Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support ...
Start Learning for Free
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______
- a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at C
- b)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at C
- c)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and C
- d)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. I...
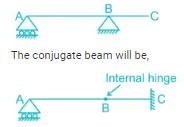
In conjugate beam – hinged at A, internal hinge at B and fixed at C.
Most Upvoted Answer
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. I...
To understand why the conjugate beam of beam ABC has a hinged end at A, an internal hinge at B, and a fixed end at C, we need to understand the concept of conjugate beams and how they relate to the original beam.
1. What is a conjugate beam?
A conjugate beam is a theoretical beam that is used to analyze the deflection and bending moments in a real beam. It is obtained by replacing the supports and loads of the real beam with their respective "conjugate" supports and loads.
2. The original beam ABC:
- Hinged end at A: A hinged end allows rotation but does not allow translation. This means that the beam can rotate freely at end A but cannot move horizontally or vertically.
- Simple support at B: A simple support allows both rotation and translation. This means that the beam can rotate and move horizontally or vertically at support B.
- Free end at C: A free end allows both rotation and translation. This means that the beam can rotate and move horizontally or vertically at end C.
3. The conjugate beam:
- Hinged end at A: The hinged end at A in the original beam becomes a fixed end in the conjugate beam. This means that the conjugate beam cannot rotate or move horizontally or vertically at end A.
- Internal hinge at B: The simple support at B in the original beam becomes an internal hinge in the conjugate beam. This means that the conjugate beam can rotate freely at the internal hinge.
- Fixed end at C: The free end at C in the original beam becomes a fixed end in the conjugate beam. This means that the conjugate beam cannot rotate or move horizontally or vertically at end C.
In summary, the conjugate beam of beam ABC has a hinged end at A, an internal hinge at B, and a fixed end at C because the original beam has a hinged end at A, a simple support at B, and a free end at C. The conjugate beam is obtained by replacing the supports and loads of the original beam with their respective conjugate supports and loads.
1. What is a conjugate beam?
A conjugate beam is a theoretical beam that is used to analyze the deflection and bending moments in a real beam. It is obtained by replacing the supports and loads of the real beam with their respective "conjugate" supports and loads.
2. The original beam ABC:
- Hinged end at A: A hinged end allows rotation but does not allow translation. This means that the beam can rotate freely at end A but cannot move horizontally or vertically.
- Simple support at B: A simple support allows both rotation and translation. This means that the beam can rotate and move horizontally or vertically at support B.
- Free end at C: A free end allows both rotation and translation. This means that the beam can rotate and move horizontally or vertically at end C.
3. The conjugate beam:
- Hinged end at A: The hinged end at A in the original beam becomes a fixed end in the conjugate beam. This means that the conjugate beam cannot rotate or move horizontally or vertically at end A.
- Internal hinge at B: The simple support at B in the original beam becomes an internal hinge in the conjugate beam. This means that the conjugate beam can rotate freely at the internal hinge.
- Fixed end at C: The free end at C in the original beam becomes a fixed end in the conjugate beam. This means that the conjugate beam cannot rotate or move horizontally or vertically at end C.
In summary, the conjugate beam of beam ABC has a hinged end at A, an internal hinge at B, and a fixed end at C because the original beam has a hinged end at A, a simple support at B, and a free end at C. The conjugate beam is obtained by replacing the supports and loads of the original beam with their respective conjugate supports and loads.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Beam ABC has hinged end at A, simple support at B and free end at C. Its conjugate beam has ______a)Fixed end at A, internal hinge at B and hinged end at Cb)Hinged end at A, internal hinge at B and fixed end at Cc)Hinged end at A, roller supports at B and Cd)Roller support at A and B and fixed support at CCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























