All Exams >
Electrical Engineering (EE) >
Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT) >
All Questions
All questions of Coordinate System & Vector Analysis for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam
The energy stored in the inductor 100mH with a current of 2A is- a)0.2
- b)0.4
- c)0.6
- d)0.8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy stored in the inductor 100mH with a current of 2A is
a)
0.2
b)
0.4
c)
0.6
d)
0.8

|
EduRev GATE answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: dw = ei dt = Li di, W = L∫ i.di
Energy E = 0.5LI2 = 0.5 X 0.1 X 22 = 0.2 Joule.
Explanation: dw = ei dt = Li di, W = L∫ i.di
Energy E = 0.5LI2 = 0.5 X 0.1 X 22 = 0.2 Joule.
Find the Laplace equation value of the following potential field
V = x2 – y2 + z2- a)0
- b)2
- c)4
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the Laplace equation value of the following potential field
V = x2 – y2 + z2
V = x2 – y2 + z2
a)
0
b)
2
c)
4
d)
6
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: (Del) V = 2x – 2y + 2z
(Del)2 V = 2 – 2 + 2= 2, which is non zero value. Thus it doesn’t satisfy Laplace equation.
Explanation: (Del) V = 2x – 2y + 2z
(Del)2 V = 2 – 2 + 2= 2, which is non zero value. Thus it doesn’t satisfy Laplace equation.
The Stoke’s theorem uses which of the following operation?- a)Divergence
- b)Gradient
- c)Curl
- d)Laplacian
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Stoke’s theorem uses which of the following operation?
a)
Divergence
b)
Gradient
c)
Curl
d)
Laplacian
|
|
Malavika Nair answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: ∫A.dl = ∫∫ Curl (A).ds is the expression for Stoke’s theorem. It is clear that the theorem uses curl operation.
Explanation: ∫A.dl = ∫∫ Curl (A).ds is the expression for Stoke’s theorem. It is clear that the theorem uses curl operation.
Find the value of divergence theorem for the field D = 2xy i + x2 j for the rectangular parallelepiped given by x = 0 and 1, y = 0 and 2, z = 0 and 3.- a)10
- b)12
- c)14
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of divergence theorem for the field D = 2xy i + x2 j for the rectangular parallelepiped given by x = 0 and 1, y = 0 and 2, z = 0 and 3.
a)
10
b)
12
c)
14
d)
16
|
|
Prisha Sen answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Div (D) = 2y
∫∫∫Div (D) dv = ∫∫∫ 2y dx dy dz. On integrating, x = 0->1, y = 0->2 and z = 0->3, we get Q = 12.
Explanation: Div (D) = 2y
∫∫∫Div (D) dv = ∫∫∫ 2y dx dy dz. On integrating, x = 0->1, y = 0->2 and z = 0->3, we get Q = 12.
False statement among the following statements regarding Coulombs law is:- a)Gives the force between two charges Q1 and Q2
- b)The magnitude of the force of attraction (or repulsion) between two-point charges is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of the two charges
- c)The magnitude of the force of attraction (or repulsion) between two-point charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
False statement among the following statements regarding Coulombs law is:
a)
Gives the force between two charges Q1 and Q2
b)
The magnitude of the force of attraction (or repulsion) between two-point charges is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of the two charges
c)
The magnitude of the force of attraction (or repulsion) between two-point charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
d)
None of the above

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
Coulomb’s law: When two charged particles of charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance r from each other then the electrostatic force between them is directly proportional to the multiplication of charges of two particles and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

Force (F) ∝ q1 × q2
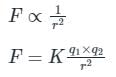
Where K is a constant = 9 × 109 Nm2/C2
Coulomb’s law: When two charged particles of charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance r from each other then the electrostatic force between them is directly proportional to the multiplication of charges of two particles and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

Force (F) ∝ q1 × q2
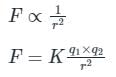
Where K is a constant = 9 × 109 Nm2/C2
- Coulomb’s Law talks about the magnitude of the attraction between the two charges.
- It says that the force is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Find the curl of A = (y cos ax)i + (y + ex)k- a)2i – ex j – cos ax k
- b)i – ex j – cos ax k
- c)2i – ex j + cos ax k
- d)i – ex j + cos ax k
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the curl of A = (y cos ax)i + (y + ex)k
a)
2i – ex j – cos ax k
b)
i – ex j – cos ax k
c)
2i – ex j + cos ax k
d)
i – ex j + cos ax k
|
|
Ishan Chawla answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Curl A = i(Dy(y + ex)) – j (Dx(y + ex) – Dz(y cos ax)) + k(-Dy(y cos ax))
= 1.i – j(ex) – k cos ax = i – ex j – cos ax k.
Explanation: Curl A = i(Dy(y + ex)) – j (Dx(y + ex) – Dz(y cos ax)) + k(-Dy(y cos ax))
= 1.i – j(ex) – k cos ax = i – ex j – cos ax k.
The divergence of a vector is a scalar. State True/False. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The divergence of a vector is a scalar. State True/False.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Divergence can be computed only for a vector. Since it is the measure of outward flow of flux from a small closed surface as the volume shrinks to zero, the result will be directionless (scalar).
Explanation: Divergence can be computed only for a vector. Since it is the measure of outward flow of flux from a small closed surface as the volume shrinks to zero, the result will be directionless (scalar).
The mathematical perception of the gradient is said to be- a)Tangent
- b)Chord
- c)Slope
- d)Arc
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The mathematical perception of the gradient is said to be
a)
Tangent
b)
Chord
c)
Slope
d)
Arc
|
|
Aman Datta answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The gradient is the rate of change of space of flux in electromagnetics. This is analogous to the slope in mathematics.
