
4 chamber, Aurelia and phylum Coelenterata

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
Euspongia, which belongs to the phylum Porifera, is commonly known as a sponge. Sponges are some of the simplest and most primitive animals in the animal kingdom.
Hence, the correct option is C.
NCERT Reference: Topic: Phylum – Porifera” of chapter Animal Kingdom
NCERT Reference: Topic: Phylum – Porifera” of chapter Animal Kingdom
Which group of chordates possesses sucking and circular mouth without jaws?- a)ClassChondrichthyes
- b)Class Cyclostomata
- c)Class Osteichthyes
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which group of chordates possesses sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
a)
ClassChondrichthyes
b)
Class Cyclostomata
c)
Class Osteichthyes
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Class-Cyclostomata is comprised of, the living jawless fishes. Their mouth is circular and lack jaws, hence they are also called agnathans. It is surrounded by tentacles (e.g., lampreys and hellish). These also presses retractable teeth.
Animals which possess cleidoic egg exhibit- a)External fertilisation and external development
- b)External fertilisation and internal development
- c)Internal fertilisation and internal development
- d)Internal fertilisation and external development
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals which possess cleidoic egg exhibit
a)
External fertilisation and external development
b)
External fertilisation and internal development
c)
Internal fertilisation and internal development
d)
Internal fertilisation and external development
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Cleidoic eggs are laid by reptiles & birds. These eggs have protective shell which is porous to air and may be flexible or calcareous (hard). Birds and reptiles exhibit internal fertilization and laid eggs contain all the food the embryo needs for external development.
In which one of the following the genus name, its two charcters and its phylum are not correctly matched, whereas the remaining three are correct
[2012]
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following the genus name, its two charcters and its phylum are not correctly matched, whereas the remaining three are correct
[2012]
[2012]

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Molluscans are soft bodied animals. Their body is unsegmented with a distinct head, muscular foot and visceral hump. In Pila the buccal cavity contains a resping organ, the radula with transverse rows of teeth.
Silk produced by Antheraea Mylitta is called- a)Eri silk
- b)Muga silk
- c)Mysore silk
- d)Tasar silk
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Silk produced by Antheraea Mylitta is called
a)
Eri silk
b)
Muga silk
c)
Mysore silk
d)
Tasar silk
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Tropical Tasar: Tasar (Tussah) is copperish colour, coarse silk mainly used for furnishings and interiors. It is less lustrous than mulberry silk, but has its own feel and appeal. Tasar silk is generated by the silkworm, Antheraea mylitta which mainly thrive on the food plants Asan and Arjun.
Select the Taxon mentioned that represents both marine and fresh water species: [2014]- a)Echinoderms
- b)Ctenophora
- c)Cephalochordata
- d)Cnidaria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the Taxon mentioned that represents both marine and fresh water species: [2014]
a)
Echinoderms
b)
Ctenophora
c)
Cephalochordata
d)
Cnidaria

|
Diya Datta answered |
(d) Members of Ctenophora, Cephalochordata and Echinodermata are exclusively marine.
Which phylum has water vascular system as a characteristic feature?- a)Phylum Ctenophora
- b)Phylum Coelenterata
- c)Phylum Echinodermata
- d)Phylum Porifera
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum has water vascular system as a characteristic feature?
a)
Phylum Ctenophora
b)
Phylum Coelenterata
c)
Phylum Echinodermata
d)
Phylum Porifera

