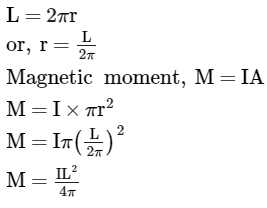All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Magnetism and Matter for NEET Exam
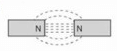
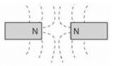
Which combination of magnetic field lines and poles shows two magnets repelling each other?- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
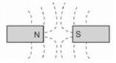
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which combination of magnetic field lines and poles shows two magnets repelling each other?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
- The discovery that one particular pole of a magnet orients northward, whereas the other pole orients southward allowed people to identify the north and south poles of any magnet.
- It was then noticed that the north poles of two different magnets repel each other, and likewise for the south poles. Conversely, the north pole of one magnet attracts the south pole of other magnets.
- This situation is analogous to that of electric charge, where like charges repel and unlike charges attract. In magnets, we simply replace the charge with a pole: Like poles repel and unlike poles attract.
When the switch is closed a magnetic field is produced by the coil. Which answer shows the shape of the field?- a)
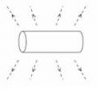
- b)
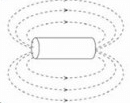
- c)
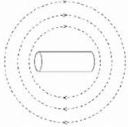
- d)
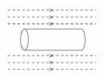
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the switch is closed a magnetic field is produced by the coil. Which answer shows the shape of the field?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Anand Kumar answered |
Ya it's B ....
Emerges from one side and enter from another side...
Emerges from one side and enter from another side...
If the susceptibility of a metal at saturation is 4500, then what is the permeability of this metal at saturation?- a)5.684 X 10-4 T-m/A
- b)5.654 X 10-3 T-m/A
- c)5.654 X 10-7 T-m/A
- d)5.658 X 10-5 T-m/A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the susceptibility of a metal at saturation is 4500, then what is the permeability of this metal at saturation?
a)
5.684 X 10-4 T-m/A
b)
5.654 X 10-3 T-m/A
c)
5.654 X 10-7 T-m/A
d)
5.658 X 10-5 T-m/A
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
μr=μ/μ0
μ= μr x μ0
μ=4500 x 4πx 10-7
μ=56520x10-7
μ=5.652x10-3
μ= μr x μ0
μ=4500 x 4πx 10-7
μ=56520x10-7
μ=5.652x10-3
What kinds of materials are used for coating magnetic tapes?- a)Diamagnetic Materials
- b)Ferrites
- c)Electromagnet
- d)Paramagnetic materials
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What kinds of materials are used for coating magnetic tapes?
a)
Diamagnetic Materials
b)
Ferrites
c)
Electromagnet
d)
Paramagnetic materials