Explanation: The gradient is the rate of change of space of flux in electromagnetics. This is analogous to the slope in mathematics.
Given the potential V = 25 sin θ, in free space, determine whether V satisfies Laplace’s equation.- a)No
- b)Yes
- c)Data sufficient
- d)Potential is not defined
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given the potential V = 25 sin θ, in free space, determine whether V satisfies Laplace’s equation.
a)
No
b)
Yes
c)
Data sufficient
d)
Potential is not defined
|
|
Ravi Singh answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: (Del)2V = 0
(Del)2V = (Del)2(25 sin θ), which is not equal to zero. Thus the field does not satisfy Laplace equation.
Explanation: (Del)2V = 0
(Del)2V = (Del)2(25 sin θ), which is not equal to zero. Thus the field does not satisfy Laplace equation.
Identify the nature of the field, if the divergence is zero and curl is also zero.- a)Solenoidal, irrotational
- b)Divergent, rotational
- c)Solenoidal, irrotational
- d)Divergent, rotational
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the nature of the field, if the divergence is zero and curl is also zero.
a)
Solenoidal, irrotational
b)
Divergent, rotational
c)
Solenoidal, irrotational
d)
Divergent, rotational

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
Since the vector field does not diverge (moves in a straight path), the divergence is zero. Also, the path does not possess any curls, so the field is irrotational.
Hence option (C) is correct
To learn more about Divergence and Curl of a vector click on the link given below:
The path traversal in calculating the Green’s theorem is- a)Clockwise
- b)Anticlockwise
- c)Inwards
- d)Outwards
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The path traversal in calculating the Green’s theorem is
a)
Clockwise
b)
Anticlockwise
c)
Inwards
d)
Outwards
|
|
Kajal Yadav answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The Green’s theorem calculates the area traversed by the functions in the region in the anticlockwise direction. This converts the line integral to surface integral.
Explanation: The Green’s theorem calculates the area traversed by the functions in the region in the anticlockwise direction. This converts the line integral to surface integral.
According to gauss theorem, the electric flux on a closed surface depends on?- a)The area of open surface
- b)Charge enclosed
- c)Magnetic field of charge
- d)Charge outside the sphere
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to gauss theorem, the electric flux on a closed surface depends on?
a)
The area of open surface
b)
Charge enclosed
c)
Magnetic field of charge
d)
Charge outside the sphere
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
CONCEPT
- Electric Flux: It is defined as the number of electric field lines passing through the perpendicular unit area.
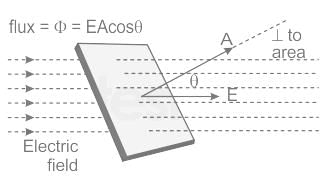
- Electric Flux = (Φ) = EA⊥ [E = electric field, A = perpendicular area]
- Electric flux (Φ) = EA cos θ [where θ is the angle between area plane and electric field]
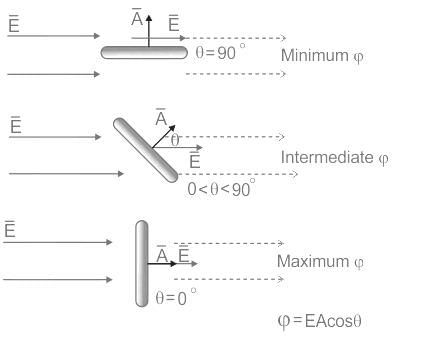
- The flux is maximum when the angle is 0°
- Gauss Law: According to gauss’s law, total electric flux through a closed surface enclosing a charge is 1/ϵ0 times the magnitude of charge enclosed.
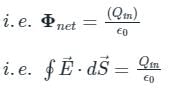
Where, Φ = electric flux, Qin = charge enclosed the sphere, ϵ0 = permittivity of space (8.85 × 10-12 C2/Nm2), dS = surface area
According to gauss’s law,
The flux of the net electric field through a closed surface equals the net charge enclosed by the surface divided by ϵ0.
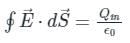
Electric flux on a closed surface only depends on the enclosed charge.
∴ Option 2 is correct
Given D = e-xsin y i – e-xcos y j
Find divergence of D.- a)3
- b)2
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given D = e-xsin y i – e-xcos y j
Find divergence of D.
Find divergence of D.
a)
3
b)
2
c)
1
d)
0
|
|
Debanshi Basak answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Div (D) = Dx(e-xsin y) + Dy(-e-xcos y ) = -e-xsin y + e-xsin y = 0.
Explanation: Div (D) = Dx(e-xsin y) + Dy(-e-xcos y ) = -e-xsin y + e-xsin y = 0.
Find the charged enclosed by a sphere of charge density ρ and radius a. - a)ρ (4πa2)
- b)ρ(4πa3/3)
- c)ρ(2πa2)
- d)ρ(2πa3/3)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the charged enclosed by a sphere of charge density ρ and radius a.
a)
ρ (4πa2)
b)
ρ(4πa3/3)
c)
ρ(2πa2)
d)
ρ(2πa3/3)
|
|
Prateek Mehra answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: The charge enclosed by the sphere is Q = ∫∫∫ ρ dv.
Where, dv = r2 sin θ dr dθ dφ and on integrating with r = 0->a, φ = 0->2π and θ = 0->π, we get Q = ρ(4πa3/3).
Explanation: The charge enclosed by the sphere is Q = ∫∫∫ ρ dv.
Where, dv = r2 sin θ dr dθ dφ and on integrating with r = 0->a, φ = 0->2π and θ = 0->π, we get Q = ρ(4πa3/3).
Let S be the portion of the plane z = 2x + 2y − 100 which lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1. If the surface area of S is απ, then the value of α is equal to ___________.- a)3
- b)4
- c)6
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Let S be the portion of the plane z = 2x + 2y − 100 which lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1. If the surface area of S is απ, then the value of α is equal to ___________.
a)
3
b)
4
c)
6
d)
8

|
EduRev GATE answered |
�� is the portion of the plane z = 2x + 2y − 100 which lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1.
zx = 2, zy = 2
then surface area of S
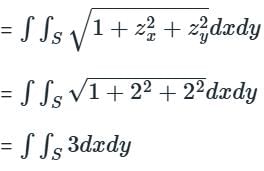
Now, the cylinder is x2 + y2 = 1
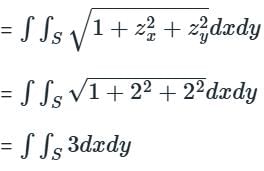
Now, the cylinder is x2 + y2 = 1
Let x = cosθ, y = sin θ
then surface area of S
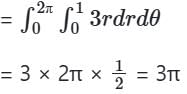
Given area S = απ
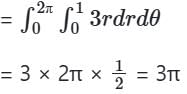
Given area S = απ
Hnece α = 3
4. The gradient of xi + yj + zk is- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
4. The gradient of xi + yj + zk is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Naveen Kapoor answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Grad (xi + yj + zk) = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3. In other words, the gradient of any position vector is 3.
Explanation: Grad (xi + yj + zk) = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3. In other words, the gradient of any position vector is 3.
Curl of gradient of a vector is- a)Unity
- b)Zero
- c)Null vector
- d)Depends on the constants of the vector
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Curl of gradient of a vector is
a)
Unity
b)
Zero
c)
Null vector
d)
Depends on the constants of the vector
|
|
Srishti Choudhary answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Gradient of any function leads to a vector. Similarly curl of that vector gives another vector, which is always zero for all constants of the vector. A zero value in vector is always termed as null vector(not simply a zero).
Explanation: Gradient of any function leads to a vector. Similarly curl of that vector gives another vector, which is always zero for all constants of the vector. A zero value in vector is always termed as null vector(not simply a zero).
The law, governing the force between electric charges is known as:- a)Ampere’s law
- b)Faraday’s law
- c)Coulomb’s law
- d)Ohm’s law
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The law, governing the force between electric charges is known as:
a)
Ampere’s law
b)
Faraday’s law
c)
Coulomb’s law
d)
Ohm’s law
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
CONCEPT:
Coulomb’s law: When two charged particles of charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance r from each other then the electrostatic force between them is directly proportional to the multiplication of charges of two particles and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

Force (F) ∝ q1 × q2
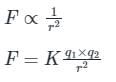
Where K is a constant = 9 × 109 Nm2/C2
Coulomb’s law: When two charged particles of charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance r from each other then the electrostatic force between them is directly proportional to the multiplication of charges of two particles and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

Force (F) ∝ q1 × q2
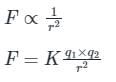
Where K is a constant = 9 × 109 Nm2/C2
- Coulomb’s Law talks about the magnitude of the attraction between the two charges.
- It says that the force is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The net electric flux through a spherical surface having 10 μC charge at the centre is- a)
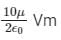
- b)
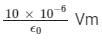
- c)
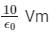
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The net electric flux through a spherical surface having 10 μC charge at the centre is
a)
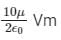
b)
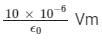
c)
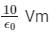
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
CONCEPT:
- Gauss's Law for electric field: It states that the total electric flux emerging out of a closed surface is directly proportional to the charge enclosed by this closed surface. It is expressed as:
ϕ = q/ϵ0
Where ϕ is the electric flux, q is the charge enclosed in the closed surface and ϵ0 is the permittivity of free space
The charge, q = 10 μC = 10 × 10-6 C
From Gauss's law, electric flux
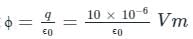
Where ϕ is the electric flux, q is the charge enclosed in the closed surface and ϵ0 is the permittivity of free space
The charge, q = 10 μC = 10 × 10-6 C
From Gauss's law, electric flux
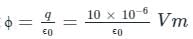
The electric field of a point charge is a linear function of the value of the charge. It is the principle applied to an electric field and states that the total resultant field at a point is the vector sum of the individual components of the field at a point. Identify the principle mentioned in the context.- a)Superposition principle of fields
- b)Coulomb's Law
- c)Ampere circuital Law
- d)Insulation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The electric field of a point charge is a linear function of the value of the charge. It is the principle applied to an electric field and states that the total resultant field at a point is the vector sum of the individual components of the field at a point. Identify the principle mentioned in the context.
a)
Superposition principle of fields
b)
Coulomb's Law
c)
Ampere circuital Law
d)
Insulation
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
CONCEPT:
Superposition Principle:
Superposition Principle:
- The principle of superposition states that when a number of charges are interacting, the total force on a given charge is the vector sum of the forces exerted on it due to all other charges.
- The force between two charges is not affected by the presence of other charges.
- This is used to calculate the following parameter at the observation point, to any configuration of charges.
- Net force.
- Net electric field.
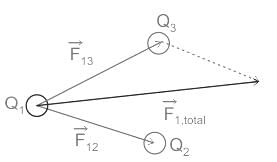
Coulomb's law in Electrostatics:
- It state’s that force of interaction between two stationary point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and acts along the straight line joining the two charges.
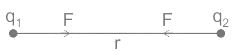
F ∝ q1 × q2
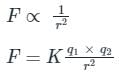
Where K = constant called electrostatic force constant.
- The value of K depends on the nature of the medium between the two charges and the system of units chosen
If two functions A and B are discrete, their Green’s value for a region of circle of radius a in the positive quadrant is- a)∞
- b)-∞
- c)0
- d)Does not exist
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If two functions A and B are discrete, their Green’s value for a region of circle of radius a in the positive quadrant is
a)
∞
b)
-∞
c)
0
d)
Does not exist
|
|
Naveen Kapoor answered |
Answer: D
Explanation: Green’s theorem is valid only for continuous functions. Since the given functions are discrete, the theorem is invalid or does not exist.
Explanation: Green’s theorem is valid only for continuous functions. Since the given functions are discrete, the theorem is invalid or does not exist.
A field in which a test charge around any closed surface in static path is zero is called- a)Solenoidal
- b)Rotational
- c)Irrotational
- d)Conservative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A field in which a test charge around any closed surface in static path is zero is called
a)
Solenoidal
b)
Rotational
c)
Irrotational
d)
Conservative
|
|
Bibek Saha answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Work done in moving a charge in a closed path is zero. It is expressed as, ∫ E.dl = 0. The field having this property is called conservative or lamellar field.
Explanation: Work done in moving a charge in a closed path is zero. It is expressed as, ∫ E.dl = 0. The field having this property is called conservative or lamellar field.
The divergence concept can be illustrated using Pascal’s law. State True/False.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The divergence concept can be illustrated using Pascal’s law. State True/False.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Gargi Mishra answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Consider the illustration of Pascal’s law, wherein a ball is pricked with holes all over its body. After water is filled in it and pressure is applied on it, the water flows out the holes uniformly. This is analogous to the flux flowing outside a closed surface as the volume reduces.
Explanation: Consider the illustration of Pascal’s law, wherein a ball is pricked with holes all over its body. After water is filled in it and pressure is applied on it, the water flows out the holes uniformly. This is analogous to the flux flowing outside a closed surface as the volume reduces.
Gauss theorem uses which of the following operations?- a)Gradient
- b)Curl
- c)Divergence
- d)Laplacian
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gauss theorem uses which of the following operations?
a)
Gradient
b)
Curl
c)
Divergence
d)
Laplacian
|
|
Mainak Pillai answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The Gauss divergence theorem uses divergence operator to convert surface to volume integral. It is used to calculate the volume of the function enclosing the region given.
Explanation: The Gauss divergence theorem uses divergence operator to convert surface to volume integral. It is used to calculate the volume of the function enclosing the region given.
Find the area of a right angled triangle with sides of 90 degree unit and the functions described by L = cos y and M = sin x.- a)0
- b)45
- c)90
- d)180
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the area of a right angled triangle with sides of 90 degree unit and the functions described by L = cos y and M = sin x.
a)
0
b)
45
c)
90
d)
180
|
|
Sanskriti Kaur answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: dM/dx = cos x and dL/dy = -sin y
∫∫(dM/dx – dL/dy)dx dy = ∫∫ (cos x + sin y)dx dy. On integrating with x = 0->90 and y = 0->90, we get area of right angled triangle as -180 units (taken in clockwise direction). Since area cannot be negative, we take 180 units.
Explanation: dM/dx = cos x and dL/dy = -sin y
∫∫(dM/dx – dL/dy)dx dy = ∫∫ (cos x + sin y)dx dy. On integrating with x = 0->90 and y = 0->90, we get area of right angled triangle as -180 units (taken in clockwise direction). Since area cannot be negative, we take 180 units.
Evaluate the surface integral ∫∫ (3x i + 2y j). dS, where S is the sphere given by x2 + y2 + z2= 9.- a)120π
- b)180π
- c)240π
- d)300π
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Evaluate the surface integral ∫∫ (3x i + 2y j). dS, where S is the sphere given by x2 + y2 + z2= 9.
a)
120π
b)
180π
c)
240π
d)
300π
|
|
Manoj Chaudhary answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: We could parameterise surface and find surface integral, but it is wise to use divergence theorem to get faster results. The divergence theorem is given by ∫∫ F.dS = ∫∫∫ Div (F).dV
Div (3x i + 2y j) = 3 + 2 = 5. Now the volume integral will be ∫∫∫ 5.dV, where dV is the volume of the sphere 4πr3/3 and r = 3units.Thus we get 180π.
Explanation: We could parameterise surface and find surface integral, but it is wise to use divergence theorem to get faster results. The divergence theorem is given by ∫∫ F.dS = ∫∫∫ Div (F).dV
Div (3x i + 2y j) = 3 + 2 = 5. Now the volume integral will be ∫∫∫ 5.dV, where dV is the volume of the sphere 4πr3/3 and r = 3units.Thus we get 180π.
The integral form of potential and field relation is given by line integral. State True/False- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The integral form of potential and field relation is given by line integral. State True/False
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Vaishnavi Singh answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Vab = -∫ E.dl is the relation between potential and field. It is clear that it is given by line integral.
Explanation: Vab = -∫ E.dl is the relation between potential and field. It is clear that it is given by line integral.
Find whether the vector is solenoidal, E = yz i + xz j + xy k- a)Yes, solenoidal
- b)No, non-solenoidal
- c)Solenoidal with negative divergence
- d)Variable divergence
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find whether the vector is solenoidal, E = yz i + xz j + xy k
a)
Yes, solenoidal
b)
No, non-solenoidal
c)
Solenoidal with negative divergence
d)
Variable divergence
|
|
Sarthak Yadav answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Div(E) = Dx(yz) + Dy(xz) + Dz(xy) = 0. The divergence is zero, thus vector is divergentless or solenoidal.
