Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > A solution of potassium bromide is treated wi...
Start Learning for Free
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]
- a)Hydrogen iodide
- b)Sulphur dioxide
- c)chlorine
- d)Iodine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following....
A stronger oxidising agent (Cl2) displaces a weaker oxidising agent (Br2) from its salt solution.
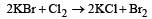
Most Upvoted Answer
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following....
Potassium Bromide and its Reaction
Potassium bromide (KBr) is an ionic compound that is highly soluble in water. When it is dissolved in water, it dissociates into potassium ions (K+) and bromide ions (Br-).
Reactions with Various Substances
When potassium bromide solution is treated with different substances, different reactions occur. Let's examine the reactions with each of the given substances:
a) Hydrogen Iodide (HI)
When potassium bromide is treated with hydrogen iodide, a redox reaction takes place. Hydrogen iodide is a stronger reducing agent than bromide ions, so it can displace bromine from potassium bromide.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
2 KBr + 2 HI → 2 KI + Br2 + H2
This reaction liberates bromine (Br2) as a product. Bromine is a reddish-brown volatile liquid that can be easily identified by its color and odor.
b) Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
Sulphur dioxide does not react with potassium bromide to liberate bromine. Therefore, it is not the correct answer.
c) Chlorine (Cl2)
Chlorine is a highly reactive and powerful oxidizing agent. When chlorine gas is passed through potassium bromide solution, a displacement reaction occurs. Chlorine displaces bromine from potassium bromide and forms potassium chloride.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
2 KBr + Cl2 → 2 KCl + Br2
This reaction liberates bromine (Br2) as a product. However, in this case, chlorine is the reagent that causes the displacement reaction, not the liberated bromine.
d) Iodine (I2)
Iodine does not react with potassium bromide to liberate bromine. Therefore, it is not the correct answer.
Conclusion
Among the given options, only hydrogen iodide (HI) can react with potassium bromide to liberate bromine. The redox reaction between potassium bromide and hydrogen iodide results in the formation of potassium iodide (KI) and bromine (Br2).
Potassium bromide (KBr) is an ionic compound that is highly soluble in water. When it is dissolved in water, it dissociates into potassium ions (K+) and bromide ions (Br-).
Reactions with Various Substances
When potassium bromide solution is treated with different substances, different reactions occur. Let's examine the reactions with each of the given substances:
a) Hydrogen Iodide (HI)
When potassium bromide is treated with hydrogen iodide, a redox reaction takes place. Hydrogen iodide is a stronger reducing agent than bromide ions, so it can displace bromine from potassium bromide.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
2 KBr + 2 HI → 2 KI + Br2 + H2
This reaction liberates bromine (Br2) as a product. Bromine is a reddish-brown volatile liquid that can be easily identified by its color and odor.
b) Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
Sulphur dioxide does not react with potassium bromide to liberate bromine. Therefore, it is not the correct answer.
c) Chlorine (Cl2)
Chlorine is a highly reactive and powerful oxidizing agent. When chlorine gas is passed through potassium bromide solution, a displacement reaction occurs. Chlorine displaces bromine from potassium bromide and forms potassium chloride.
The reaction can be represented as follows:
2 KBr + Cl2 → 2 KCl + Br2
This reaction liberates bromine (Br2) as a product. However, in this case, chlorine is the reagent that causes the displacement reaction, not the liberated bromine.
d) Iodine (I2)
Iodine does not react with potassium bromide to liberate bromine. Therefore, it is not the correct answer.
Conclusion
Among the given options, only hydrogen iodide (HI) can react with potassium bromide to liberate bromine. The redox reaction between potassium bromide and hydrogen iodide results in the formation of potassium iodide (KI) and bromine (Br2).

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]a)Hydrogen iodideb)Sulphur dioxidec)chlorined)IodineCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















