Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex ...
Start Learning for Free
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4 )2(H2O)2]2- is :
- a)+2
- b)+3
- c)+4
- d)+5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O...
Let the O. N. of Mo in the complex is x
2x + (–2) × 2 + 0 × 2 + 0 × 2 = – 2
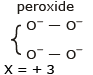
2x + (–2) × 2 + 0 × 2 + 0 × 2 = – 2
Most Upvoted Answer
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O...
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2- is 3.
In order to determine the oxidation state of Mo in the given oxo-complex species, we need to consider the oxidation states of the other elements present in the compound and the overall charge of the complex.
Step 1: Identify the oxidation state of the other elements
- Oxygen (O) typically has an oxidation state of -2.
- Hydrogen (H) typically has an oxidation state of +1.
- Carbon (C) typically has an oxidation state of +4.
- Ethene (C2H4) is a neutral molecule, so the sum of the oxidation states of carbon and hydrogen is zero.
Step 2: Determine the overall charge of the complex
The overall charge of the complex is 2-, which means that the sum of the oxidation states of all the elements in the complex must equal -2.
Step 3: Assign the oxidation state of Mo
Let's assume the oxidation state of Mo in the complex is x.
- The oxidation state of O is -2, and there are a total of 4 oxygen atoms in the complex. So, the total oxidation state contribution from O is -8.
- The oxidation state of H is +1, and there are a total of 2 hydrogen atoms in the complex. So, the total oxidation state contribution from H is +2.
- The oxidation state of C is +4, and there are a total of 2 carbon atoms in the complex (from C2H4). So, the total oxidation state contribution from C is +8.
The sum of the oxidation state contributions from O, H, and C is: -8 + 2 + 8 = +2.
Since the overall charge of the complex is 2-, the sum of the oxidation state contributions from all elements must equal -2. Therefore, we can set up the equation: x + 2 = -2.
Solving for x, we find that x = -2 - 2 = -4.
Therefore, the oxidation state of Mo in the complex is -4.
However, the oxidation state of Mo cannot be negative, as it is a transition metal. Therefore, we need to consider the d-electron count of Mo to determine its oxidation state.
Step 4: Consider the d-electron count of Mo
In the given complex, Mo is in the +3 oxidation state. This means that Mo has lost 3 electrons.
Mo is a transition metal, and its d-orbitals have a maximum capacity of 10 electrons. By losing 3 electrons, Mo retains 7 electrons in its d-orbitals, which corresponds to the +3 oxidation state.
Therefore, the oxidation state of Mo in the oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2- is 3.
In order to determine the oxidation state of Mo in the given oxo-complex species, we need to consider the oxidation states of the other elements present in the compound and the overall charge of the complex.
Step 1: Identify the oxidation state of the other elements
- Oxygen (O) typically has an oxidation state of -2.
- Hydrogen (H) typically has an oxidation state of +1.
- Carbon (C) typically has an oxidation state of +4.
- Ethene (C2H4) is a neutral molecule, so the sum of the oxidation states of carbon and hydrogen is zero.
Step 2: Determine the overall charge of the complex
The overall charge of the complex is 2-, which means that the sum of the oxidation states of all the elements in the complex must equal -2.
Step 3: Assign the oxidation state of Mo
Let's assume the oxidation state of Mo in the complex is x.
- The oxidation state of O is -2, and there are a total of 4 oxygen atoms in the complex. So, the total oxidation state contribution from O is -8.
- The oxidation state of H is +1, and there are a total of 2 hydrogen atoms in the complex. So, the total oxidation state contribution from H is +2.
- The oxidation state of C is +4, and there are a total of 2 carbon atoms in the complex (from C2H4). So, the total oxidation state contribution from C is +8.
The sum of the oxidation state contributions from O, H, and C is: -8 + 2 + 8 = +2.
Since the overall charge of the complex is 2-, the sum of the oxidation state contributions from all elements must equal -2. Therefore, we can set up the equation: x + 2 = -2.
Solving for x, we find that x = -2 - 2 = -4.
Therefore, the oxidation state of Mo in the complex is -4.
However, the oxidation state of Mo cannot be negative, as it is a transition metal. Therefore, we need to consider the d-electron count of Mo to determine its oxidation state.
Step 4: Consider the d-electron count of Mo
In the given complex, Mo is in the +3 oxidation state. This means that Mo has lost 3 electrons.
Mo is a transition metal, and its d-orbitals have a maximum capacity of 10 electrons. By losing 3 electrons, Mo retains 7 electrons in its d-orbitals, which corresponds to the +3 oxidation state.
Therefore, the oxidation state of Mo in the oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2- is 3.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O...
B

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4)2(H2O)2]2-is :a)+2b)+3c)+4d)+5Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















