All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Human Reproduction for NEET Exam
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between______.- a)Basal lamina
- b)Seminiferous tubules
- c)Tubuli recti
- d)Sertoli cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between______.
a)
Basal lamina
b)
Seminiferous tubules
c)
Tubuli recti
d)
Sertoli cells
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Interstitial cells or leydig cells are present between seminiferous tubules..they secrete androgens..mainly testosterone
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
- A:
Lactogen
- B:
Primary milk
- C:
Colostrum
- D:
None of these
The answer is c.
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
Lactogen
Primary milk
Colostrum
None of these
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Colostrum is a thick and sticky, yellow to orange colored milk that is created by your breasts to give your baby the nutrition he needs immediately after birth. It is low in fat, high in carbohydrates and has a laxative effect on the baby which helps him pass the first meconium stools that are sitting in his intestines. This also helps get rid of the bile and helps lessen the chance of jaundice in your newborn.
Ovulation occurs on the ------ day of menstrual cycle. - a)08-10
- b)12-14
- c)14-16
- d)16-18
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ovulation occurs on the ------ day of menstrual cycle.
a)
08-10
b)
12-14
c)
14-16
d)
16-18

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
The release of ovum from ovary during menstrual cycle is is called ovulation. Ovulation occurs in the middle of menstrual cycle that is on 14-16th day of start of menstrual cycle.
The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again is _______.
- a)Dermis of skin
- b)Endometrium of uterus
- c)Cornea of eye
- d)Endometrium of blood vessels
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cellular layer that disintegrates and regenerates again and again is _______.
a)
Dermis of skin
b)
Endometrium of uterus
c)
Cornea of eye
d)
Endometrium of blood vessels

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
- The functional layer of the human endometrium is a highly regenerative tissue undergoing monthly cycles of growth, differentiation, and shedding during a woman's reproductive years.
- Fluctuating levels of circulating estrogen and progesterone orchestrate this dramatic remodelling of human endometrium.
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: topic “MENSTRUAL CYCLE” of chapter: Human Reproduction.
NCERT Reference: topic “MENSTRUAL CYCLE” of chapter: Human Reproduction.
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is:
- a)Progesterone
- b)vasopressin
- c)Estrogens
- d)Oxytocin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is:
a)
Progesterone
b)
vasopressin
c)
Estrogens
d)
Oxytocin
|
|
Naina Choudhary answered |
Hormone responsible for milk ejection after the birth of baby is oxytocin.
Explanation:
After the birth of a baby, the mother's body undergoes various hormonal changes that promote milk production and ejection. The primary hormone responsible for milk ejection is oxytocin, which is produced in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
When a baby suckles at the breast, nerve endings in the nipple and areola are stimulated, which triggers the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin then causes the smooth muscle cells in the milk ducts to contract, which pushes the milk out of the breast and into the baby's mouth. This process is known as the milk ejection reflex or let-down reflex.
Other hormones that are involved in milk production and ejection include:
- Prolactin: This hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- Estrogens: These hormones are produced in the ovaries and play a role in breast development and milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced in the ovaries and plays a role in preparing the breast for milk production.
However, in terms of milk ejection specifically, oxytocin is the primary hormone involved.
Explanation:
After the birth of a baby, the mother's body undergoes various hormonal changes that promote milk production and ejection. The primary hormone responsible for milk ejection is oxytocin, which is produced in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
When a baby suckles at the breast, nerve endings in the nipple and areola are stimulated, which triggers the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin then causes the smooth muscle cells in the milk ducts to contract, which pushes the milk out of the breast and into the baby's mouth. This process is known as the milk ejection reflex or let-down reflex.
Other hormones that are involved in milk production and ejection include:
- Prolactin: This hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates milk production in the mammary glands.
- Estrogens: These hormones are produced in the ovaries and play a role in breast development and milk production.
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced in the ovaries and plays a role in preparing the breast for milk production.
However, in terms of milk ejection specifically, oxytocin is the primary hormone involved.
The number of polar bodies formed during oogenesis in human being is:
- a)2
- b)3
- c)1
- d)Both 2 and 3.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of polar bodies formed during oogenesis in human being is:
a)
2
b)
3
c)
1
d)
Both 2 and 3.
|
|
Raj Yadav answered |
Polar bodies formed during oogenesis in humans
- During human oogenesis, three polar bodies are created.
- Polar bodies are tiny cytoplasmic exclusion structures that form to contain extra DNA produced during oocyte meiosis, which occurs after sperm fertilization.
- The zygote contains roughly 2-3 polar bodies, which are derived from the oocyte.
- This figure is determined by whether or not the first polar body (produced during meiosis I) splits during meiosis II.
- Excess DNA generated from reductive division makes up such an exclusion body (2nd and 3rd polar bodies are formed from meiosis II at the time of fertilization).
- Such polar bodies do not contribute to the zygote's, foetus', or embryo's future genetic complement.
Which of the following hormone is produced in female only during pregnancy?
- a)Testosterone
- b)Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG).
- c)Progesterone
- d)Estrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormone is produced in female only during pregnancy?
a)
Testosterone
b)
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG).
c)
Progesterone
d)
Estrogen
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
- It is made almost exclusively in the placenta.
- hCG hormone levels found in the mother's blood and urine, rise a lot during the first trimester.
- hCG Maintains the corpus luteum throughout the early stages of pregnancy. It is used to detect pregnancy.
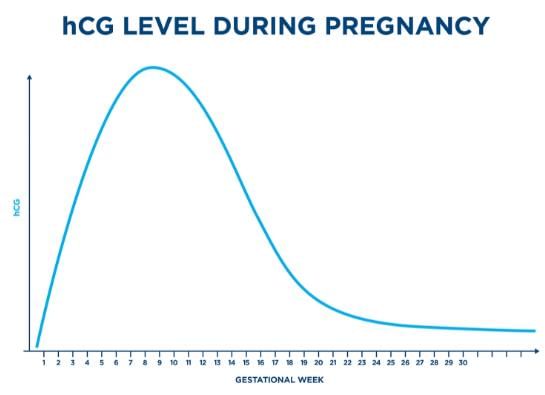
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 53 of topic “3.6 PREGNANCY AND EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT” of chapter 3.
