Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueou...
Start Learning for Free
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.
- a)chlorine
- b)fluorine
- c)bromine
- d)iodine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium...
Cl2 + KI → K Cl + I2
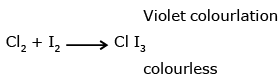
Most Upvoted Answer
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium...
Explanation:
When chlorine gas (Cl2) is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide (e.g., KCl) in the presence of chloroform (CHCl3), a violet coloration is observed. This reaction is specifically used to test for the presence of iodide ions (I-) in the aqueous solution.
1. Formation of Iodine:
The reaction between chlorine gas and iodide ions in the presence of chloroform leads to the formation of molecular iodine (I2). This is represented by the following equation:
2Cl2 + 2KCl + 2CHCl3 → 2KCl + 2HCl + I2
2. Violet Coloration:
The presence of molecular iodine (I2) imparts a violet color to the solution. This is due to the formation of a complex called triiodide ion (I3-) when iodine reacts with excess iodide ions present in the solution. The triiodide ion is responsible for the violet coloration.
3. Disappearance of Violet Color:
When more chlorine water (aqueous chlorine) is added to the solution, it reacts with the iodine present, converting it back to iodide ions. This is represented by the following equation:
I2 + Cl2 → 2ICl
The formation of iodine chloride (ICl) from iodine and chlorine leads to the disappearance of the violet color. The solution becomes colorless because the triiodide ions, responsible for the violet coloration, are converted back to iodide ions.
4. Confirmation of Iodine:
The disappearance of the violet color and the formation of a colorless solution when more chlorine water is added confirms the presence of iodine in the aqueous solution. This reaction is specific to iodine and helps differentiate it from other halogens like chlorine, fluorine, and bromine.
Conclusion:
In summary, the test involving the passage of chlorine gas through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform is used to confirm the presence of iodine (I-) in the solution. The initial violet coloration is due to the formation of triiodide ions, and the subsequent disappearance of the color confirms the presence of iodine.
When chlorine gas (Cl2) is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide (e.g., KCl) in the presence of chloroform (CHCl3), a violet coloration is observed. This reaction is specifically used to test for the presence of iodide ions (I-) in the aqueous solution.
1. Formation of Iodine:
The reaction between chlorine gas and iodide ions in the presence of chloroform leads to the formation of molecular iodine (I2). This is represented by the following equation:
2Cl2 + 2KCl + 2CHCl3 → 2KCl + 2HCl + I2
2. Violet Coloration:
The presence of molecular iodine (I2) imparts a violet color to the solution. This is due to the formation of a complex called triiodide ion (I3-) when iodine reacts with excess iodide ions present in the solution. The triiodide ion is responsible for the violet coloration.
3. Disappearance of Violet Color:
When more chlorine water (aqueous chlorine) is added to the solution, it reacts with the iodine present, converting it back to iodide ions. This is represented by the following equation:
I2 + Cl2 → 2ICl
The formation of iodine chloride (ICl) from iodine and chlorine leads to the disappearance of the violet color. The solution becomes colorless because the triiodide ions, responsible for the violet coloration, are converted back to iodide ions.
4. Confirmation of Iodine:
The disappearance of the violet color and the formation of a colorless solution when more chlorine water is added confirms the presence of iodine in the aqueous solution. This reaction is specific to iodine and helps differentiate it from other halogens like chlorine, fluorine, and bromine.
Conclusion:
In summary, the test involving the passage of chlorine gas through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform is used to confirm the presence of iodine (I-) in the solution. The initial violet coloration is due to the formation of triiodide ions, and the subsequent disappearance of the color confirms the presence of iodine.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice when chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a potassium halide in the presence of chloroform a violet colouration is obtained. On passing more of chlorine water, the violet colour is disappeared and solution becomes colourless. This test confirms the presence of ........ in aqueous solution.a)chlorineb)fluorinec)bromined)iodineCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















