JEE Exam > JEE Questions > PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than ...
Start Learning for Free
PASSAGE - 6
The mass of a nucleus 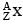 is less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference is known as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:
is less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference is known as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:
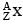 is less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference is known as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:
is less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference is known as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below: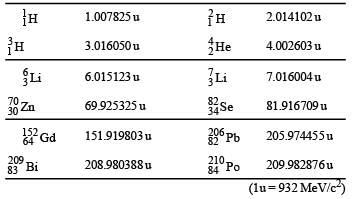
Q. The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleus 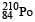 at rest undergoes alpha decay, is
at rest undergoes alpha decay, is
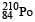 at rest undergoes alpha decay, is
at rest undergoes alpha decay, is- a)5319
- b)5422
- c)5707
- d)5818
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of ...
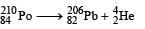
Here Δm = [209.982876 – (205.974455 + 4.002603)] × 932 MeV
= 5.422 MeV = 5422 keV
= 5.422 MeV = 5422 keV
By conservation of linear momentum
Linear momentum of α-particle = linear momentum of lead
Linear momentum of α-particle = linear momentum of lead
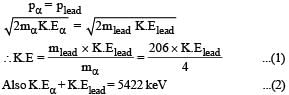
On solving the above two equations we get K.Eα = 5319 keV
(a) is the correct option.
(a) is the correct option.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice PASSAGE - 6The mass of a nucleusis less than the sum of the masses of (A-Z) number of neutrons and Z number of protons in the nucleus. The energy equivalent to the corresponding mass difference isknown as the binding energy of the nucleus. A heavy nucleus of mass M can break into two light nuclei of masses m1 and m2 only if (m1 + m2) < M. Also two light nuclei of masses m3 and m4 can undergo complete fusion and form a heavy nucleus of mass M' only if (m3 + m4) > M'. The masses of some neutral atoms are given in the table below:Q.The kinetic energy (in keV) of the alpha particle, when the nucleusat rest undergoes alpha decay, isa)5319b)5422c)5707d)5818Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