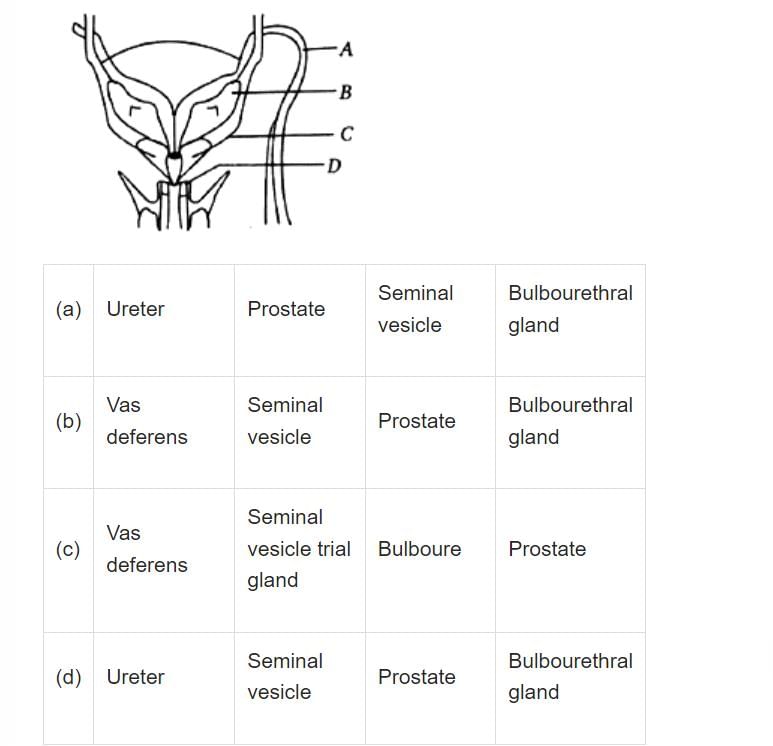
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland- a)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
a)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Kiran Singh answered |
Contributors to Seminal Plasma
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen that carries sperm. It is composed of a mixture of secretions from various male reproductive organs. The following are the contributors of seminal plasma:
(i) Seminal Vesicle - The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands that secrete a fluid that makes up 60-70% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains fructose, prostaglandins, and other substances that provide energy to the sperm and help them survive in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Prostate - The prostate gland is a single gland located below the bladder that produces a milky fluid that makes up about 15-30% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains enzymes, citric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation.
(iii) Urethra - The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and carries semen and urine out of the body. It contributes a small amount of fluid to the seminal plasma.
(iv) Bulbourethral Gland - The bulbourethral gland, also known as Cowper's gland, is a pair of small glands located at the base of the penis. They secrete a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidic urine remaining in the urethra.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seminal plasma is a mixture of secretions from different male reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, and bulbourethral gland. The various secretions work together to provide energy to the sperm, help them survive in the female reproductive tract, and ensure that the semen can be ejaculated and transported effectively.
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen that carries sperm. It is composed of a mixture of secretions from various male reproductive organs. The following are the contributors of seminal plasma:
(i) Seminal Vesicle - The seminal vesicle is a pair of glands that secrete a fluid that makes up 60-70% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains fructose, prostaglandins, and other substances that provide energy to the sperm and help them survive in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Prostate - The prostate gland is a single gland located below the bladder that produces a milky fluid that makes up about 15-30% of the volume of semen. The fluid contains enzymes, citric acid, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation.
(iii) Urethra - The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis and carries semen and urine out of the body. It contributes a small amount of fluid to the seminal plasma.
(iv) Bulbourethral Gland - The bulbourethral gland, also known as Cowper's gland, is a pair of small glands located at the base of the penis. They secrete a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the urethra and neutralize any acidic urine remaining in the urethra.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seminal plasma is a mixture of secretions from different male reproductive organs, including the seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, and bulbourethral gland. The various secretions work together to provide energy to the sperm, help them survive in the female reproductive tract, and ensure that the semen can be ejaculated and transported effectively.
During which month of pregnancy first movement of fetus is observed?- a)Sixth month
- b)Fourth month
- c)Fifth month
- d)Third month
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During which month of pregnancy first movement of fetus is observed?
a)
Sixth month
b)
Fourth month
c)
Fifth month
d)
Third month
|
|
Saranya Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option C, i.e., fifth month.
Explanation:
The first movement of the fetus is called quickening. It is the first noticeable movement of the fetus by the mother. Quickening is the first sign that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. It usually occurs between the 16th and 25th weeks of pregnancy. However, it is most commonly felt around the 20th week of pregnancy, which is the fifth month.
During the first trimester, the fetus is too small and underdeveloped to produce movements that can be felt by the mother. The fetal movements at this stage are mostly uncoordinated and involuntary.
During the second trimester, the fetus grows and becomes more active. The movements become more coordinated and frequent. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound. The movements of the fetus become more pronounced and can be felt by the mother.
In summary, the first movement of the fetus can be observed in the fifth month of pregnancy, which is around the 20th week.
Explanation:
The first movement of the fetus is called quickening. It is the first noticeable movement of the fetus by the mother. Quickening is the first sign that the pregnancy is progressing as expected. It usually occurs between the 16th and 25th weeks of pregnancy. However, it is most commonly felt around the 20th week of pregnancy, which is the fifth month.
During the first trimester, the fetus is too small and underdeveloped to produce movements that can be felt by the mother. The fetal movements at this stage are mostly uncoordinated and involuntary.
During the second trimester, the fetus grows and becomes more active. The movements become more coordinated and frequent. By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs around 1 pound. The movements of the fetus become more pronounced and can be felt by the mother.
In summary, the first movement of the fetus can be observed in the fifth month of pregnancy, which is around the 20th week.
Beginning of menstrual cycle is called as ___.- a)Ovulation
- b)Oogenesis
- c)Menarche
- d)Menopause
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Beginning of menstrual cycle is called as ___.
a)
Ovulation
b)
Oogenesis
c)
Menarche
d)
Menopause
|
|
NEET Aspirant 2021 answered |
The first menstrual period occurs after the onset of pubertal growth, and is called menarche.
so the correct answer is option c) Menarche
so the correct answer is option c) Menarche
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Each testis has about 250 compartment called as____.
- A:
Oogonia
- B:
Seminiferous tubules
- C:
Lactiferous lobules
- D:
Testicular lobules
The answer is d.
Each testis has about 250 compartment called as____.
Oogonia
Seminiferous tubules
Lactiferous lobules
Testicular lobules

|
Pooja Pillai answered |
Each testis contains about 250 compartments called testicular lobules. Each testicular lobule contains one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules that produce sperms.
