Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > what is the difference between hypertonic and...
Start Learning for Free
what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution?
Most Upvoted Answer
what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution?
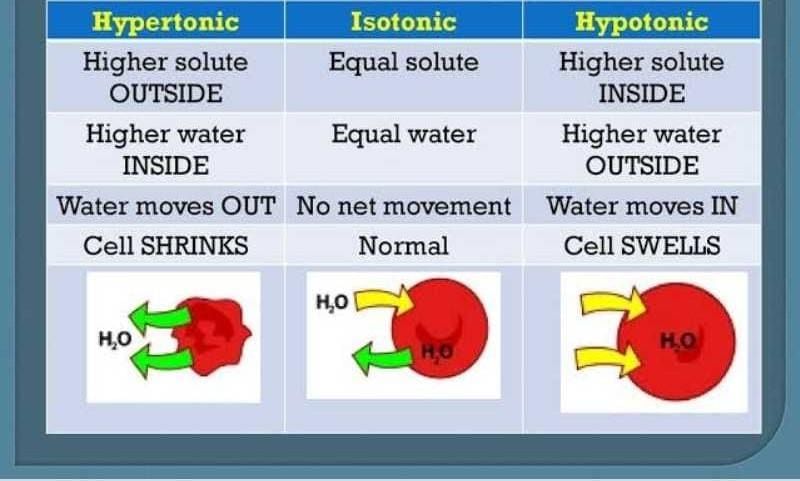
Community Answer
what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution?
Difference between Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions
Hypertonic and hypotonic solutions are terms used to describe the concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution or a cell. These terms are commonly used in biology and chemistry to explain the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane. Understanding the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions is essential to comprehend osmosis, the process by which water moves across membranes.
Hypertonic Solution:
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes (such as salts or sugars) compared to another solution or a cell. In this solution, water molecules tend to move out of the cell or across the membrane into the region with higher solute concentration.
Hypotonic Solution:
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution or a cell. In this solution, water molecules tend to move into the cell or across the membrane into the region with lower solute concentration.
Key Differences:
1. Concentration Gradient:
In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside, creating a concentration gradient that drives the movement of water out of the cell. Conversely, in a hypotonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is lower than inside, creating a concentration gradient that drives the movement of water into the cell.
2. Cell Behavior:
In a hypertonic solution, cells tend to shrink or shrivel due to the loss of water, a process known as crenation in animal cells and plasmolysis in plant cells. On the other hand, in a hypotonic solution, cells tend to swell or burst due to the intake of water, a process called lysis.
3. Osmosis Direction:
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. In a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cell or across the membrane towards the higher solute concentration. In a hypotonic solution, water moves into the cell or across the membrane towards the lower solute concentration.
4. Effect on Biological Systems:
Hypertonic solutions can cause dehydration and cell damage due to the loss of water from cells. They are commonly used in preserving food by creating an environment where bacteria and other microorganisms cannot survive. Hypotonic solutions, on the other hand, can cause cells to swell and burst, leading to cell damage. They are often used in medical settings for rehydration purposes.
In summary, the key difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions lies in the concentration of solutes and the resulting movement of water. Hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration and cause water to move out of cells, while hypotonic solutions have a lower solute concentration and cause water to move into cells. Understanding these concepts is crucial in various biological and chemical processes, including osmosis and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Hypertonic and hypotonic solutions are terms used to describe the concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution or a cell. These terms are commonly used in biology and chemistry to explain the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane. Understanding the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions is essential to comprehend osmosis, the process by which water moves across membranes.
Hypertonic Solution:
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes (such as salts or sugars) compared to another solution or a cell. In this solution, water molecules tend to move out of the cell or across the membrane into the region with higher solute concentration.
Hypotonic Solution:
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution or a cell. In this solution, water molecules tend to move into the cell or across the membrane into the region with lower solute concentration.
Key Differences:
1. Concentration Gradient:
In a hypertonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside, creating a concentration gradient that drives the movement of water out of the cell. Conversely, in a hypotonic solution, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is lower than inside, creating a concentration gradient that drives the movement of water into the cell.
2. Cell Behavior:
In a hypertonic solution, cells tend to shrink or shrivel due to the loss of water, a process known as crenation in animal cells and plasmolysis in plant cells. On the other hand, in a hypotonic solution, cells tend to swell or burst due to the intake of water, a process called lysis.
3. Osmosis Direction:
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. In a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cell or across the membrane towards the higher solute concentration. In a hypotonic solution, water moves into the cell or across the membrane towards the lower solute concentration.
4. Effect on Biological Systems:
Hypertonic solutions can cause dehydration and cell damage due to the loss of water from cells. They are commonly used in preserving food by creating an environment where bacteria and other microorganisms cannot survive. Hypotonic solutions, on the other hand, can cause cells to swell and burst, leading to cell damage. They are often used in medical settings for rehydration purposes.
In summary, the key difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions lies in the concentration of solutes and the resulting movement of water. Hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration and cause water to move out of cells, while hypotonic solutions have a lower solute concentration and cause water to move into cells. Understanding these concepts is crucial in various biological and chemical processes, including osmosis and maintaining cellular homeostasis.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Question Description
what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution?.
what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution?.
Solutions for what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution?, a detailed solution for what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? has been provided alongside types of what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



