|
Shounak Nair answered |
The most distinctive feature is the presence of water vascular system.
The scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito- a)Aedes aegypti
- b)Aedes albolineatus
- c)Aedes taeniorhynchus
- d)Aedes albopictus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito
a)
Aedes aegypti
b)
Aedes albolineatus
c)
Aedes taeniorhynchus
d)
Aedes albopictus
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is a small black and white mosquito, about 1/4-inch long.
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Echinodermata
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Aschelminthes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Echinodermata
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Aschelminthes
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Symmetry is an attribute of an organism showing regularity in body parts on a plane or around an axis. In Phylum Echinodermata, the adult echinoderms are radially symmetrical but the larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
Air bladder is absent in- a)Sea horse
- b)Shark
- c)Flying fish
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Air bladder is absent in
a)
Sea horse
b)
Shark
c)
Flying fish
d)
All of the above
|
|
Roshni Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
Air bladder is a gas-filled sac that helps fish to maintain buoyancy in water. However, not all fish have air bladders. The correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., shark, as sharks do not have air bladders.
Reasons why sharks do not have an air bladder are:
1. Buoyancy control: Sharks have a special organ called the liver that is filled with oil. This oil is less dense than water and provides buoyancy to the shark, allowing it to stay afloat.
2. Depth control: Unlike bony fish that have a swim bladder to adjust their depth in water, sharks are able to control their depth by swimming. They can swim at different angles to adjust their depth in water.
3. Adaptation to environment: Sharks have evolved to live in their environment, and their body shape and buoyancy control mechanisms have adapted to suit their needs.
Therefore, it can be concluded that while some fish have air bladders to maintain buoyancy in water, sharks have evolved different mechanisms to control their buoyancy and depth in water.
Air bladder is a gas-filled sac that helps fish to maintain buoyancy in water. However, not all fish have air bladders. The correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., shark, as sharks do not have air bladders.
Reasons why sharks do not have an air bladder are:
1. Buoyancy control: Sharks have a special organ called the liver that is filled with oil. This oil is less dense than water and provides buoyancy to the shark, allowing it to stay afloat.
2. Depth control: Unlike bony fish that have a swim bladder to adjust their depth in water, sharks are able to control their depth by swimming. They can swim at different angles to adjust their depth in water.
3. Adaptation to environment: Sharks have evolved to live in their environment, and their body shape and buoyancy control mechanisms have adapted to suit their needs.
Therefore, it can be concluded that while some fish have air bladders to maintain buoyancy in water, sharks have evolved different mechanisms to control their buoyancy and depth in water.
One of there presentatives of phylum Arthropoda is : [NEET 2013]- a)Silverfish
- b)Pufferfish
- c)Flying fish
- d)Cuttlefish
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of there presentatives of phylum Arthropoda is : [NEET 2013]
a)
Silverfish
b)
Pufferfish
c)
Flying fish
d)
Cuttlefish

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Representive of Phylum Ar thropoda is silverfish. Arthropoda is the largest phylum of Animalia, which covers two-thirds of all named species.
Which one of the following statements is totally wrong about the occurrence of notochord, while the other three are correct? [2011M]- a)It is present only in larval tail in Ascidians
- b)It is replaced by a vertebral column in adult frog
- c)It is absent throughout life in humans from the very beginning
- d)It is present throughout life in Amphioxus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is totally wrong about the occurrence of notochord, while the other three are correct? [2011M]
a)
It is present only in larval tail in Ascidians
b)
It is replaced by a vertebral column in adult frog
c)
It is absent throughout life in humans from the very beginning
d)
It is present throughout life in Amphioxus