Which of the following arise from endoderm?- a)Eye
- b)Heart
- c)Pigment cells
- d)Lungs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following arise from endoderm?
a)
Eye
b)
Heart
c)
Pigment cells
d)
Lungs
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Ectoderm is the germ layer that develops primarily into skin and neural tissue. Mesoderm primarily develops into muscle tissues and red blood cells. Endoderm develops into many of the internal organs including the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, and endocrine system.
Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as- a)chorion
- b)zona pellucida
- c)corona radiata
- d)vitelline membrane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as
a)
chorion
b)
zona pellucida
c)
corona radiata
d)
vitelline membrane
|
|
Navya Tiwari answered |
The mammalian egg is covered by a series of membranes that protect it and aid in fertilization. Immediately after ovulation, the egg is surrounded by a membrane known as the zona pellucida.
Explanation:
Zona Pellucida:
- The zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer that forms around the mammalian egg immediately after ovulation.
- It is secreted by the egg as it travels through the oviduct towards the uterus.
- The zona pellucida is composed of three layers: an outer layer, a middle layer, and an inner layer.
- The outer layer is the thinnest and is composed of glycoproteins that help to bind sperm to the zona pellucida.
- The middle layer is the thickest and is composed of a matrix of glycoproteins and proteoglycans.
- The inner layer is the thinnest and is composed of glycoproteins that are involved in the sperm-binding process.
Functions of the Zona Pellucida:
- The zona pellucida plays a key role in fertilization, as it is the first barrier that sperm must penetrate in order to reach the egg.
- The glycoproteins on the surface of the zona pellucida bind to specific receptors on the surface of sperm, allowing them to attach and begin the process of fertilization.
- Once sperm have attached to the zona pellucida, they release enzymes that help to dissolve the outer layer, allowing them to penetrate to the egg.
Other Membranes Surrounding the Egg:
- In addition to the zona pellucida, the mammalian egg is also surrounded by a layer of follicle cells called the corona radiata.
- The corona radiata is composed of cells that have surrounded the egg within the follicle and are released along with the egg during ovulation.
- The corona radiata provides additional protection to the egg and helps to guide sperm towards the zona pellucida.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as the zona pellucida. This glycoprotein layer plays a key role in fertilization by allowing sperm to bind to its surface and penetrate to the egg. The corona radiata, another layer of follicle cells, also surrounds the egg and provides additional protection during fertilization.
Explanation:
Zona Pellucida:
- The zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer that forms around the mammalian egg immediately after ovulation.
- It is secreted by the egg as it travels through the oviduct towards the uterus.
- The zona pellucida is composed of three layers: an outer layer, a middle layer, and an inner layer.
- The outer layer is the thinnest and is composed of glycoproteins that help to bind sperm to the zona pellucida.
- The middle layer is the thickest and is composed of a matrix of glycoproteins and proteoglycans.
- The inner layer is the thinnest and is composed of glycoproteins that are involved in the sperm-binding process.
Functions of the Zona Pellucida:
- The zona pellucida plays a key role in fertilization, as it is the first barrier that sperm must penetrate in order to reach the egg.
- The glycoproteins on the surface of the zona pellucida bind to specific receptors on the surface of sperm, allowing them to attach and begin the process of fertilization.
- Once sperm have attached to the zona pellucida, they release enzymes that help to dissolve the outer layer, allowing them to penetrate to the egg.
Other Membranes Surrounding the Egg:
- In addition to the zona pellucida, the mammalian egg is also surrounded by a layer of follicle cells called the corona radiata.
- The corona radiata is composed of cells that have surrounded the egg within the follicle and are released along with the egg during ovulation.
- The corona radiata provides additional protection to the egg and helps to guide sperm towards the zona pellucida.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, immediately after ovulation, the mammalian egg is covered by a membrane known as the zona pellucida. This glycoprotein layer plays a key role in fertilization by allowing sperm to bind to its surface and penetrate to the egg. The corona radiata, another layer of follicle cells, also surrounds the egg and provides additional protection during fertilization.
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in_____.- a)Fructose and Calcium
- b)Ribose and Potassium
- c)DNA and testosterone
- d)Glucose and Calcium
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in_____.
a)
Fructose and Calcium
b)
Ribose and Potassium
c)
DNA and testosterone
d)
Glucose and Calcium
|
|
Rahul answered |
The male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate and paired bulbourethral gland. Secretions of these glands constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in Fructose calcium and certain enzymes
Enzyme for fertilization present in -- a)Acrosome of Sperm
- b)Nucleus of Sperm
- c)Tail of Sperm
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzyme for fertilization present in -
a)
Acrosome of Sperm
b)
Nucleus of Sperm
c)
Tail of Sperm
d)
None
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
In Eutherian mammals the acrosome contains degradative enzymes (including hyaluronidase and acrosin). These enzymes break down the outer membrane of the ovum, called the zona pellucida, allowing the haploid nucleus in the sperm cell to join with the haploid nucleus in the ovum.
So, correct answer is "Acrosome of sperm".
In which part of sperm, mitochondria are present?- a)Head
- b)Middle piece
- c)Tail
- d)Neck
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which part of sperm, mitochondria are present?
a)
Head
b)
Middle piece
c)
Tail
d)
Neck
|
|
Jaya Chavan answered |
Mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Explanation:
The sperm is composed of three parts: head, middle piece, and tail.
1. Head:
The head of the sperm contains the nucleus which carries genetic material in the form of DNA.
2. Middle piece:
The middle piece of the sperm contains a large number of mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the movement of the sperm.
3. Tail:
The tail of the sperm is also known as the flagellum. It provides motility to the sperm and helps in the movement towards the egg.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' that mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Explanation:
The sperm is composed of three parts: head, middle piece, and tail.
1. Head:
The head of the sperm contains the nucleus which carries genetic material in the form of DNA.
2. Middle piece:
The middle piece of the sperm contains a large number of mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the movement of the sperm.
3. Tail:
The tail of the sperm is also known as the flagellum. It provides motility to the sperm and helps in the movement towards the egg.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' that mitochondria are present in the middle piece of the sperm.
Fixing up of blastocyst in the wall of the uterus is- a)Impregnation
- b)Placentation
- c)Implantation
- d)Fertilization
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fixing up of blastocyst in the wall of the uterus is
a)
Impregnation
b)
Placentation
c)
Implantation
d)
Fertilization
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The fixing of the blastocyst in the wall of the uterus is known as implantation. The implantation takes place after seven days of fertilization.
`
Acrosome is filled with _________.- a)Lipids
- b)Hormones
- c)Enzymes
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Acrosome is filled with _________.
a)
Lipids
b)
Hormones
c)
Enzymes
d)
None of the above
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- The head of mature mammalian sperm is made of elongated nucleus covered by acrosome.