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Ceramics are used for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player or for building memory stores in a modern computer. Ceramics are specially treated barium-iron oxides and are also called ferrites.
The units of magnetic pole strength and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet are- a)A-m, JT-1
- b)JT-1, Am-1
- c)JT-1, Am
- d)Am-1, JT-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The units of magnetic pole strength and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet are
a)
A-m, JT-1
b)
JT-1, Am-1
c)
JT-1, Am
d)
Am-1, JT-1
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The units of magnetic pole strength is (A-m) and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet is (JT-1)
What is the unit of susceptibility?- a)Am-1
- b)Am2
- c)No units
- d)Am
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the unit of susceptibility?
a)
Am-1
b)
Am2
c)
No units
d)
Am
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In electromagnetism the magnetic susceptibility (Latin: susceptibilis, “receptive”; denoted X) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. Mathematically, it is the ratio of magnetization M(magnetic moment per unit volume) to the applied magnetizing field intensity H.
Declination is the angle between:- a)horizontal and vertical components of earth’s magnetic field
- b)horizontal component and total magnetic field of the earth
- c)geographic and magnetic meridian
- d)geographic meridian and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Declination is the angle between:
a)
horizontal and vertical components of earth’s magnetic field
b)
horizontal component and total magnetic field of the earth
c)
geographic and magnetic meridian
d)
geographic meridian and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) and true north (the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North Pole).
Which one of the Maxwell’s laws leads to the conclusion that there are no magnetic field loops that are not closed?- a)Faraday’s law
- b)Gauss’ law for magnetism
- c)Gauss’ law for electricity
- d)Ampere-Maxwell law
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the Maxwell’s laws leads to the conclusion that there are no magnetic field loops that are not closed?
a)
Faraday’s law
b)
Gauss’ law for magnetism
c)
Gauss’ law for electricity
d)
Ampere-Maxwell law
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
In physics, Gauss's law for magnetism is one of the four Maxwell's equations that underlie classical electrodynamics. It states that the magnetic field B has divergence equal to zero,in other words, that it is a solenoidal vector field. It is equivalent to the statement that magnetic monopoles do not exist.Rather than "magnetic charges", the basic entity for magnetism is the magnetic dipole. (If monopoles were ever found, the law would have to be modified, as elaborated below.)
Gauss's law for magnetism can be written in two forms, a differential form and an integral form. These forms are equivalent due to the divergence theorem.
The name "Gauss's law for magnetism"is not universally used. The law is also called "Absence of free magnetic poles";one reference even explicitly says the law has "no name".It is also referred to as the "transversality requirement"because for plane waves it requires that the polarization be transverse to the direction of propagation.
How can a magnetic field be produced?- a)Using a permanent magnet
- b)Electric current
- c)Using a temporary magnet
- d)Using a permanent magnet or electric current
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How can a magnetic field be produced?
a)
Using a permanent magnet
b)
Electric current
c)
Using a temporary magnet
d)
Using a permanent magnet or electric current
|
|
Sanaya Kumar answered |
Production of Magnetic Field
Magnetic field can be produced in various ways. The correct answer is option 'D', which states that a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. Let's discuss both of these methods in detail.
Using a Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties even in the absence of an external magnetic field. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is due to the alignment of its atomic dipoles. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static and does not change in strength or direction over time.
Using an Electric Current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge through a conductor. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The strength and direction of the magnetic field depend on the strength and direction of the current flowing through the conductor. The magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. While the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static, the magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Magnetic field can be produced in various ways. The correct answer is option 'D', which states that a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. Let's discuss both of these methods in detail.
Using a Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties even in the absence of an external magnetic field. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is due to the alignment of its atomic dipoles. The magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static and does not change in strength or direction over time.
Using an Electric Current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge through a conductor. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The strength and direction of the magnetic field depend on the strength and direction of the current flowing through the conductor. The magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a magnetic field can be produced using a permanent magnet or electric current. While the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet is static, the magnetic field produced by an electric current is dynamic and can change in strength and direction over time.
Magnetic field strength due to a short bar magnet on its axial line at a distance x is B. What is its value at the same distance on the equatorial line?- a)B/2
- b)B
- c)2B
- d)4B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Magnetic field strength due to a short bar magnet on its axial line at a distance x is B. What is its value at the same distance on the equatorial line?
a)
B/2
b)
B
c)
2B
d)
4B
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The magnetic field at any axial point is given by, B = 2μo/ 4πx3
Similarly, the field at any equatorial point is given by, B = μo/ 4πx3
Thus, the field at any equatorial point is half of what it is at an axial point.
Similarly, the field at any equatorial point is given by, B = μo/ 4πx3
Thus, the field at any equatorial point is half of what it is at an axial point.
The ferromagnetic materials can be magnetised easily because- a)Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and permeability
- b)Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and low permeability
- c)Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and permeability
- d)Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and high permeability
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ferromagnetic materials can be magnetised easily because
a)
Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and permeability
b)
Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and low permeability
c)
Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and permeability
d)
Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and high permeability

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
Such materials are called ferromagnetic, after the Latin word for iron, ferrum. Not only do ferromagnetic materials respond strongly to magnets (the way iron is attracted to magnets), they can also be magnetized themselves—that is, they can be induced to be magnetic or made into permanent magnets.
The magnetic induction left behind in the sample after the magnetizing field has been removed is called- a)Hyteresis
- b)Retentivity
- c)Coercivity
- d)Ferromagnetism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic induction left behind in the sample after the magnetizing field has been removed is called
a)
Hyteresis
b)
Retentivity
c)
Coercivity
d)
Ferromagnetism
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Remanence or remanent magnetization or residual magnetism is the magnetization left behind in a ferromagnetic material (such as iron) after an external magnetic field is removed. It is also the measure of that magnetization. Colloquially, when a magnet is "magnetized" it has remanence.The remanence of magnetic materials provides the magnetic memory in magnetic storage devices, and is used as a source of information on the past Earth's magnetic field in paleomagnetism.The equivalent term residual magnetization is generally used in engineering applications. In transformers, electric motors and generators a large residual magnetization is not desirable (see also electrical steel) as it is an unwanted contamination, for example a magnetization remaining in an electromagnet after the current in the coil is turned off. Where it is unwanted, it can be removed by degaussing.Sometimes the term retentivity is used for remanence measured in units of magnetic flux density.
A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed. The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on- a)q and m
- b)ω and q
- c)ω, q and m
- d)ω and m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed. The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on
a)
q and m
b)
ω and q
c)
ω, q and m
d)
ω and m

|
Sanchita Iyer answered |
To find the magnetic moment due to a single particle, it is advisable to consider the equivalent current due to it
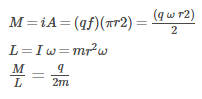
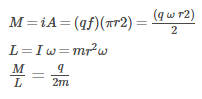
Chapter doubts & questions for Magnetism and Matter - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Magnetism and Matter - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup