NEET Exam > NEET Questions > In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or ...
Start Learning for Free
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG?
Most Upvoted Answer
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proporti...
Introduction:
Pisum sativum is a plant species that exhibits a variety of traits. One of these traits is the color of the pods, which can be either green or yellow. The color of the pods is determined by the genotype of the plant, with the dominant allele being G for green and the recessive allele being g for yellow. This means that an individual with GG or Gg genotype will have green pods, while an individual with gg genotype will have yellow pods.
Expected Proportions:
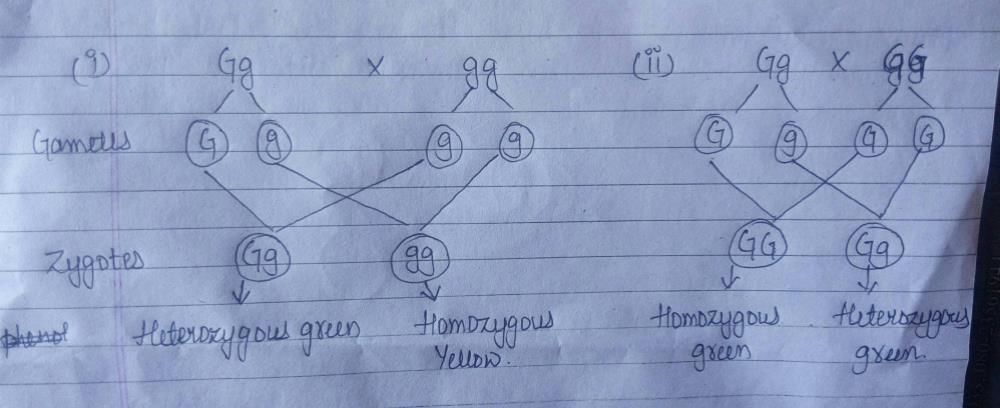
1. Gg x gg cross:
When Gg (heterozygous) is crossed with gg (homozygous recessive), the offspring will be:
- 50% Gg (heterozygous green)
- 50% gg (homozygous recessive yellow)
Therefore, the proportion of offspring that would be expected to be homozygous green is 0.
2. Gg x GG cross:
When Gg (heterozygous) is crossed with GG (homozygous dominant), the offspring will be:
- 50% Gg (heterozygous green)
- 50% GG (homozygous dominant green)
Therefore, the proportion of offspring that would be expected to be homozygous green is 50%.
Explanation:
The reason why no offspring are expected to be homozygous green in the Gg x gg cross is that gg is homozygous recessive for the yellow pod color, and Gg is heterozygous for the green pod color. This means that for a green pod color to be expressed, the dominant G allele must be present. Since gg is homozygous recessive, it can only contribute the recessive g allele, which means that all of the offspring will be heterozygous Gg.
On the other hand, in the Gg x GG cross, GG is homozygous dominant for the green pod color, and Gg is heterozygous for the green pod color. This means that every offspring will have at least one dominant G allele, which will result in a green pod color. Half of the offspring will inherit the dominant G allele from both parents, resulting in homozygous green offspring.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the expected proportion of offspring that would be homozygous green in a cross between Gg x gg is 0, while the expected proportion of offspring that would be homozygous green in a cross between Gg x GG is 50%. This is due to the different genotypes of the parents and the inheritance patterns of the G and g alleles that determine the color of the pods in Pisum sativum.
Pisum sativum is a plant species that exhibits a variety of traits. One of these traits is the color of the pods, which can be either green or yellow. The color of the pods is determined by the genotype of the plant, with the dominant allele being G for green and the recessive allele being g for yellow. This means that an individual with GG or Gg genotype will have green pods, while an individual with gg genotype will have yellow pods.
Expected Proportions:
1. Gg x gg cross:
When Gg (heterozygous) is crossed with gg (homozygous recessive), the offspring will be:
- 50% Gg (heterozygous green)
- 50% gg (homozygous recessive yellow)
Therefore, the proportion of offspring that would be expected to be homozygous green is 0.
2. Gg x GG cross:
When Gg (heterozygous) is crossed with GG (homozygous dominant), the offspring will be:
- 50% Gg (heterozygous green)
- 50% GG (homozygous dominant green)
Therefore, the proportion of offspring that would be expected to be homozygous green is 50%.
Explanation:
The reason why no offspring are expected to be homozygous green in the Gg x gg cross is that gg is homozygous recessive for the yellow pod color, and Gg is heterozygous for the green pod color. This means that for a green pod color to be expressed, the dominant G allele must be present. Since gg is homozygous recessive, it can only contribute the recessive g allele, which means that all of the offspring will be heterozygous Gg.
On the other hand, in the Gg x GG cross, GG is homozygous dominant for the green pod color, and Gg is heterozygous for the green pod color. This means that every offspring will have at least one dominant G allele, which will result in a green pod color. Half of the offspring will inherit the dominant G allele from both parents, resulting in homozygous green offspring.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the expected proportion of offspring that would be homozygous green in a cross between Gg x gg is 0, while the expected proportion of offspring that would be homozygous green in a cross between Gg x GG is 50%. This is due to the different genotypes of the parents and the inheritance patterns of the G and g alleles that determine the color of the pods in Pisum sativum.
Community Answer
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proporti...

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG?
Question Description
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG?.
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG?.
Solutions for In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG?, a detailed solution for In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? has been provided alongside types of In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In pisum sativum the pods may be green(G) or yellow (g). What proportion of the offspring in the following crosses would be expected to be homozygous green? (1)Gg×gg (2)Gg ×GG? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.