- The acrosome is filled with hydrolytic enzymes that help in fertilization of ovum.
- These enzymes called sperm lysins that dissolve the membranes enveloping the ovum and help the sperm cell to enter the ovum by penetrating egg membrane.
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. This is necessary as:- a)The scrotum can contain lengthy ducts for the transfer of sperms
- b)Scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes necessary for spermatogenesis
- c)Scrotum reduces the pressure around testes necessary for spermatogenesis
- d)Scrotum can store huge amounts of sperms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. This is necessary as:
a)
The scrotum can contain lengthy ducts for the transfer of sperms
b)
Scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes necessary for spermatogenesis
c)
Scrotum reduces the pressure around testes necessary for spermatogenesis
d)
Scrotum can store huge amounts of sperms
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum. The scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes (2-2.5°C lower than the normal internal body temperature) necessary for spermatogenesis.
Hence, the Correct Answer is B
NCERT Reference: page no. 43 topic “3.1 THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ” of chapter 3 of NCERT
In human females, meiosis-ll is not completed until?
- a)Puberty
- b)Fertilisation
- c)Uterine implantation
- d)Birth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In human females, meiosis-ll is not completed until?
a)
Puberty
b)
Fertilisation
c)
Uterine implantation
d)
Birth
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
- At the end of meiosis I females have two daughter cells and meiosis II only occurs if and when the fertilization occurs by the sperm cell.
- Meiosis II starts after the sperm proceeds fertilization process in female
- Meiosis II starts after the sperm proceeds fertilization process in female

Sertoli cells present in the testis act as _____.- a)Germ cell
- b)Nurse cell
- c)Protective cell
- d)Receptor cell
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sertoli cells present in the testis act as _____.
a)
Germ cell
b)
Nurse cell
c)
Protective cell
d)
Receptor cell
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Nurse cells are specialized macrophages residing in the bone marrow that assist in the development of red blood cells. They absorb the nuclei of immature red blood cells and may provide growth factors to help the red blood cells mature.
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland- a)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen is contributed by:
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
(i) Seminal vesicle
(ii) Prostate
(iii) Urethra
(iv) Bulbourethral gland
a)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)

|
Sravya Datta answered |
The male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostate and paired bulb urethral glands. Secretions of these glands constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes. The secretions of bulbourethral glands also helps in the lubrication of the penis. Urethra is the duct that extends through the penis in male reproductive system and serve a common passage for both sperm and urine. In female, urethra has no reproductive function.
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the placenta?
A. Human chorionic gonadotropin
B. Chorionic thyrotropin
C. Estrogen
D. Progesterone- a)A only
- b)A & B
- c)A, B & C
- d)A, B, C & D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A. Human chorionic gonadotropin
B. Chorionic thyrotropin
C. Estrogen
D. Progesterone
a)
A only
b)
A & B
c)
A, B & C
d)
A, B, C & D
|
|
Krithika Sharma answered |
Introduction
The placenta plays a crucial role in pregnancy by producing various hormones that support fetal development and maintain the pregnancy. The hormones secreted by the placenta include:
1. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- hCG is one of the first hormones produced by the placenta.
- It helps maintain the corpus luteum, which in turn produces progesterone during early pregnancy.
- hCG is also the hormone detected in pregnancy tests.
2. Chorionic Thyrotropin
- Chorionic thyrotropin, also known as human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), is involved in stimulating the thyroid gland.
- It helps increase the production of thyroid hormones, which are essential for the metabolism and development of both the mother and the fetus.
3. Estrogen
- The placenta produces significant amounts of estrogen, particularly estriol.
- Estrogen plays a vital role in the growth and development of the uterus and breast tissues.
- It also helps regulate other hormones and supports fetal development.
4. Progesterone
- Progesterone is another critical hormone secreted by the placenta.
- It maintains the uterine lining, allowing for implantation and growth of the embryo.
- Progesterone also helps suppress maternal immune responses to prevent rejection of the fetus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the placenta secretes all four hormones: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, Chorionic Thyrotropin, Estrogen, and Progesterone. Each of these hormones plays a significant role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and supporting fetal growth, making option 'D' the correct answer.
The placenta plays a crucial role in pregnancy by producing various hormones that support fetal development and maintain the pregnancy. The hormones secreted by the placenta include:
1. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- hCG is one of the first hormones produced by the placenta.
- It helps maintain the corpus luteum, which in turn produces progesterone during early pregnancy.
- hCG is also the hormone detected in pregnancy tests.
2. Chorionic Thyrotropin
- Chorionic thyrotropin, also known as human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), is involved in stimulating the thyroid gland.
- It helps increase the production of thyroid hormones, which are essential for the metabolism and development of both the mother and the fetus.
3. Estrogen
- The placenta produces significant amounts of estrogen, particularly estriol.
- Estrogen plays a vital role in the growth and development of the uterus and breast tissues.
- It also helps regulate other hormones and supports fetal development.
4. Progesterone
- Progesterone is another critical hormone secreted by the placenta.
- It maintains the uterine lining, allowing for implantation and growth of the embryo.
- Progesterone also helps suppress maternal immune responses to prevent rejection of the fetus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the placenta secretes all four hormones: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, Chorionic Thyrotropin, Estrogen, and Progesterone. Each of these hormones plays a significant role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and supporting fetal growth, making option 'D' the correct answer.
Select the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups:- a)Primary oocyte, Secondary oocyte, Spermatid
- b)Secondary spermatocyte, First polar body, Ovum
- c)Spermatogonia, Primary spermatocyte, Spermatid
- d)Primary spermatocyte, Secondary spermatocyte, Second polar body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups:
a)
Primary oocyte, Secondary oocyte, Spermatid
b)
Secondary spermatocyte, First polar body, Ovum
c)
Spermatogonia, Primary spermatocyte, Spermatid
d)
Primary spermatocyte, Secondary spermatocyte, Second polar body
|
|
Sakshi Yadav answered |
Haploid Cells in Meiosis
In meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes, haploid cells are formed through two rounds of division. Each round of division involves a reduction in the number of chromosomes from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
Option B is the correct answer because all three cells listed are haploid:
- Secondary spermatocyte: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the male reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary spermatocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n) instead of 46 (2n).
- First polar body: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
- Ovum: This cell is formed during meiosis II in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a secondary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
Options A, C, and D are incorrect because they include cells that are not haploid:
- Primary oocyte and secondary oocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they have not yet undergone meiosis I.
- Spermatogonia and primary spermatocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they are in the early stages of meiosis in the male reproductive system.
- Spermatid, secondary spermatocyte, and second polar body: These cells are haploid, but they are not all present in the same stage of meiosis. Spermatids are formed during meiosis II in the male reproductive system, while secondary spermatocytes and second polar bodies are formed during meiosis I in the male and female reproductive systems, respectively.
In meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes, haploid cells are formed through two rounds of division. Each round of division involves a reduction in the number of chromosomes from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
Option B is the correct answer because all three cells listed are haploid:
- Secondary spermatocyte: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the male reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary spermatocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n) instead of 46 (2n).
- First polar body: This cell is formed during meiosis I in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a primary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
- Ovum: This cell is formed during meiosis II in the female reproductive system. It is the result of the division of a secondary oocyte and contains 23 chromosomes (n).
Options A, C, and D are incorrect because they include cells that are not haploid:
- Primary oocyte and secondary oocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they have not yet undergone meiosis I.
- Spermatogonia and primary spermatocyte: These cells are both diploid (2n) because they are in the early stages of meiosis in the male reproductive system.
- Spermatid, secondary spermatocyte, and second polar body: These cells are haploid, but they are not all present in the same stage of meiosis. Spermatids are formed during meiosis II in the male reproductive system, while secondary spermatocytes and second polar bodies are formed during meiosis I in the male and female reproductive systems, respectively.
The ligaments help the ovaries to be in place by:- a)Forming a connection with the pelvic wall and uterine wall
- b)Forming a connection with the pelvic wall
- c)Forming a connection with the uterine wall
- d)Forming a connection with the ovarian walls
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Forming a connection with the pelvic wall and uterine wall
b)
Forming a connection with the pelvic wall
c)
Forming a connection with the uterine wall
d)
Forming a connection with the ovarian walls

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The ligaments that support the ovaries help to keep them in place by forming connections with both the pelvic wall and the uterine wall. These ligaments ensure that the ovaries remain properly positioned within the female reproductive system.
Corpus luteum is- a)Outer part of the brain
- b)Tissue joining two cerebral hemispheres
- c)Remnant of the follicle in the ovary
- d)Tissue in testes to produce testosterone E Inner part of the brain
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Corpus luteum is
a)
Outer part of the brain
b)
Tissue joining two cerebral hemispheres
c)
Remnant of the follicle in the ovary
d)
Tissue in testes to produce testosterone E Inner part of the brain
|
|
Pavya Sree answered |
Corpus leutem is formed during the leutal phase or secretary phase.This is formed after the rupture of graffin follicle & eliminating the ova. During the leutal phase , corpus leutem secret the progesteron which induce the uterine gland to produce watery mucus.. And also, if fertilization is not happened, then it leave a scar called corpus albican.
The body of sperm is covered by _______- a)Cell membrane
- b)Head
- c)Cell wall
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The body of sperm is covered by _______
a)
Cell membrane
b)
Head
c)
Cell wall
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Anastasia Orlova answered |
The entire body of the sperm is covered by a plasma membrane. The head consists of a cap-like structure called the acrosome which contains digestive enzymes that help in the fertilization of the ovum.
The number of egg cells produced as a result of meiosis in humans is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of egg cells produced as a result of meiosis in humans is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
Primary oocyte undergoes first meiotic division to produce one secondary oocyte (egg cell) and first polar body (nonfunctional cell). Secondary oocyte completes meiosis II and produces one functional ovum and second polar body. First and second polar bodies are nonfunctional cells; so, oogenesis produce one functional egg cell in each round. Thus, the correct answer is 'A'.
All of the following are true of gametes except- a)They contain a haploid set of chromosomes.
- b)They are produced through the process of mitosis.
- c)They are produced in gonads such as testicles and ovaries.
- d)They undergo two sets of cell divisions.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following are true of gametes except
a)
They contain a haploid set of chromosomes.
b)
They are produced through the process of mitosis.
c)
They are produced in gonads such as testicles and ovaries.
d)
They undergo two sets of cell divisions.

|
Anushka Sharma answered |
Gamete are produced by the process of 1st: mitosis, which is an equational division and after that it undergoes meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 which is reductional devision so, if I sum this up.. gamete are produced by the process of meiosis and not mitosis.
you can also check this in class 11th biology book in cell division chapter
you can also check this in class 11th biology book in cell division chapter
A human female is born with a million of eggs(primary oocyte) at the time of birth, only some 500 eggs get a chance of maturity. What is the destiny of rest of the eggs?- a)Rest of the eggs differentiate back to thecal and granulosa cells
- b)Rest of the eggs nurture the dominant follicular cell
- c)Rest of the eggs move out of the ovary and are destroyed by leucocytes
- d)Rest of the eggs break down and are absorbed i.e., degenerative follicular atresia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A human female is born with a million of eggs(primary oocyte) at the time of birth, only some 500 eggs get a chance of maturity. What is the destiny of rest of the eggs?
a)
Rest of the eggs differentiate back to thecal and granulosa cells
b)
Rest of the eggs nurture the dominant follicular cell
c)
Rest of the eggs move out of the ovary and are destroyed by leucocytes
d)
Rest of the eggs break down and are absorbed i.e., degenerative follicular atresia
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The total number of follicles in two ovaries of a normal young adult woman is about four lakhs but only about 500 eggs reach maturity because many ovarian follicles (during primary oocyte stage) undergo degeneration. This degenerative process of follicles is called follicular atresia and such follicles are known as atretic follicles.
The secondary sexual characters develop in females because of:- a)estrogen
- b)androgens
- c)absence of androgens
- d)absence of estrogens
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The secondary sexual characters develop in females because of:
a)
estrogen
b)
androgens
c)
absence of androgens
d)
absence of estrogens
|
|
Bhaskar Yadav answered |
The Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics in Females
Introduction
Secondary sexual characteristics are physical traits that develop during puberty and distinguish males from females. In females, these characteristics include the growth and development of breasts, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, and the onset of menstruation. The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen.
Explanation
Estrogen is a primary female sex hormone that plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of female reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. It is produced primarily by the ovaries, although small amounts are also produced by the adrenal glands and fat cells.
Role of Estrogen in the Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Estrogen is responsible for the development of several secondary sexual characteristics in females, including:
1. Breast Development: Estrogen stimulates the growth and development of breast tissue. It promotes the accumulation of fat in the breasts and increases the size and number of mammary glands.
2. Widening of Hips: Estrogen influences the deposition of fat in the hip and thigh regions, leading to an increase in hip width. This contributes to the characteristic feminine body shape.