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Notochord is a flexible rod like structure that forms the main support of the body in the lowest chordates. It is not absent in humans through out their life. Notochord is present in embryonic stage and get changed or replaced by vertebral column in the adult.
Sharks and dogfishes differ from skates and rays by [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Their pectoral fins distinctly marked off from cyclindrical bodies
- b)Gill slits are ventrally placed
- c)Head and trunk are widened considerably
- d)Distinct demarcation between body and tail
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sharks and dogfishes differ from skates and rays by [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Their pectoral fins distinctly marked off from cyclindrical bodies
b)
Gill slits are ventrally placed
c)
Head and trunk are widened considerably
d)
Distinct demarcation between body and tail
|
|
Janani Iyer answered |
Difference between Sharks and Dogfishes from Skates and Rays
Sharks and dogfishes are a group of fishes that belong to the class Chondrichthyes. Skates and rays are also part of this class. However, there are some distinguishing characteristics that set sharks and dogfishes apart from skates and rays.
Distinctly Marked Pectoral Fins
One of the main differences between sharks and dogfishes from skates and rays is the distinct marking off of their pectoral fins from their cylindrical bodies. Sharks and dogfishes have paddle-like pectoral fins that are not fused to their bodies, which allow them to swim more efficiently. In contrast, skates and rays have flattened pectoral fins that are fused to their bodies.
Ventrally Placed Gill Slits
Sharks and dogfishes have gill slits that are ventrally placed, which means they are located on the underside of their bodies. This allows for more efficient breathing while swimming. Skates and rays, on the other hand, have gill slits that are located on the top of their bodies.
Considerably Widened Head and Trunk
Another difference between sharks and dogfishes from skates and rays is the considerably widened head and trunk. Sharks and dogfishes have a broad and flattened head that tapers towards the tail. This allows for greater maneuverability while swimming. Skates and rays have a flattened body that is wider towards the head and tapers towards the tail.
No Distinct Demarcation Between Body and Tail
Sharks and dogfishes also lack a distinct demarcation between their body and tail. Their tails are generally symmetrical and streamlined, allowing for efficient swimming. Skates and rays, on the other hand, have a distinct demarcation between their body and tail. Their tails are generally flattened and broad, which allows for efficient movement on the ocean floor.
In conclusion, sharks and dogfishes differ from skates and rays in several notable ways, including their distinctly marked pectoral fins, ventrally placed gill slits, considerably widened head and trunk, and lack of a distinct demarcation between body and tail.
Sharks and dogfishes are a group of fishes that belong to the class Chondrichthyes. Skates and rays are also part of this class. However, there are some distinguishing characteristics that set sharks and dogfishes apart from skates and rays.
Distinctly Marked Pectoral Fins
One of the main differences between sharks and dogfishes from skates and rays is the distinct marking off of their pectoral fins from their cylindrical bodies. Sharks and dogfishes have paddle-like pectoral fins that are not fused to their bodies, which allow them to swim more efficiently. In contrast, skates and rays have flattened pectoral fins that are fused to their bodies.
Ventrally Placed Gill Slits
Sharks and dogfishes have gill slits that are ventrally placed, which means they are located on the underside of their bodies. This allows for more efficient breathing while swimming. Skates and rays, on the other hand, have gill slits that are located on the top of their bodies.
Considerably Widened Head and Trunk
Another difference between sharks and dogfishes from skates and rays is the considerably widened head and trunk. Sharks and dogfishes have a broad and flattened head that tapers towards the tail. This allows for greater maneuverability while swimming. Skates and rays have a flattened body that is wider towards the head and tapers towards the tail.
No Distinct Demarcation Between Body and Tail
Sharks and dogfishes also lack a distinct demarcation between their body and tail. Their tails are generally symmetrical and streamlined, allowing for efficient swimming. Skates and rays, on the other hand, have a distinct demarcation between their body and tail. Their tails are generally flattened and broad, which allows for efficient movement on the ocean floor.
In conclusion, sharks and dogfishes differ from skates and rays in several notable ways, including their distinctly marked pectoral fins, ventrally placed gill slits, considerably widened head and trunk, and lack of a distinct demarcation between body and tail.
A jawless fish, which lays eggs in fresh water and whose ammocoetes larvae after metamorphosis return to the ocean is: [2015 RS]- a)myxine
- b)Neomyxine
- c)Petromyzon
- d)Eptatretus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A jawless fish, which lays eggs in fresh water and whose ammocoetes larvae after metamorphosis return to the ocean is: [2015 RS]
a)
myxine
b)
Neomyxine
c)
Petromyzon
d)
Eptatretus

|
Yash Saha answered |
(c) Petrormyzon marinus, commonly known as sea lamprey lays eggs in fresh water and its larvae after metamorphosis return to the ocean (saline water).
Which of the following does not have an excretory system?- a)Carcharodon
- b)Myxine
- c)Asterias
- d)Catla
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not have an excretory system?
a)
Carcharodon
b)
Myxine
c)
Asterias
d)
Catla

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Asterias does not have an excretory system.Asterias includes starfish or sea star. They are exclusively marine,
Body having meshwork of cell, internal cavities lined with food filtering flagellated cells and indirect development are the characteristics of phylum. [2015 RS]- a)Porifera
- b)Mollusca
- c)Protozoa
- d)Coelenterate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Body having meshwork of cell, internal cavities lined with food filtering flagellated cells and indirect development are the characteristics of phylum. [2015 RS]
a)
Porifera
b)
Mollusca
c)
Protozoa
d)
Coelenterate

|
Subham Chavan answered |
(a) The given characteristic features define the phylum porifera.
Which of the following characteristic features always holds true for the corresponding group of animals? [2016]- a)Cartilaginous Chondrichthyes endoskeleton
- b)Viviparous Mammalia
- c)Possess a mouth Chordata with an upper and a lower jaw
- d)3 - chambered heart Reptilia with one incompletely divided ventricle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following characteristic features always holds true for the corresponding group of animals? [2016]
a)
Cartilaginous Chondrichthyes endoskeleton
b)
Viviparous Mammalia
c)
Possess a mouth Chordata with an upper and a lower jaw
d)
3 - chambered heart Reptilia with one incompletely divided ventricle

