Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]
- a)Ethyl chloride
- b)Isopropyl chlor ide
- c)Chlorobenzene
- d)Benzyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively...
SN1 reaction is favour ed by heavy gr oups on the carbon atom attached to halogen i.e Benzyl > allyl > tertiary > primary > secondary > primary > alkyl halides
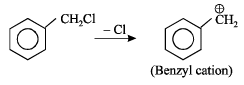
Obtained from SN1 path.
This molecule is resonance stabilised.
This molecule is resonance stabilised.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively...
Explanation:
Nucleophilic substitution reactions can proceed via two mechanisms: SN1 (substitution nucleophilic unimolecular) and SN2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular). The choice of mechanism depends on the nature of the substrate and the nucleophile.
SN1 Mechanism:
- In SN1 mechanism, the reaction proceeds in two steps: the formation of a carbocation intermediate followed by the attack of a nucleophile on the carbocation.
- This mechanism is favored when the substrate is a tertiary alkyl halide or a benzylic/allylic halide.
- The rate of the reaction depends only on the concentration of the substrate, as the nucleophile attacks the carbocation formed independently of its concentration.
- The leaving group leaves before the nucleophile attacks, resulting in a racemic mixture of products if the carbocation is chiral.
SN2 Mechanism:
- In SN2 mechanism, the reaction proceeds in a single step where the nucleophile attacks the substrate and displaces the leaving group.
- This mechanism is favored when the substrate is a primary or methyl alkyl halide.
- The rate of the reaction depends on both the concentration of the substrate and the nucleophile, as the nucleophile directly attacks the substrate.
- The stereochemistry of the product is inverted (Walden inversion) due to the backside attack of the nucleophile.
Analysis of the options:
a) Ethyl chloride - Ethyl chloride is a primary alkyl halide, and primary halides typically undergo nucleophilic substitution via the SN2 mechanism. Therefore, it does not exclusively undergo SN1 mechanism.
b) Isopropyl chloride - Isopropyl chloride is a secondary alkyl halide, and secondary halides can undergo nucleophilic substitution via both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. Therefore, it does not exclusively undergo SN1 mechanism.
c) Chlorobenzene - Chlorobenzene is an aryl halide, and aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution via either SN1 or SN2 mechanisms. Therefore, it does not undergo SN1 mechanism.
d) Benzyl chloride - Benzyl chloride is a benzylic halide, which is a type of substrate that prefers the SN1 mechanism. The benzyl carbocation formed in the first step is stabilized by resonance, making the SN1 mechanism more favorable. Therefore, it exclusively undergoes nucleophilic substitution via the SN1 mechanism.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Benzyl chloride.
Nucleophilic substitution reactions can proceed via two mechanisms: SN1 (substitution nucleophilic unimolecular) and SN2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular). The choice of mechanism depends on the nature of the substrate and the nucleophile.
SN1 Mechanism:
- In SN1 mechanism, the reaction proceeds in two steps: the formation of a carbocation intermediate followed by the attack of a nucleophile on the carbocation.
- This mechanism is favored when the substrate is a tertiary alkyl halide or a benzylic/allylic halide.
- The rate of the reaction depends only on the concentration of the substrate, as the nucleophile attacks the carbocation formed independently of its concentration.
- The leaving group leaves before the nucleophile attacks, resulting in a racemic mixture of products if the carbocation is chiral.
SN2 Mechanism:
- In SN2 mechanism, the reaction proceeds in a single step where the nucleophile attacks the substrate and displaces the leaving group.
- This mechanism is favored when the substrate is a primary or methyl alkyl halide.
- The rate of the reaction depends on both the concentration of the substrate and the nucleophile, as the nucleophile directly attacks the substrate.
- The stereochemistry of the product is inverted (Walden inversion) due to the backside attack of the nucleophile.
Analysis of the options:
a) Ethyl chloride - Ethyl chloride is a primary alkyl halide, and primary halides typically undergo nucleophilic substitution via the SN2 mechanism. Therefore, it does not exclusively undergo SN1 mechanism.
b) Isopropyl chloride - Isopropyl chloride is a secondary alkyl halide, and secondary halides can undergo nucleophilic substitution via both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. Therefore, it does not exclusively undergo SN1 mechanism.
c) Chlorobenzene - Chlorobenzene is an aryl halide, and aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution via either SN1 or SN2 mechanisms. Therefore, it does not undergo SN1 mechanism.
d) Benzyl chloride - Benzyl chloride is a benzylic halide, which is a type of substrate that prefers the SN1 mechanism. The benzyl carbocation formed in the first step is stabilized by resonance, making the SN1 mechanism more favorable. Therefore, it exclusively undergoes nucleophilic substitution via the SN1 mechanism.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Benzyl chloride.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism? [2005]a)Ethyl chlorideb)Isopropyl chlor idec)Chlorobenzened)Benzyl chlorideCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