Explanation: Div(E) = Dx(yz) + Dy(xz) + Dz(xy) = 0. The divergence is zero, thus vector is divergentless or solenoidal.
Divergence of gradient of a vector function is equivalent to- a)Laplacian operation
- b)Curl operation
- c)Double gradient operation
- d)Null vector
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Divergence of gradient of a vector function is equivalent to
a)
Laplacian operation
b)
Curl operation
c)
Double gradient operation
d)
Null vector
|
|
Juhi Joshi answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Div (Grad V) = (Del)2V, which is the Laplacian operation. A function is said to be harmonic in nature, when its Laplacian tends to zero.
Explanation: Div (Grad V) = (Del)2V, which is the Laplacian operation. A function is said to be harmonic in nature, when its Laplacian tends to zero.
If a function is said to be harmonic, then- a)Curl(Grad V) = 0
- b)Div(Curl V) = 0
- c)Div(Grad V) = 0
- d)Grad(Curl V) = 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a function is said to be harmonic, then
a)
Curl(Grad V) = 0
b)
Div(Curl V) = 0
c)
Div(Grad V) = 0
d)
Grad(Curl V) = 0
|
|
Sneha Bose answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Though option a & b are also correct, for harmonic fields, the Laplacian of electric potential is zero. Now, Laplacian refers to Div(Grad V), which is zero for harmonic fields.
Explanation: Though option a & b are also correct, for harmonic fields, the Laplacian of electric potential is zero. Now, Laplacian refers to Div(Grad V), which is zero for harmonic fields.
When gradient of a function is zero, the function lies parallel to the x-axis. State True/False. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When gradient of a function is zero, the function lies parallel to the x-axis. State True/False.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Harsh Kulkarni answered |
True
Explanation:
When the gradient of a function is zero, it means that the derivative of the function with respect to the independent variable is zero at that point. In the case of a function of one variable, such as f(x), the derivative represents the rate of change of the function with respect to x.
When the derivative is zero, it means that the function is not changing at that point, and hence the graph of the function is parallel to the x-axis. This is because the slope of the tangent line to the graph at that point is zero, which means that the tangent line is horizontal and parallel to the x-axis.
To understand this concept further, let's consider an example:
Let's say we have a function f(x) = x^2. The derivative of this function with respect to x is f'(x) = 2x.
To find the points where the gradient is zero, we set the derivative equal to zero and solve for x:
2x = 0
x = 0
So, at x = 0, the gradient of the function is zero. This means that the function f(x) = x^2 is parallel to the x-axis at x = 0.
In general, when the gradient of a function is zero, it means that the function is not changing at that point and is parallel to the x-axis. Therefore, the statement "When the gradient of a function is zero, the function lies parallel to the x-axis" is true.
Explanation:
When the gradient of a function is zero, it means that the derivative of the function with respect to the independent variable is zero at that point. In the case of a function of one variable, such as f(x), the derivative represents the rate of change of the function with respect to x.
When the derivative is zero, it means that the function is not changing at that point, and hence the graph of the function is parallel to the x-axis. This is because the slope of the tangent line to the graph at that point is zero, which means that the tangent line is horizontal and parallel to the x-axis.
To understand this concept further, let's consider an example:
Let's say we have a function f(x) = x^2. The derivative of this function with respect to x is f'(x) = 2x.
To find the points where the gradient is zero, we set the derivative equal to zero and solve for x:
2x = 0
x = 0
So, at x = 0, the gradient of the function is zero. This means that the function f(x) = x^2 is parallel to the x-axis at x = 0.
In general, when the gradient of a function is zero, it means that the function is not changing at that point and is parallel to the x-axis. Therefore, the statement "When the gradient of a function is zero, the function lies parallel to the x-axis" is true.
Compute divergence theorem for D = 5r2/4 i in spherical coordinates between r = 1 and r = 2 in volume integral.- a)80 π
- b)5 π
- c)75 π
- d)85 π
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Compute divergence theorem for D = 5r2/4 i in spherical coordinates between r = 1 and r = 2 in volume integral.
a)
80 π
b)
5 π
c)
75 π
d)
85 π
|
|
Mahesh Datta answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: D.ds = ∫∫∫ Div (D) dv, where RHS needs to be computed.
The divergence of D given is, Div(D) = 5r and dv = r2 sin θ dr dθ dφ. On integrating, r = 1->2, φ = 0->2π and θ = 0->π, we get Q = 75 π.
Explanation: D.ds = ∫∫∫ Div (D) dv, where RHS needs to be computed.
The divergence of D given is, Div(D) = 5r and dv = r2 sin θ dr dθ dφ. On integrating, r = 1->2, φ = 0->2π and θ = 0->π, we get Q = 75 π.
If a unit positive charge is placed inside a sphere of radius r, then the electric flux through the sphere will be:- a)ϵor
- b)ϵo/r
- c)ϵo-1
- d)ϵo
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a unit positive charge is placed inside a sphere of radius r, then the electric flux through the sphere will be:
a)
ϵor
b)
ϵo/r
c)
ϵo-1
d)
ϵo
|
|
Pooja Patel answered |
CONCEPT:
Gauss's law:
Gauss's law:
- According to Gauss law, the total electric flux linked with a closed surface called Gaussian surface is 1/ϵo the charge enclosed by the closed surface.
⇒ ϕ = Q/ϵo
Where ϕ = electric flux linked with a closed surface, Q = total charge enclosed in the surface, and ϵo = permittivity
Given Q = 1, and r = radius of the sphere
By the Gauss law, if the total charge enclosed in a closed surface is Q, then the total electric flux associated with it will be given as,
⇒ ϕ = Q/ϵo -----(1)
By equation 1 the total flux linked with the sphere is given as,
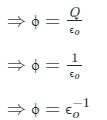
Hence, option 3 is correct.
Where ϕ = electric flux linked with a closed surface, Q = total charge enclosed in the surface, and ϵo = permittivity
Given Q = 1, and r = radius of the sphere
By the Gauss law, if the total charge enclosed in a closed surface is Q, then the total electric flux associated with it will be given as,
⇒ ϕ = Q/ϵo -----(1)
By equation 1 the total flux linked with the sphere is given as,
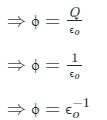
Hence, option 3 is correct.
Two charges of + 4 μC and -16 μC are separated from each other by a distance of 0.6 m. At what distance should a third charge of + 6 μC be placed from + 4 μC so that net force exerts on it will be zero?- a)0.4 m
- b)0.6 m
- c)1.2 m
- d)0.3 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two charges of + 4 μC and -16 μC are separated from each other by a distance of 0.6 m. At what distance should a third charge of + 6 μC be placed from + 4 μC so that net force exerts on it will be zero?
a)
0.4 m
b)
0.6 m
c)
1.2 m
d)
0.3 m
|
|
Gayatri Menon answered |
The given information is incomplete. Please provide more information about the charges.
The ultimate result of the divergence theorem evaluates which one of the following?- a)Field intensity
- b)Field density
- c)Potential
- d)Charge and flux
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The ultimate result of the divergence theorem evaluates which one of the following?
a)
Field intensity
b)
Field density
c)
Potential
d)
Charge and flux
|
|
Subham Chaudhary answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Gauss law states that the electric flux passing through any closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by the surface. Thus, it is given by, ψ = ∫∫ D.ds= Q, where the divergence theorem computes the charge and flux, which are both the same.
Explanation: Gauss law states that the electric flux passing through any closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by the surface. Thus, it is given by, ψ = ∫∫ D.ds= Q, where the divergence theorem computes the charge and flux, which are both the same.
The Gauss divergence theorem converts- a)line to surface integral
- b)line to volume integral
- c)surface to line integral
- d)surface to volume integral
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Gauss divergence theorem converts
a)
line to surface integral
b)
line to volume integral
c)
surface to line integral
d)
surface to volume integral
|
|
Debanshi Basak answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: The divergence theorem for a function F is given by ∫∫ F.dS = ∫∫∫ Div (F).dV. Thus it converts surface to volume integral
Explanation: The divergence theorem for a function F is given by ∫∫ F.dS = ∫∫∫ Div (F).dV. Thus it converts surface to volume integral
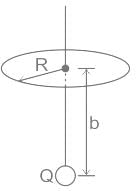
A point charge Q is located on the axis of a disk of radius R at a distance b from the plane of the disk as shown in below figure. Find the value of R, if 1/4th of the electric flux from the charge passes through the disk?
- a)
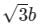
- b)
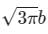
- c)
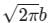
- d)
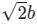
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A point charge Q is located on the axis of a disk of radius R at a distance b from the plane of the disk as shown in below figure. Find the value of R, if 1/4th of the electric flux from the charge passes through the disk?


a)
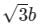
b)
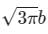
c)
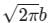
d)
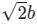

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Concept:
We know that the flux passing through a segment which makes angle θ at the center of the circle is:
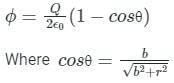
Calculation:
Given if 1/4th of the flux passes through the disk
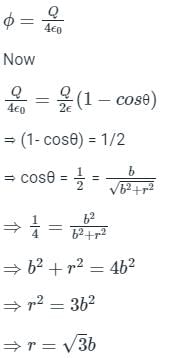
We know that the flux passing through a segment which makes angle θ at the center of the circle is:
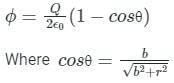
Calculation:
Given if 1/4th of the flux passes through the disk
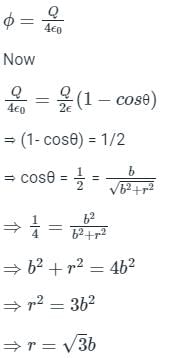
The volume integral is three dimensional. State True/False- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume integral is three dimensional. State True/False
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Aarya Basu answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: Volume integral integrates the independent quantities by three times. Thus it is said to be three dimensional integral or triple integral.
Explanation: Volume integral integrates the independent quantities by three times. Thus it is said to be three dimensional integral or triple integral.
When a potential satisfies Laplace equation, then it is said to be- a)Solenoidal
- b)Divergent
- c)Lamellar
- d)Harmonic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a potential satisfies Laplace equation, then it is said to be
a)
Solenoidal
b)
Divergent
c)
Lamellar
d)
Harmonic
|
|
Jyoti Basak answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: A field satisfying the Laplace equation is termed as harmonic field.
Explanation: A field satisfying the Laplace equation is termed as harmonic field.
Find the Laplace equation value of the following potential field
V = ρ cosφ + z- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the Laplace equation value of the following potential field
V = ρ cosφ + z
V = ρ cosφ + z
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Dipanjan Nambiar answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: (Del)2 (ρ cosφ + z)= (cos φ/r) – (cos φ/r) + 0
= 0, this satisfies Laplace equation. The value is 0.
Explanation: (Del)2 (ρ cosφ + z)= (cos φ/r) – (cos φ/r) + 0
= 0, this satisfies Laplace equation. The value is 0.
Compute the Gauss law for D= 10ρ3/4 i, in cylindrical coordinates with ρ= 4m, z=0 and z=5.- a)6100 π
- b)6200 π
- c)6300 π
- d)6400 π
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Compute the Gauss law for D= 10ρ3/4 i, in cylindrical coordinates with ρ= 4m, z=0 and z=5.
a)
6100 π
b)
6200 π
c)
6300 π
d)
6400 π
|
|
Srestha Gupta answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: ∫∫ D.ds = ∫∫ (10ρ3/4).(ρ dφ dz), which is the integral to be evaluated. Put ρ = 4m, z = 0→5 and φ = 0→2π, the integral evaluates to 6400π.
Explanation: ∫∫ D.ds = ∫∫ (10ρ3/4).(ρ dφ dz), which is the integral to be evaluated. Put ρ = 4m, z = 0→5 and φ = 0→2π, the integral evaluates to 6400π.
Find the curl of the vector and state its nature at (1,1,-0.2)F = 30 i + 2xy j + 5xz2 k- a)√4.01
- b)√4.02
- c)√4.03
- d)√4.04
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the curl of the vector and state its nature at (1,1,-0.2)F = 30 i + 2xy j + 5xz2 k
a)
√4.01
b)
√4.02
c)
√4.03
d)
√4.04
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Curl F = -5z^2 j + 2y k. At (1,1,-0.2), Curl F = -0.2 j + 2 k. |Curl F| = √(-0.2^2+2^2) = √4.04.
Curl cannot be employed in which one of the following?- a)Directional coupler
- b)Magic Tee
- c)Isolator and Terminator
- d)Waveguides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Curl cannot be employed in which one of the following?
a)
Directional coupler
b)
Magic Tee
c)
Isolator and Terminator
d)
Waveguides
|
|
Maulik Choudhury answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: In the options a, b, c, the EM waves travel both in linear and angular motion, which involves curl too. But in waveguides, as the name suggests, only guided propagation occurs (no bending or curl of waves).
Explanation: In the options a, b, c, the EM waves travel both in linear and angular motion, which involves curl too. But in waveguides, as the name suggests, only guided propagation occurs (no bending or curl of waves).
The electric flux from a cube of side ‘a’ is ‘Φ’. What will be its value if the side of the cube is made ‘2a’ and the charge enclosed is made half?- a)Φ/2
- b)Φ
- c)4 Φ
- d)2 Φ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The electric flux from a cube of side ‘a’ is ‘Φ’. What will be its value if the side of the cube is made ‘2a’ and the charge enclosed is made half?
a)
Φ/2
b)
Φ
c)
4 Φ
d)
2 Φ
|
|
Sushant Mukherjee answered |
Understanding Electric Flux
Electric flux is defined as the flow of electric field through a surface. According to Gauss's Law, the electric flux (Φ) through a closed surface is proportional to the charge (Q) enclosed by that surface:
Φ = Q / ε₀
where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space.
Scenario 1: Original Cube
- Consider a cube with side length 'a.'
- The electric flux through this cube is given as Φ.
- The charge enclosed in this cube is Q.
Scenario 2: Modified Cube
- The side of the cube is now doubled to '2a.'
- The volume of the cube increases, but the charge enclosed is halved (Q/2).
Applying Gauss's Law
- For the new cube, using Gauss's Law:
Φ' = Q' / ε₀
- Since the new charge Q' = Q/2, we have:
Φ' = (Q/2) / ε₀
Relating New Flux to Original Flux
- The original flux Φ was:
Φ = Q / ε₀
- Therefore, substituting Q' into the equation for the new electric flux:
Φ' = (1/2) * (Q / ε₀) = (1/2) * Φ
Final Answer
- The electric flux for the cube with side '2a' and half the enclosed charge is:
Φ' = Φ / 2
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A' (Φ/2).
Electric flux is defined as the flow of electric field through a surface. According to Gauss's Law, the electric flux (Φ) through a closed surface is proportional to the charge (Q) enclosed by that surface:
Φ = Q / ε₀
where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space.
Scenario 1: Original Cube
- Consider a cube with side length 'a.'
- The electric flux through this cube is given as Φ.
- The charge enclosed in this cube is Q.
Scenario 2: Modified Cube
- The side of the cube is now doubled to '2a.'
- The volume of the cube increases, but the charge enclosed is halved (Q/2).
Applying Gauss's Law
- For the new cube, using Gauss's Law:
Φ' = Q' / ε₀
- Since the new charge Q' = Q/2, we have:
Φ' = (Q/2) / ε₀
Relating New Flux to Original Flux
- The original flux Φ was:
Φ = Q / ε₀
- Therefore, substituting Q' into the equation for the new electric flux:
Φ' = (1/2) * (Q / ε₀) = (1/2) * Φ
Final Answer
- The electric flux for the cube with side '2a' and half the enclosed charge is:
Φ' = Φ / 2
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A' (Φ/2).
Find the value of Stoke’s theorem for A = x i + y j + z k. The state of the function will be- a)Solenoidal
- b)Divergent
- c)Rotational
- d)Curl free
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of Stoke’s theorem for A = x i + y j + z k. The state of the function will be
a)
Solenoidal
b)
Divergent
c)
Rotational
d)
Curl free
|
|
Athul Banerjee answered |
The term "Stoke" could refer to multiple things, so it is important to clarify the context in which it is being used. Here are some possible interpretations:
1. Stoke as a city: Stoke-on-Trent is a city in Staffordshire, England. As of 2021, the estimated population of Stoke-on-Trent is around 256,400 people.
2. Stoke as a unit of measurement: Stoke is a unit used to measure kinematic viscosity in fluid mechanics. It is equal to 1 cm^2/s.
3. Stoke as a surname: Stoke could be a surname of a person. The value of Stoke as a surname would be subjective and depend on the individual or family associated with it.
If you provide more information or specify the context in which you are referring to "Stoke," I can provide a more accurate answer.
1. Stoke as a city: Stoke-on-Trent is a city in Staffordshire, England. As of 2021, the estimated population of Stoke-on-Trent is around 256,400 people.
2. Stoke as a unit of measurement: Stoke is a unit used to measure kinematic viscosity in fluid mechanics. It is equal to 1 cm^2/s.
3. Stoke as a surname: Stoke could be a surname of a person. The value of Stoke as a surname would be subjective and depend on the individual or family associated with it.
If you provide more information or specify the context in which you are referring to "Stoke," I can provide a more accurate answer.
The voltage of a capacitor 12F with a rating of 2J energy is- a)0.57
- b)5.7
- c)57
- d)570
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The voltage of a capacitor 12F with a rating of 2J energy is
a)
0.57
b)
5.7
c)
57
d)
570
|
|
Mainak Pillai answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: We can compute the energy stored in a capacitor from Stoke’s theorem as 0.5Cv2. Thus given energy is 0.5 X 12 X v2. We get v = 0.57 volts.
Explanation: We can compute the energy stored in a capacitor from Stoke’s theorem as 0.5Cv2. Thus given energy is 0.5 X 12 X v2. We get v = 0.57 volts.
If V = 2x2y – 5z, find its electric field at point (-4,3,6)
- a)47.905
- b)57.905
- c)67.905
- d)77.905
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If V = 2x2y – 5z, find its electric field at point (-4,3,6)
a)
47.905
b)
57.905
c)
67.905
d)
77.905
|
|
Alok Khanna answered |
The electric field (E) at a point in space is the force per unit charge experienced by a test charge at that point, hence the unit of E is newton per coulomb (N/C). The electric field is defined as E = - grad V
where grad is the gradient operator and V is the electric potential.
If V = 2x²y - 5z
the electric field at point (-4, 3, 6) is given as follows:
E = - grad V
From the formula above, the gradient of V = (2x²y - 5z)
is given by grad V = (dV/dx)i + (dV/dy)j + (dV/dz)k
Where i, j and k are the unit vectors along the x, y and z axes respectively.
Thus,grad V = (4xy)i + (2x²)j - 5k
Now, evaluating at (-4, 3, 6)
we get the electric field,E = - grad V
=(-4)(3)(4)i + (2)(16)j - (5)k
= -48i + 32j - 5k
Therefore, the electric field at point (-4,3,6) is E = -48i + 32j - 5k
which implies that the magniture of the electric field is given by sqrt[(-48)² + (32)² + (-5)²] = 57.905 N/C.
Find the value of Green’s theorem for F = x2 and G = y2 is- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the value of Green’s theorem for F = x2 and G = y2 is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Sarthak Yadav answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: ∫∫(dG/dx – dF/dy)dx dy = ∫∫(0 – 0)dx dy = 0. The value of Green’s theorem gives zero for the functions given.
Explanation: ∫∫(dG/dx – dF/dy)dx dy = ∫∫(0 – 0)dx dy = 0. The value of Green’s theorem gives zero for the functions given.
Which of the following theorem use the curl operation?- a)Green’s theorem
- b)Gauss Divergence theorem
- c)Stoke’s theorem
- d)Maxwell equation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following theorem use the curl operation?
a)
Green’s theorem
b)
Gauss Divergence theorem
c)
Stoke’s theorem
d)
Maxwell equation
|
|
Tanishq Chauhan answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: The Stoke’s theorem is given by ∫ A.dl = ∫Curl(A).ds, which uses the curl operation. There can be confusion with Maxwell equation also, but it uses curl in electromagnetics specifically, whereas the Stoke’s theorem uses it in a generalised manner. Thus the best option is c.
Explanation: The Stoke’s theorem is given by ∫ A.dl = ∫Curl(A).ds, which uses the curl operation. There can be confusion with Maxwell equation also, but it uses curl in electromagnetics specifically, whereas the Stoke’s theorem uses it in a generalised manner. Thus the best option is c.
Find the gradient of the function given by, x2 + y2 + z2 at (1,1,1)- a)i + j + k
- b)2i + 2j + 2k
- c)2xi + 2yj + 2zk
- d)4xi + 2yj + 4zk
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the gradient of the function given by, x2 + y2 + z2 at (1,1,1)
a)
i + j + k
b)
2i + 2j + 2k
c)
2xi + 2yj + 2zk
d)
4xi + 2yj + 4zk
|
|
Rajesh Verma answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Grad(x2+y2+z2) = 2xi + 2yj + 2zk. Put x=1, y=1, z=1, the gradient will be 2i + 2j + 2k.
Explanation: Grad(x2+y2+z2) = 2xi + 2yj + 2zk. Put x=1, y=1, z=1, the gradient will be 2i + 2j + 2k.
Chapter doubts & questions for Coordinate System & Vector Analysis - Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Coordinate System & Vector Analysis - Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT) in English & Hindi are available as part of Electrical Engineering (EE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Electromagnetic Fields Theory (EMFT)
10 videos|45 docs|56 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