|
Yash Saha answered |
(a) Chondrichthyes always have cartilaginous endoskeleton. Most mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypuses and the echidnas, lay eggs. Chordates have jawless animals (Agnatha) as well. Most reptiles have 3 chambered heart. Crocodilians have 4 chambered hearts. Turtles have 3 chambered heart but with an incomplete wall in the single ventricle, so their hearts are functionally 4 chambered.
Which of the following is NOT a poisonous snake?
- a)Vipera
- b)Naja
- c)Bangarus
- d)Python
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a poisonous snake?
a)
Vipera
b)
Naja
c)
Bangarus
d)
Python
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Poisonous snakes – Naja(Cobra), Bangarus(Krait), Vipera(Viper).
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe- a)the number of in vaginations during embryonic development
- b)the number of heads during embryonic development
- c)the number of germinal layers during embryonic development
- d)the number of cell types during development
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe
a)
the number of in vaginations during embryonic development
b)
the number of heads during embryonic development
c)
the number of germinal layers during embryonic development
d)
the number of cell types during development
|
|
Pooja Mukherjee answered |
Germinal Layers in Embryonic Development and Diploblastic/Triploblastic Classification
Embryonic development is a complex process that involves the formation of various tissues and organs from a single cell. During this process, the embryo undergoes several stages of development that are marked by the formation of germinal layers. Germinal layers are the layers of cells that differentiate into specific tissues and organs during embryonic development. These layers form the basis of the body plan of an organism and are classified as either diploblastic or triploblastic.
Diploblastic Organisms
Diploblastic organisms are those that have only two germinal layers: the ectoderm and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, which is the process by which the embryo folds in on itself to form a hollow ball of cells called the gastrula. In diploblastic organisms, the ectoderm gives rise to the outer layer of the body and the nervous system, while the endoderm gives rise to the inner layer of the body.
Examples of diploblastic organisms include cnidarians (e.g. jellyfish, corals, sea anemones) and ctenophores (comb jellies).
Triploblastic Organisms
Triploblastic organisms are those that have three germinal layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, but unlike in diploblastic organisms, the mesoderm layer is also formed. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, circulatory system, and other internal organs.
Examples of triploblastic organisms include most animals, including humans.
Conclusion
The diploblastic/triploblastic classification is based on the number of germinal layers that are present during embryonic development. Diploblastic organisms have two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm), while triploblastic organisms have three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). This classification is important for understanding the basic body plan of organisms and how different tissues and organs are formed during embryonic development.
Embryonic development is a complex process that involves the formation of various tissues and organs from a single cell. During this process, the embryo undergoes several stages of development that are marked by the formation of germinal layers. Germinal layers are the layers of cells that differentiate into specific tissues and organs during embryonic development. These layers form the basis of the body plan of an organism and are classified as either diploblastic or triploblastic.
Diploblastic Organisms
Diploblastic organisms are those that have only two germinal layers: the ectoderm and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, which is the process by which the embryo folds in on itself to form a hollow ball of cells called the gastrula. In diploblastic organisms, the ectoderm gives rise to the outer layer of the body and the nervous system, while the endoderm gives rise to the inner layer of the body.
Examples of diploblastic organisms include cnidarians (e.g. jellyfish, corals, sea anemones) and ctenophores (comb jellies).
Triploblastic Organisms
Triploblastic organisms are those that have three germinal layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, but unlike in diploblastic organisms, the mesoderm layer is also formed. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, circulatory system, and other internal organs.
Examples of triploblastic organisms include most animals, including humans.
Conclusion
The diploblastic/triploblastic classification is based on the number of germinal layers that are present during embryonic development. Diploblastic organisms have two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm), while triploblastic organisms have three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). This classification is important for understanding the basic body plan of organisms and how different tissues and organs are formed during embryonic development.
Bilaterally symmetrical and acoelomate animals are exemplified by : [NEET 2020]- a)Aschelminthes
- b)Annelida
- c)Ctenophora
- d)Platyhelminthes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bilaterally symmetrical and acoelomate animals are exemplified by : [NEET 2020]
a)
Aschelminthes
b)
Annelida
c)
Ctenophora
d)
Platyhelminthes
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Flatworms are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and acoelomate animals with organ level of organisation. Aschelminthes is triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical and pseudocoelomate. Annelida is triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical and acoelomate. Ctenophora is radially symmetrical, diploblastic.
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
- a)Body can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane only.
- b)The organisms that show bilateral symmetry have paired body organs that occur on the two sides of a central axis.
- c)It is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates.
- d)Spider and crab show bilateral symmetry.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
a)
Body can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane only.
b)
The organisms that show bilateral symmetry have paired body organs that occur on the two sides of a central axis.
c)
It is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates.
d)
Spider and crab show bilateral symmetry.
|
|
Poulomi Roy answered |
Bilateral Symmetry
Bilateral symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts in such a way that an organism can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane passing through the central axis of the body. This type of symmetry is found in many animals, especially invertebrates and some vertebrates.
Incorrect statement
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that bilateral symmetry is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates. This statement is incorrect because bilateral symmetry is actually found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. Almost all animals belonging to the phyla Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Examples of animals with bilateral symmetry
- Invertebrates like insects, crustaceans, spiders, and worms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
- Vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Advantages of bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry provides several advantages to animals:
- It allows for more efficient movement and coordination since paired limbs and muscles can work together to produce more precise movements.
- It facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, such as eyes and ears, that are paired and located on opposite sides of the body.
- It enables animals to have directional movement, since paired limbs can be used to move forward or backward, up or down, and left or right.
Conclusion
Bilateral symmetry is a common type of symmetry found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. It allows for more efficient movement and coordination, facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, and enables directional movement.
Bilateral symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts in such a way that an organism can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane passing through the central axis of the body. This type of symmetry is found in many animals, especially invertebrates and some vertebrates.
Incorrect statement
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that bilateral symmetry is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates. This statement is incorrect because bilateral symmetry is actually found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. Almost all animals belonging to the phyla Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Examples of animals with bilateral symmetry
- Invertebrates like insects, crustaceans, spiders, and worms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
- Vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Advantages of bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry provides several advantages to animals:
- It allows for more efficient movement and coordination since paired limbs and muscles can work together to produce more precise movements.
- It facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, such as eyes and ears, that are paired and located on opposite sides of the body.
- It enables animals to have directional movement, since paired limbs can be used to move forward or backward, up or down, and left or right.
Conclusion
Bilateral symmetry is a common type of symmetry found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. It allows for more efficient movement and coordination, facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, and enables directional movement.
Which of the following are correctly matched with respect to their taxonomic classification? [NEET 2013]- a)Centipede, millipede, spider, scorpionInsecta
- b)House fly, butterfly, tse tse fly, silverfishInsecta
- c)Spiny anteater, sea urchin, sea cucumberEchinodermata
- d)Flying fish, cuttlefish, silverfish-Pisces
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are correctly matched with respect to their taxonomic classification? [NEET 2013]
a)
Centipede, millipede, spider, scorpionInsecta
b)
House fly, butterfly, tse tse fly, silverfishInsecta
c)
Spiny anteater, sea urchin, sea cucumberEchinodermata
d)
Flying fish, cuttlefish, silverfish-Pisces

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
House fly, butterfly, tse tse fly, silverfish all belongs to insecta.
The figure shows four animals (A), (B), (C) and (D). Select the correct answer with respect to a common characteristics of two of these animals. [2011M](A) 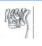 (B)
(B) 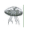 (C)
(C) 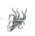 (D)
(D) 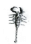
- a)(A) and (D) respire mainly through body wall
- b)(B) and (C) show radial symmetry
- c)(A) and (B) have cnidoblasts for selfdefense
- d)(C) and (D) have a true coelom
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure shows four animals (A), (B), (C) and (D). Select the correct answer with respect to a common characteristics of two of these animals. [2011M]
(A)  (B)
(B) 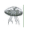
 (B)
(B) 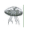
(C) 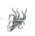 (D)
(D) 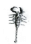
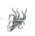 (D)
(D) 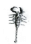
a)
(A) and (D) respire mainly through body wall
b)
(B) and (C) show radial symmetry
c)
(A) and (B) have cnidoblasts for selfdefense
d)
(C) and (D) have a true coelom

|
Palak Khanna answered |
From annelida to chordata all are eucoelomate. C-Mollusca (Octopus), D-Arthropoda (Scorpion) have a true coelom.
Which one of the following statements about certain given animals is correct? [2010]- a)Round worms (Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates
- b)Molluscs are acoelomates
- c)Insects are pseudocoelomates
- d)Flat worms (Platyhelminthes) are coelomates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about certain given animals is correct? [2010]
a)
Round worms (Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates
b)
Molluscs are acoelomates
c)
Insects are pseudocoelomates
d)
Flat worms (Platyhelminthes) are coelomates