3. Changes in Body Fat Distribution: Estrogen influences the distribution of body fat, causing it to be stored more in the breasts, hips, and thighs rather than the abdominal region. This leads to a more curvaceous and feminine body shape.
4. Onset of Menstruation: Estrogen plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of the reproductive system, including the uterus and ovaries. It triggers the release of hormones that initiate the menstrual cycle.
5. Softening of Skin: Estrogen contributes to the softness and smoothness of female skin. It promotes the production of collagen, which helps maintain the elasticity and hydration of the skin.
6. Development of Female Reproductive Organs: Estrogen is involved in the growth and development of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina. It helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
Conclusion
The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen. Estrogen is responsible for breast development, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, the onset of menstruation, softening of skin, and the development of female reproductive organs. Without estrogen, these characteristics would not develop fully, and the individual would not exhibit the typical traits associated with femininity.
Note: Estrogen levels can vary among individuals, and some individuals may have conditions or disorders that affect estrogen production or response, resulting in variations in the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Introduction
Secondary sexual characteristics are physical traits that develop during puberty and distinguish males from females. In females, these characteristics include the growth and development of breasts, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, and the onset of menstruation. The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen.
Explanation
Estrogen is a primary female sex hormone that plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of female reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. It is produced primarily by the ovaries, although small amounts are also produced by the adrenal glands and fat cells.
Role of Estrogen in the Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Estrogen is responsible for the development of several secondary sexual characteristics in females, including:
1. Breast Development: Estrogen stimulates the growth and development of breast tissue. It promotes the accumulation of fat in the breasts and increases the size and number of mammary glands.
2. Widening of Hips: Estrogen influences the deposition of fat in the hip and thigh regions, leading to an increase in hip width. This contributes to the characteristic feminine body shape.
3. Changes in Body Fat Distribution: Estrogen influences the distribution of body fat, causing it to be stored more in the breasts, hips, and thighs rather than the abdominal region. This leads to a more curvaceous and feminine body shape.
4. Onset of Menstruation: Estrogen plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of the reproductive system, including the uterus and ovaries. It triggers the release of hormones that initiate the menstrual cycle.
5. Softening of Skin: Estrogen contributes to the softness and smoothness of female skin. It promotes the production of collagen, which helps maintain the elasticity and hydration of the skin.
6. Development of Female Reproductive Organs: Estrogen is involved in the growth and development of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina. It helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
Conclusion
The development of secondary sexual characteristics in females is primarily driven by the hormone estrogen. Estrogen is responsible for breast development, widening of hips, changes in body fat distribution, the onset of menstruation, softening of skin, and the development of female reproductive organs. Without estrogen, these characteristics would not develop fully, and the individual would not exhibit the typical traits associated with femininity.
Note: Estrogen levels can vary among individuals, and some individuals may have conditions or disorders that affect estrogen production or response, resulting in variations in the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
The signals for parturition originate from- a)Placenta only
- b)Placenta as well as the fully developed foetus
- c)Oxytocin released from maternal pituitary
- d)Fully developed foetus only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The signals for parturition originate from
a)
Placenta only
b)
Placenta as well as the fully developed foetus
c)
Oxytocin released from maternal pituitary
d)
Fully developed foetus only
|
|
Avesh Sharma answered |
Placenta and fully developed foetus sending signals for parturition to pituitary gland...
option B
option B
Which of the following is the correct number of chromosomes based on the cell type?- a)Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 23
- b)Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 46
- c)Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 46
- d)Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 23
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct number of chromosomes based on the cell type?
a)
Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 23
b)
Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 46
c)
Sperm: 23; Egg: 23; Zygote: 46
d)
Sperm: 46; Egg: 46; Zygote: 23

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Sperm and egg are haploid cells hence have only one set of chromosomes.
- Zygote on the other hand is diploid thus has 46 chromosomes.
Below is given the unorganised list of some important events in the human female reproductive cycle. Identify the correct sequence of these events and select the correct option.
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
- a)(i)→(iv)→(iii)→(v)→(ii)
- b)(ii)→(i)→(iii)→(iv)→(v)
- c)(iii)→(i)→(iv)→(ii)→(v)
- d)(i)→(iii)→(v)→(iv)→(ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Below is given the unorganised list of some important events in the human female reproductive cycle. Identify the correct sequence of these events and select the correct option.
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
(i) Secretion of FSH
(ii) Growth of corpus luteum
(iii) Growth of the follicle
(iv) Ovulation
(v) Sudden increase in the levels of LH
a)
(i)→(iv)→(iii)→(v)→(ii)
b)
(ii)→(i)→(iii)→(iv)→(v)
c)
(iii)→(i)→(iv)→(ii)→(v)
d)
(i)→(iii)→(v)→(iv)→(ii)
|
|
Akash Menon answered |
(iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii)
Explanation:
The sequence of events in the human female reproductive cycle is as follows:
1. Secretion of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland
2. Growth of the follicle in the ovary
3. Ovulation, where the mature egg is released from the ovary
4. Growth of the corpus luteum, which is the remains of the follicle after ovulation
5. Sudden increase in the levels of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) which triggers ovulation
Therefore, the correct sequence of events is (iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii).
Explanation:
The sequence of events in the human female reproductive cycle is as follows:
1. Secretion of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland
2. Growth of the follicle in the ovary
3. Ovulation, where the mature egg is released from the ovary
4. Growth of the corpus luteum, which is the remains of the follicle after ovulation
5. Sudden increase in the levels of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) which triggers ovulation
Therefore, the correct sequence of events is (iii) - (i) - (iv) - (ii).
The nutritive cells found in seminiferous tubules are- a)Leydig's cells
- b)atretic follicular cells
- c)Sertoli cells
- d)chromaffin cells.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The nutritive cells found in seminiferous tubules are
a)
Leydig's cells
b)
atretic follicular cells
c)
Sertoli cells
d)
chromaffin cells.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Wall of each seminiferous tubule is formed of a single layered germinal epithelium. Majority of cells in this epithelium are male germ cells and at centain places, there are persent tall Sertoli cells. These cells act as nurse cells providing nutrition to the developing sperms.
What layer of egg cell prevents entry of other sperms?- a)Corpus luteum
- b)Zona pellucida
- c)Endometrium
- d)Corona radiata
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What layer of egg cell prevents entry of other sperms?
a)
Corpus luteum
b)
Zona pellucida
c)
Endometrium
d)
Corona radiata
|
|
Baishali Joshi answered |
Explanation:
The process of fertilization involves the fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell. However, only one sperm can fertilize an egg cell. If more than one sperm fertilizes an egg cell, it can result in a genetic abnormality which is non-viable for development. Therefore, the entry of other sperms needs to be prevented. This is achieved by the presence of the zona pellucida layer in the egg cell.
Zona Pellucida:
The zona pellucida is a thick glycoprotein layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of the mammalian oocyte. It is formed after the egg is released from the ovary and helps maintain the shape of the egg cell. It also plays a vital role in fertilization by preventing the entry of other sperm cells.
Prevents Entry of Other Sperms:
When a sperm cell approaches an egg cell, it releases enzymes that break down the outer layer of the zona pellucida. This allows the sperm to bind to the egg cell and fuse with it, resulting in fertilization. However, once a sperm has penetrated the zona pellucida and fused with the egg cell, the zona pellucida becomes impenetrable to other sperm cells. This is because the zona pellucida undergoes a biochemical change that makes it resistant to the penetration of other sperm cells.
Therefore, the zona pellucida layer of the egg cell prevents the entry of other sperm cells. This ensures that only one sperm fertilizes the egg cell, and the genetic material from both parents is mixed in the correct amount to produce a viable offspring.
The process of fertilization involves the fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell. However, only one sperm can fertilize an egg cell. If more than one sperm fertilizes an egg cell, it can result in a genetic abnormality which is non-viable for development. Therefore, the entry of other sperms needs to be prevented. This is achieved by the presence of the zona pellucida layer in the egg cell.
Zona Pellucida:
The zona pellucida is a thick glycoprotein layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of the mammalian oocyte. It is formed after the egg is released from the ovary and helps maintain the shape of the egg cell. It also plays a vital role in fertilization by preventing the entry of other sperm cells.
Prevents Entry of Other Sperms:
When a sperm cell approaches an egg cell, it releases enzymes that break down the outer layer of the zona pellucida. This allows the sperm to bind to the egg cell and fuse with it, resulting in fertilization. However, once a sperm has penetrated the zona pellucida and fused with the egg cell, the zona pellucida becomes impenetrable to other sperm cells. This is because the zona pellucida undergoes a biochemical change that makes it resistant to the penetration of other sperm cells.
Therefore, the zona pellucida layer of the egg cell prevents the entry of other sperm cells. This ensures that only one sperm fertilizes the egg cell, and the genetic material from both parents is mixed in the correct amount to produce a viable offspring.
Which one is correct for mammalian testis?- a)Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells
- b)Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells and Seminiferous tubules
- c)Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells
- d)Graffian follicles, Leydig's cells and Seminiferous tubules
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is correct for mammalian testis?
a)
Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells
b)
Graffian follicles, Sertoli cells and Seminiferous tubules
c)
Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules, Leydig cells
d)
Graffian follicles, Leydig's cells and Seminiferous tubules
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Graafian follicles are present in human ovaries.
Leydig cells:- a)Are present in seminiferous tubules and secrete androgens
- b)Are present in seminiferous tubules and help in maturation of sperms
- c)Are present in interstitial space and secrete androgens
- d)Are present in interstitial space and help in maturation of sperms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Leydig cells:
a)
Are present in seminiferous tubules and secrete androgens
b)
Are present in seminiferous tubules and help in maturation of sperms
c)
Are present in interstitial space and secrete androgens
d)
Are present in interstitial space and help in maturation of sperms
|
|
Moumita Datta answered |
**Leydig Cells:**
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of Leydig, are specialized cells found in the interstitial space of the testes. These cells play a crucial role in the production and secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
**Location and Function:**
Leydig cells are located in the connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules, which are responsible for sperm production. They are not present within the seminiferous tubules themselves. Therefore, option C, which states that Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space, is the correct answer.
**Androgen Secretion:**
Leydig cells are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. These androgens are crucial for the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. Testosterone plays a vital role in the development of the male reproductive organs, such as the testes and prostate gland, as well as the growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and muscle development.
**Regulation of Androgen Secretion:**
The secretion of androgens by Leydig cells is regulated by the luteinizing hormone (LH) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. LH stimulates the production and release of testosterone from Leydig cells. In turn, testosterone negatively regulates the secretion of LH through a negative feedback loop. This mechanism helps maintain optimal levels of testosterone in the body.
**Role in Sperm Maturation:**
While Leydig cells do not directly participate in the maturation of sperm, the androgens they secrete, such as testosterone, play a crucial role in the process. Testosterone is required for the initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis, the process by which sperms are produced. It supports the maturation of spermatogonia, promotes the division and differentiation of germ cells, and influences the development of spermatozoa.
In conclusion, Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space of the testes and are responsible for the secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. They play a vital role in the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics, as well as in supporting the process of spermatogenesis.
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of Leydig, are specialized cells found in the interstitial space of the testes. These cells play a crucial role in the production and secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
**Location and Function:**
Leydig cells are located in the connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules, which are responsible for sperm production. They are not present within the seminiferous tubules themselves. Therefore, option C, which states that Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space, is the correct answer.
**Androgen Secretion:**
Leydig cells are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. These androgens are crucial for the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics. Testosterone plays a vital role in the development of the male reproductive organs, such as the testes and prostate gland, as well as the growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and muscle development.
**Regulation of Androgen Secretion:**
The secretion of androgens by Leydig cells is regulated by the luteinizing hormone (LH) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. LH stimulates the production and release of testosterone from Leydig cells. In turn, testosterone negatively regulates the secretion of LH through a negative feedback loop. This mechanism helps maintain optimal levels of testosterone in the body.
**Role in Sperm Maturation:**
While Leydig cells do not directly participate in the maturation of sperm, the androgens they secrete, such as testosterone, play a crucial role in the process. Testosterone is required for the initiation and maintenance of spermatogenesis, the process by which sperms are produced. It supports the maturation of spermatogonia, promotes the division and differentiation of germ cells, and influences the development of spermatozoa.
In conclusion, Leydig cells are present in the interstitial space of the testes and are responsible for the secretion of androgens, particularly testosterone. They play a vital role in the development and maintenance of male reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics, as well as in supporting the process of spermatogenesis.
What is released at ovulation?- a)Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
- b)Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis II
- c)Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
- d)Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
b)
Primary oocyte arrested at meiosis II
c)
Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis I
d)
Secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis II

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
At ovulation, a secondary oocyte arrested at meiosis II is released from the ovary. This secondary oocyte will only complete meiosis II if it is fertilized by a sperm.
