JEE Exam > JEE Questions > PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to devel...
Start Learning for Free
PASSAGE-2
Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.
Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,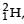 known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction is
known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction is 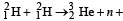 energy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection of
energy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection of  nuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.
nuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.
Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.
It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constant
Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,
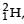 known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction is
known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction is 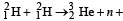 energy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection of
energy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection of 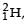 nuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.
nuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.
It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constant
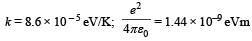
Q. Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?
- a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 s
- b)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 s
- c)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 s
- d)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor...
For the reading B we get nto > 5 × 1014 which is the Lawson criterion for a reactor to work successfully.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice PASSAGE-2Scientists are working hard to develop nuclear fusion reactor.Nuclei of heavy hydrogen,known as deuteron and denoted by D, can be thought of as a candidate for fusion reactor. The D-D r eaction isenergy. In the core of fusion reactor, a gas of heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collection ofnuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the reactor core are too high and no material wall can be used to confine the plasma.Special techniques are used which confine the plasma for a time t0 before the particles fly away form the core. If n is the density (number/volume) of deuterons, the product nt0 is called Lawson number. In one of the criteria, a reactor is termed successful if Lawson number is greater than 5 × 1014 s/cm3.It may be helpful to use the following: Boltzmann constantQ.Results of calculations for four different designs of a fusion reactor using D-D reaction are given below. Which of these is most promising based on Lawson criterion?a)deuteron density = 2.0 × 1012 cm–3, confinement time = 5.0 × 10–3 sb)deuteron density = 8.0 × 1014 cm–3, confinement time = 9.0 × 10–1 sc)deuteron density = 4.0 × 1023 cm–3, confinement time = 1.0 × 10–11 sd)deuteron density = 1.0 × 1024 cm–3, confinement time = 4.0 × 10–12 sCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