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
Acoelomates are animals that have no body cavity or coelom. The examples are poriferans, coelenterates, ctenophore, Platyhelminthes and nemertean. pseudocoelomates are animals that has false or pseudo coelom. Examples are aschelminthes. Coelomates are animals that has true coelom enclosed by mesoderm on both sides. Examples: from annelida to arthropoda are coelomates. Hence roundworms are pseudocoelomates, molluses and insects are coelomates while flatworms are acoelomates.
Which one of the following pairs of animals are similar to each other pertaining to the feature stated against them? [2012M]- a)Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus - Viviparity
- b)Garden lizard and Crocodile - Three chambered heart
- c)Ascaris and Ancylostoma - Metameric segmentation
- d)Sea horse and Flying fish - Cold blooded (poikilothermal)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of animals are similar to each other pertaining to the feature stated against them? [2012M]
a)
Pteropus and Ornithorhyncus - Viviparity
b)
Garden lizard and Crocodile - Three chambered heart
c)
Ascaris and Ancylostoma - Metameric segmentation
d)
Sea horse and Flying fish - Cold blooded (poikilothermal)

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Sea horse and flying fish are cold blooded animals. Ornithorhyncus is oviparous. Crocodile has four chambered heart. Ascaris and Ancylostoma are segmented roundworms.
Frogs differ from humans in possessing:- a)paired cerebral hemispheres [2011M]
- b)hepatic portal system
- c)nucleated red blood cells
- d)thyroid as well as parathyroid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Frogs differ from humans in possessing:
a)
paired cerebral hemispheres [2011M]
b)
hepatic portal system
c)
nucleated red blood cells
d)
thyroid as well as parathyroid

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
Human possesses enucleated RBC in mature state. But frog blood has both white and red blood cells which are nucleated. Frog cells do not lack platelets.
Consider following features. [NEET 2019](A) Organ system level of organisation
(B) Bilateral symmetry
(C) True coelomates with segmentation of bodySelect the correct option of animal groups which possess all the above characteristics.- a)Annelida, Mollusca and Chordata
- b)Annelida, Arthropoda and Chordata
- c)Annelida, Arthropoda and Mollusca
- d)Arthropoda, Mollusca and Chordata
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider following features. [NEET 2019]
(A) Organ system level of organisation
(B) Bilateral symmetry
(C) True coelomates with segmentation of body
(B) Bilateral symmetry
(C) True coelomates with segmentation of body
Select the correct option of animal groups which possess all the above characteristics.
a)
Annelida, Mollusca and Chordata
b)
Annelida, Arthropoda and Chordata
c)
Annelida, Arthropoda and Mollusca
d)
Arthropoda, Mollusca and Chordata
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Mollusca shows organ system level of organisation with unsegmented body (except Neopilina which is a segmented mollusc) having distinct head, muscular foot and visceral hump. They usually show bilateral symmetry but some molluscs (example Pila) become asymmetrical due to torsion.
What will you look for to identify the sex of the following? [2011]- a)Female Ascaris- Sharply curved posterior end
- b)Male frog- A copulatory pad on the first digit of the hind limb
- c)Female cockroach-Anal cerci
- d)Male shark-Claspers borne on pelvic fins
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What will you look for to identify the sex of the following? [2011]
a)
Female Ascaris- Sharply curved posterior end
b)
Male frog- A copulatory pad on the first digit of the hind limb
c)
Female cockroach-Anal cerci
d)
Male shark-Claspers borne on pelvic fins

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
A male shark possesses a pair of claspers which are inserted into a female shark’s cloaca (an opening on the underside of the body) at the time of mating. Claspers are located on the inner edge of the pelvic fins near the male’s cloaca. The function of claspers is to introduce sperm into a female shark’s body for the purpose of fertilizing her eggs. Female sharks do not have claspers.
Chapter doubts & questions for Animal Kingdom - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Animal Kingdom - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