Seminal plasma in humans is rich in- a)Fructose and certain enzymes but poor in calcium
- b)Fructose and calcium but has no enzyme
- c)Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes
- d)Glucose and certain enzymes but has no calcium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Seminal plasma in humans is rich in
a)
Fructose and certain enzymes but poor in calcium
b)
Fructose and calcium but has no enzyme
c)
Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes
d)
Glucose and certain enzymes but has no calcium
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Secretion of seminal vesicle, prostrate gland and bulbourethral gland Constitute seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes.
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?- a)Lactogen
- b)Primary milk
- c)Colostrum
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The yellowish coloured milk secreted from the breast shortly after birth of the baby is called?
a)
Lactogen
b)
Primary milk
c)
Colostrum
d)
None of these

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
After parturition, mammary glands start producing milk. The yellowish coloured milk is called colostrums. This milk contains antibodies that provide immunity newly born baby.
Read the following statements about menstrual cycle and select two correct statements.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements about menstrual cycle and select two correct statements.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.
(i) Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy.
(ii) The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones only.
(iii) LH surge induces ovulation.
(iv) If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates immediately.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iv)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Lack of menstruation may be indicative of pregnancy. During pregnancy, the levels of estrogen and progesterone are high in the blood, which are required for the maintenance of uterus and thus, menstruation does not occur. On 14th day of the menstrual cycle, there is rapid increase in LH (called LH surge), that induces ovulation. The changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of ovarian hormones and pituitary hormones. If fertilisation occurs, corpus luteum degenerates by 16th week of pregnancy.
The cleavage divisions in humans is:- a)holoblastic, equal and indeterminate
- b)holoblastic, unequal and indeterminate
- c)holoblastic, equal and determinate
- d)holoblastic, unequal and determinate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cleavage divisions in humans is:
a)
holoblastic, equal and indeterminate
b)
holoblastic, unequal and indeterminate
c)
holoblastic, equal and determinate
d)
holoblastic, unequal and determinate
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The process of cleavage or cellulation happens through repeated mitotic divisions. These divisions result in cells called blastomeres. The mitotic process is very rapid. As the cleavage progresses the resultant daughter cells, namely the blastomeres get reduced in size. During cleavage, there is no growth in the blastomeres. The total size and volume of the embryo remain the same. The cleavages result in a compact mass of blastomeres called morula. It gets transformed into a blastula. While the wall of the blastula is called the blastoderm, the central cavity is called the blastocoel. Types of cleavages:
Equal holoblastic cleavage - In microlecithal and isolecithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of equal size. Eg: Amphioxus and placental mammals.
Unequal holoblastic cleavage - In mesolecithal and telolocithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of unequal size. Among the blastomeres, there are many small-sized micromeres and a few large-sized macromeres.
Equal holoblastic cleavage - In microlecithal and isolecithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of equal size. Eg: Amphioxus and placental mammals.
Unequal holoblastic cleavage - In mesolecithal and telolocithal eggs, cleavage leads to the formation of blastomeres of unequal size. Among the blastomeres, there are many small-sized micromeres and a few large-sized macromeres.
What is the correct order of travel of sperm through the female reproductive tract before it reaches the egg?- a)Vagina → Fallopian tube → Uterus → Cervix
- b)Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Oviduct
- c)Vagina → Uterus → Cervix → Oviduct
- d)Vagina → Fallopian tube → Cervix → Uterus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct order of travel of sperm through the female reproductive tract before it reaches the egg?
a)
Vagina → Fallopian tube → Uterus → Cervix
b)
Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Oviduct
c)
Vagina → Uterus → Cervix → Oviduct
d)
Vagina → Fallopian tube → Cervix → Uterus
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Sperms are released into the vagina. From here, they travel through the cervix and uterus before reaching oviduct or fallopian tube, where they can encounter an egg.
The given figure depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of the human female reproductive system. Which set of three parts out of I -VI have been correctly identified?- a)(II) endometrium, (III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae
- b)(III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae, (V) cervix
- c)(IV) oviducal funnel, (V)uterus,(VI)cervix
- d)(I) perimetrium, (II) myometrium, (III) Fallopian tube
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The given figure depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of the human female reproductive system. Which set of three parts out of I -VI have been correctly identified?
a)
(II) endometrium, (III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae
b)
(III) infundibulum, (IV) fimbriae, (V) cervix
c)
(IV) oviducal funnel, (V)uterus,(VI)cervix
d)
(I) perimetrium, (II) myometrium, (III) Fallopian tube
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
In the given figure, I-endometrium, II-perimetrium, III-infundibulum, IV-fimbriae, V-cervix, VI-vagina.
Prostate glands are located below- a)gubernaculum
- b)seminal vesicles
- c)epididymis
- d)bulbourethral glands
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Prostate glands are located below
a)
gubernaculum
b)
seminal vesicles
c)
epididymis
d)
bulbourethral glands
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The prostate gland (small and walnut-shaped) is located beneath the seminal vesicle and secretes a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. The prostate is just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.
The mature follicle that holds the secondary oocyte before release from the ovary is called _________- a)Tertiary follicle
- b)Primary follicle
- c)Secondary follicle
- d)Graafian follicle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mature follicle that holds the secondary oocyte before release from the ovary is called _________
a)
Tertiary follicle
b)
Primary follicle
c)
Secondary follicle
d)
Graafian follicle

|
Lead Academy answered |
- Primary oocyte completes the first round of meiosis in the tertiary oocyte, thus forming a secondary oocyte.
- The tertiary follicle further matures to form a Graafian follicle which ruptures and releases the secondary oocyte in the fallopian tube for fertilization.
In a pregnant woman having prolonged labour pains, if the childbirth has to be hastened, it is advisable to administer a hormone that can- a)Activate the smooth muscles
- b)Increase the metabolic rate
- c)Release glucose into the blood
- d)Stimulate the ovary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a pregnant woman having prolonged labour pains, if the childbirth has to be hastened, it is advisable to administer a hormone that can
a)
Activate the smooth muscles
b)
Increase the metabolic rate
c)
Release glucose into the blood
d)
Stimulate the ovary
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- During birth, prostaglandins initiate the contraction in smooth muscles of uterine wall which causes labor pains.
- The pressure of fetus’s head against the cervix and send signals to make hypothalamus to trigger the release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary. Together, oxytocin (OT) and prostaglandins stimulate strong uterine muscle contraction forcing the fetus downwards and thereby expelling it out of the uterus. Thus, to hasten the childbirth, it is advisable to administer the hormone that stimulates uterine smooth muscle contraction i.e. oxytocin. This makes option A correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for Human Reproduction - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Human Reproduction - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup