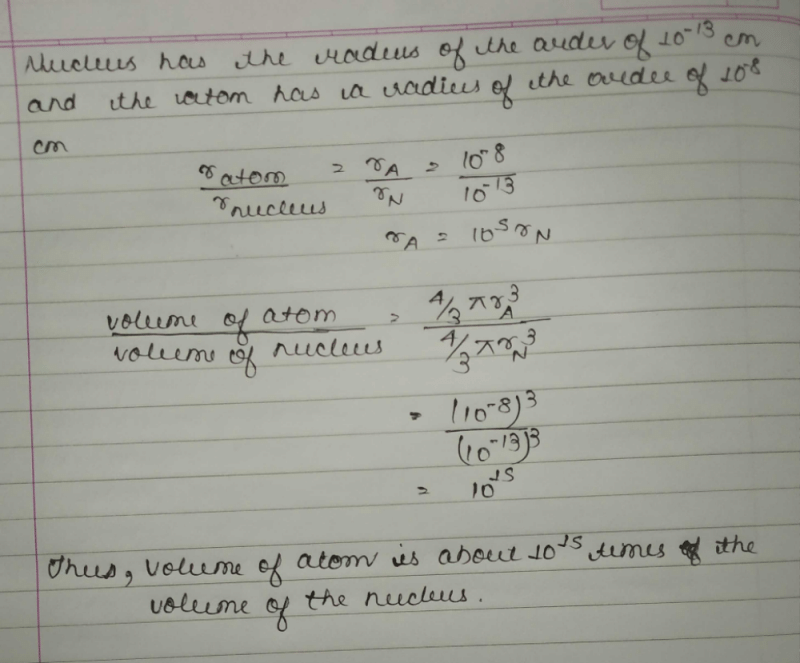All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Nuclei for NEET Exam
Nucleus ”a” contains 5 protons and 5 neutrons and has radius R. The radius of nucleus ”b”, which contains 35 protons and 45 neutrons, is closest to:- a)2R
- b)8R
- c)1.4R
- d)R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleus ”a” contains 5 protons and 5 neutrons and has radius R. The radius of nucleus ”b”, which contains 35 protons and 45 neutrons, is closest to:
a)
2R
b)
8R
c)
1.4R
d)
R
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
R∝A1/3
A(mass no.)=n+p
R/x=(10/80)1/3
R/x=(13/23)1/3
R/x=1/2
X=2R
A(mass no.)=n+p
R/x=(10/80)1/3
R/x=(13/23)1/3
R/x=1/2
X=2R
The number of electrons in an atom X of atomic number Z and mass number A is- a)Zero
- b)A
- c)Z
- d)A-Z
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of electrons in an atom X of atomic number Z and mass number A is
a)
Zero
b)
A
c)
Z
d)
A-Z

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
No of neutrons are given by: (A−Z)
Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), you can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom. For example, a lithium atom (Z=3,A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7–3=4).
Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), you can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom. For example, a lithium atom (Z=3,A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7–3=4).
The nuclide 92U238 has all the following except- a)92 protons
- b)146 neutrons
- c)238 nucleons
- d)92 neutrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The nuclide 92U238 has all the following except
a)
92 protons
b)
146 neutrons
c)
238 nucleons
d)
92 neutrons

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
The nuclide (nucleus) consists of neutrons and protons (when combined called nucleons).
Thus,
No. of protons in 92U238 = 92,
No. of neutrons = 146 (238 – 92)
No. of nucleons = 238 (146 + 92)
Thus,
No. of protons in 92U238 = 92,
No. of neutrons = 146 (238 – 92)
No. of nucleons = 238 (146 + 92)
In the following reaction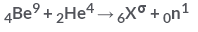 What is following value of a?
What is following value of a?- a)14
- b)10
- c)16
- d)12
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reaction
What is following value of a?
a)
14
b)
10
c)
16
d)
12
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
The sum of the atomic no. and atomic mass no. on the reactant and product should be equal .
therefore 9+4 = a+1
a = 12
therefore 9+4 = a+1
a = 12
The atomic number Z of the nucleus is- a)Number of deutrons.
- b)Number of neutrons in it.
- c)Number if electrons in it.
- d)Number of protons in it.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomic number Z of the nucleus is
a)
Number of deutrons.
b)
Number of neutrons in it.
c)
Number if electrons in it.
d)
Number of protons in it.
|
|
Shraddha Dey answered |
**Explanation:**
The atomic number (Z) of an atom refers to the number of protons in the nucleus. Here, we will discuss why the correct answer is option 'D' and explain the significance of atomic number in an atom.
**Atomic Number (Z):**
The atomic number of an atom is a fundamental property that determines its identity and place in the periodic table. It is denoted by the symbol 'Z'. Each element on the periodic table has a unique atomic number.
**Protons in the Nucleus:**
Protons are subatomic particles that carry a positive charge. They are located in the nucleus of an atom, which is the central core of the atom. The number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the atomic number of the atom.
**Electrons in the Atom:**
Electrons are subatomic particles that carry a negative charge. They orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons, ensuring that the atom has a balanced charge overall.
**Neutrons in the Nucleus:**
Neutrons are subatomic particles that have no charge (they are electrically neutral). They are also located in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, resulting in different isotopes of the same element. Isotopes have the same atomic number (same number of protons) but different mass numbers (different number of neutrons).
**Significance of Atomic Number:**
The atomic number is a crucial characteristic of an atom because it determines the element's identity. Elements are organized in increasing order of their atomic numbers on the periodic table. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, helium has an atomic number of 2, and so on.
The atomic number defines the unique properties and behavior of an element. It determines the number of electrons in the atom, which influences the atom's chemical reactivity and bonding. It also provides information about the element's position in the periodic table, its atomic mass, and its isotopes.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'D' – the atomic number (Z) of the nucleus represents the number of protons in it.
The atomic number (Z) of an atom refers to the number of protons in the nucleus. Here, we will discuss why the correct answer is option 'D' and explain the significance of atomic number in an atom.
**Atomic Number (Z):**
The atomic number of an atom is a fundamental property that determines its identity and place in the periodic table. It is denoted by the symbol 'Z'. Each element on the periodic table has a unique atomic number.
**Protons in the Nucleus:**
Protons are subatomic particles that carry a positive charge. They are located in the nucleus of an atom, which is the central core of the atom. The number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the atomic number of the atom.
**Electrons in the Atom:**
Electrons are subatomic particles that carry a negative charge. They orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons, ensuring that the atom has a balanced charge overall.
**Neutrons in the Nucleus:**
Neutrons are subatomic particles that have no charge (they are electrically neutral). They are also located in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, resulting in different isotopes of the same element. Isotopes have the same atomic number (same number of protons) but different mass numbers (different number of neutrons).
**Significance of Atomic Number:**
The atomic number is a crucial characteristic of an atom because it determines the element's identity. Elements are organized in increasing order of their atomic numbers on the periodic table. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, helium has an atomic number of 2, and so on.
The atomic number defines the unique properties and behavior of an element. It determines the number of electrons in the atom, which influences the atom's chemical reactivity and bonding. It also provides information about the element's position in the periodic table, its atomic mass, and its isotopes.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'D' – the atomic number (Z) of the nucleus represents the number of protons in it.
The radius of a nucleus is directly proportional to (A=mass number)- a)A1/3
- b)A2
- c)A3
- d)A1/2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The radius of a nucleus is directly proportional to (A=mass number)
a)
A1/3
b)
A2
c)
A3
d)
A1/2
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
For A nucleons
R=RoA1/3 [Ro=constant]
So, R∝A1/3
R=RoA1/3 [Ro=constant]
So, R∝A1/3
What amount of energy is released in the fission of 95U235 ?- a)200 keV
- b)20 eV
- c)200 eV
- d)200 MeV
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What amount of energy is released in the fission of 95U235 ?
a)
200 keV
b)
20 eV
c)
200 eV
d)
200 MeV

|
Divey Sethi answered |
The fission process represented by the equation, 92U235+0n1→56Ba144+36Kr89+30n1
Masses of reactants =234.39+1.01=235.4amu
Masses of products =143.28+88.89+3(1.01) =235.2amu
Energy released = mass difference =235.4−235.2=0.2amu=0.2×931∼200MeV
Masses of reactants =234.39+1.01=235.4amu
Masses of products =143.28+88.89+3(1.01) =235.2amu
Energy released = mass difference =235.4−235.2=0.2amu=0.2×931∼200MeV
The average binding energy of nucleus is- a)8 BeV
- b)8 Mev
- c)8 eV
- d)8 KeV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The average binding energy of nucleus is
a)
8 BeV
b)
8 Mev
c)
8 eV
d)
8 KeV
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Excluding the lighter nuclei, the average binding energy per nucleon is about 8 MeV. The maximum binding energy per nucleon occurs at around mass number A = 50, and corresponds to the most stable nuclei.
Given M = mass of the nucleus, A = atomic mass. What is packing fraction?- a)
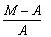
- b)
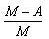
- c)
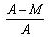
- d)
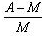
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given M = mass of the nucleus, A = atomic mass. What is packing fraction?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Packing fraction: - It tells about the stability of a nucleus.
Packing fraction=isotonic mass=molecular mass (atomic mass)/atomic mass
p.f.=M-A/A
Packing fraction=isotonic mass=molecular mass (atomic mass)/atomic mass
p.f.=M-A/A
Which of the following statements is true for nuclear forces?- a)They are short range forces
- b)They are equal in strength to the electromagnetic forces
- c)They obey the inverse third power law of distance
- d)They obey the inverse square law of distance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true for nuclear forces?
a)
They are short range forces
b)
They are equal in strength to the electromagnetic forces
c)
They obey the inverse third power law of distance
d)
They obey the inverse square law of distance
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Nuclear forces are short range forces. This is the only correct answer. Others are wrong. They are the strongest forces in nature and do not obey inverse square law.
Which one of the following statements about the atomic nucleus is accurate?- a)The nucleus is held together mostly by the electrical and gravitational forces
- b)Large nuclei are denser than light nuclei
- c)All nuclei have nearly the same density
- d)Smaller nuclei are denser than larger nuclei
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about the atomic nucleus is accurate?
a)
The nucleus is held together mostly by the electrical and gravitational forces
b)
Large nuclei are denser than light nuclei
c)
All nuclei have nearly the same density
d)
Smaller nuclei are denser than larger nuclei
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Most nuclei are approximately spherical. The average radius of a nucleus with A nucleons is R = R0A1/3, where R0 = 1.2*10-15 m. The volume of the nucleus is directly proportional to the total number of nucleons. This suggests that all nuclei have nearly the same density.
The density of nuclear matter is:- a)independent of the number of nucleons in the nucleus
- b)directly proportional to the number of neutrons in the nucleus
- c)directly proportional to the number of protons in the nucleus
- d)directly proportional to the square of the number of nucleons in the nucleus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The density of nuclear matter is:
a)
independent of the number of nucleons in the nucleus
b)
directly proportional to the number of neutrons in the nucleus
c)
directly proportional to the number of protons in the nucleus
d)
directly proportional to the square of the number of nucleons in the nucleus
|
|
Maulik Dasgupta answered |
Density of Nuclear Matter
The density of nuclear matter refers to the mass per unit volume of the nucleus of an atom.
It is independent of the number of nucleons in the nucleus because the volume of the nucleus is proportional to the cube of the radius, while the number of nucleons is proportional to the cube of the radius. Therefore, the density remains constant regardless of the number of nucleons.
The density of nuclear matter is estimated to be around 2.3 x 10^17 kg/m^3, which is much higher than the density of ordinary matter.
The high density of nuclear matter is due to the strong nuclear force that binds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'A', i.e., the density of nuclear matter is independent of the number of nucleons in the nucleus.
The density of nuclear matter refers to the mass per unit volume of the nucleus of an atom.
It is independent of the number of nucleons in the nucleus because the volume of the nucleus is proportional to the cube of the radius, while the number of nucleons is proportional to the cube of the radius. Therefore, the density remains constant regardless of the number of nucleons.
The density of nuclear matter is estimated to be around 2.3 x 10^17 kg/m^3, which is much higher than the density of ordinary matter.
The high density of nuclear matter is due to the strong nuclear force that binds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'A', i.e., the density of nuclear matter is independent of the number of nucleons in the nucleus.
A fusion bomb involves:- a)breaking of a heavy nucleus into a lighter ones
- b)explosion of TNT
- c)synthesis of lighter nuclei into heavier ones
- d)burning of huge amount of coal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A fusion bomb involves:
a)
breaking of a heavy nucleus into a lighter ones
b)
explosion of TNT
c)
synthesis of lighter nuclei into heavier ones
d)
burning of huge amount of coal

|
Akshay Shah answered |
An atomic bomb, by contrast, uses the energy released when a heavy atomic nucleus splits, or fissions, into two lighter nuclei. ... The energy thus produced forms the explosive power of a hydrogen bomb. Deuterium and tritium, which are isotopes of hydrogen, provide ideal interacting nuclei for the fusion process.
Why does the fusion occur at high temperature?- a)kinetic energy is high enough to overcome repulsion between nuclei.
- b)nuclei break up at high temperature
- c)atoms are ionised at high temperature
- d)molecules break up at high temperature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why does the fusion occur at high temperature?
a)
kinetic energy is high enough to overcome repulsion between nuclei.
b)
nuclei break up at high temperature
c)
atoms are ionised at high temperature
d)
molecules break up at high temperature
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
The high temperature gives the hydrogen atoms enough energy to overcome the electrical repulsion between the protons. Fusion requires temperatures about 100 million Kelvin (approximately six times hotter than the sun's core). At these temperatures, hydrogen is a plasma, not a gas.
Binding energy per nucleon is the ratio of- a)the binding energy of the nucleus to the number of nucleons in that nucleus.
- b)energy required to remove a nucleon to atomic weight
- c)binding energy of a nucleon to the atomic number
- d)binding energy of a nucleus to the atomic number
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Binding energy per nucleon is the ratio of
a)
the binding energy of the nucleus to the number of nucleons in that nucleus.
b)
energy required to remove a nucleon to atomic weight
c)
binding energy of a nucleon to the atomic number
d)
binding energy of a nucleus to the atomic number
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Binding energy per nucleon is the ratio of the binding energy of a nucleus to the number of the nucleons.
Binding energy per nucleon = (Total binding energy) / (Number of nucleon)
Measure of stability of the nucleus: Larger the binding energy per nucleon, the greater the work that must be done to remove the nucleon from the nucleus, the more stable the nucleus.
In a nuclear reactor:- a)moderator is used to slow down the neutrons
- b)moderator is used to control the number of neutrons
- c)control rods are used to slow down the neutrons
- d)coolant is used to slow down the neutrons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a nuclear reactor:
a)
moderator is used to slow down the neutrons
b)
moderator is used to control the number of neutrons
c)
control rods are used to slow down the neutrons
d)
coolant is used to slow down the neutrons
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
A moderator in a nuclear reactor is used to slow down the neutrons. The neutrons produced by fission are very fast, around 2 MeV. (Neutron “speed” is generally expressed by it's energy.) At that speed the probability of the neutron causing a fission in another uranium or plutonium atom is fairly low.
The fusion of hydrogen into helium is more likely to take place:- a)at high temperature and high pressure
- b)at high temperature and low pressure
- c)at low temperature and low pressure
- d)at low temperature and high pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The fusion of hydrogen into helium is more likely to take place:
a)
at high temperature and high pressure
b)
at high temperature and low pressure
c)
at low temperature and low pressure
d)
at low temperature and high pressure
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The fusion of hydrogen into helium is more likely to take place at high temperature and high pressure, like the sun.
Chapter doubts & questions for Nuclei - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Nuclei - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup