Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid ...
Start Learning for Free
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -
- a)sub-grade
- b)sub-base
- c)base
- d)wearing course
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-grade...
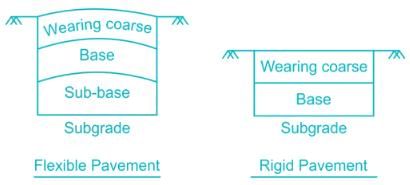
∴ A pavement is classified as flexible or rigid based on sub-base.
Most Upvoted Answer
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-grade...
Flexible and Rigid Pavements in Civil Engineering
Pavements are the most critical components of transportation infrastructure. They provide a smooth and safe riding surface for vehicles, thus reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing the comfort of passengers. Pavements are classified into two types: Flexible Pavements and Rigid Pavements. The classification is based on the type of material used for the pavement construction.
Flexible Pavements
Flexible pavements are those pavements that are constructed with flexible materials, such as bitumen, asphalt, and other petroleum-based materials. These pavements are designed to distribute the wheel loads over a large area, thereby reducing the stress on the subgrade. The key features of flexible pavements are:
- The pavement structure is composed of several layers of different materials, each with a specific function.
- The top layer is the wearing course, which provides a smooth and skid-resistant surface for vehicles.
- The lower layers consist of the base course and the sub-base course, which provide structural support and drainage.
- The subgrade is the native soil or the prepared foundation, which serves as the ultimate support for the pavement structure.
Rigid Pavements
Rigid pavements are those pavements that are constructed with rigid materials, such as concrete and reinforced concrete. These pavements are designed to distribute the wheel loads over a large area, similar to flexible pavements. However, the key difference is that the rigid pavement structure is monolithic, meaning that the entire pavement structure acts as a single unit. The key features of rigid pavements are:
- The pavement structure is composed of a single layer of concrete or reinforced concrete, which provides the structural support and the riding surface for vehicles.
- The joint spacing and joint sealing are critical for the performance of rigid pavements, as they allow for the natural expansion and contraction of the concrete due to temperature changes.
- The subgrade is the native soil or the prepared foundation, which serves as the ultimate support for the pavement structure.
Classification based on the Wearing Course
The wearing course is the top layer of the pavement structure, which provides the riding surface for vehicles. Based on the type of material used for the wearing course, the pavements can be classified as:
- Flexible Pavements: If the wearing course is made of bituminous materials, such as asphalt or tar, the pavement is classified as a flexible pavement.
- Rigid Pavements: If the wearing course is made of concrete or reinforced concrete, the pavement is classified as a rigid pavement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pavements are classified as flexible or rigid based on the type of material used for the pavement construction. Flexible pavements are constructed with flexible materials, such as bitumen and asphalt, while rigid pavements are constructed with rigid materials, such as concrete and reinforced concrete. The classification is not based on the subgrade, sub-base, or base course, but rather on the wearing course.
Pavements are the most critical components of transportation infrastructure. They provide a smooth and safe riding surface for vehicles, thus reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing the comfort of passengers. Pavements are classified into two types: Flexible Pavements and Rigid Pavements. The classification is based on the type of material used for the pavement construction.
Flexible Pavements
Flexible pavements are those pavements that are constructed with flexible materials, such as bitumen, asphalt, and other petroleum-based materials. These pavements are designed to distribute the wheel loads over a large area, thereby reducing the stress on the subgrade. The key features of flexible pavements are:
- The pavement structure is composed of several layers of different materials, each with a specific function.
- The top layer is the wearing course, which provides a smooth and skid-resistant surface for vehicles.
- The lower layers consist of the base course and the sub-base course, which provide structural support and drainage.
- The subgrade is the native soil or the prepared foundation, which serves as the ultimate support for the pavement structure.
Rigid Pavements
Rigid pavements are those pavements that are constructed with rigid materials, such as concrete and reinforced concrete. These pavements are designed to distribute the wheel loads over a large area, similar to flexible pavements. However, the key difference is that the rigid pavement structure is monolithic, meaning that the entire pavement structure acts as a single unit. The key features of rigid pavements are:
- The pavement structure is composed of a single layer of concrete or reinforced concrete, which provides the structural support and the riding surface for vehicles.
- The joint spacing and joint sealing are critical for the performance of rigid pavements, as they allow for the natural expansion and contraction of the concrete due to temperature changes.
- The subgrade is the native soil or the prepared foundation, which serves as the ultimate support for the pavement structure.
Classification based on the Wearing Course
The wearing course is the top layer of the pavement structure, which provides the riding surface for vehicles. Based on the type of material used for the wearing course, the pavements can be classified as:
- Flexible Pavements: If the wearing course is made of bituminous materials, such as asphalt or tar, the pavement is classified as a flexible pavement.
- Rigid Pavements: If the wearing course is made of concrete or reinforced concrete, the pavement is classified as a rigid pavement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pavements are classified as flexible or rigid based on the type of material used for the pavement construction. Flexible pavements are constructed with flexible materials, such as bitumen and asphalt, while rigid pavements are constructed with rigid materials, such as concrete and reinforced concrete. The classification is not based on the subgrade, sub-base, or base course, but rather on the wearing course.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A pavement is classifed as flexible or rigid based on its -a)sub-gradeb)sub-basec)based)wearing courseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























