Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Four successive members of the first row tran...
Start Learning for Free
Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]
- a)Vanadium (Z = 23)
- b)Chromium (Z = 24)
- c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)
- d)Ir on (Z = 26)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Four successive members of the first row transition elements are liste...
For third ion ization enthalpy last configuration of
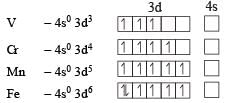
For third Ionization enthalpy Mn has stable configuration due to half filled d-orbital.
Most Upvoted Answer
Four successive members of the first row transition elements are liste...
Explanation:
The third ionization enthalpy refers to the energy required to remove the third electron from an atom. It is generally higher than the first and second ionization enthalpies because removing a third electron requires breaking into a filled inner shell.
To determine which element is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy among the given options, we need to consider their electronic configurations and atomic structures.
Electronic Configurations of the Given Elements:
a) Vanadium (Z = 23): [Ar] 3d3 4s2
b) Chromium (Z = 24): [Ar] 3d5 4s1
c) Manganese (Z = 25): [Ar] 3d5 4s2
d) Iron (Z = 26): [Ar] 3d6 4s2
Factors Affecting Ionization Enthalpy:
1. Effective Nuclear Charge: The greater the effective nuclear charge experienced by an electron, the more energy it will require to remove it.
2. Shielding Effect: The electron-electron repulsion reduces the effective nuclear charge experienced by outer electrons, making them easier to remove.
Factors Affecting Third Ionization Enthalpy:
1. Electron Configuration: The third ionization enthalpy involves removing an electron from a filled inner shell, which requires more energy due to increased electron-electron repulsion.
2. Effective Nuclear Charge: The effective nuclear charge experienced by the third electron will be influenced by the remaining electrons and the shielding effect.
Analysis:
Based on the given electronic configurations, we can observe the following:
1. Vanadium (Z = 23): The third electron is being removed from the 4s orbital, which is farther from the nucleus and experiences less effective nuclear charge.
2. Chromium (Z = 24): The third electron is being removed from the 4s orbital, similar to Vanadium.
3. Manganese (Z = 25): The third electron is being removed from the 3d orbital, which is closer to the nucleus and experiences a higher effective nuclear charge compared to the 4s orbital.
4. Iron (Z = 26): The third electron is being removed from the 3d orbital, similar to Manganese.
Conclusion:
Since Manganese (Z = 25) has the highest effective nuclear charge experienced by the third electron due to its electron configuration, it is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy among the given options. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer.
The third ionization enthalpy refers to the energy required to remove the third electron from an atom. It is generally higher than the first and second ionization enthalpies because removing a third electron requires breaking into a filled inner shell.
To determine which element is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy among the given options, we need to consider their electronic configurations and atomic structures.
Electronic Configurations of the Given Elements:
a) Vanadium (Z = 23): [Ar] 3d3 4s2
b) Chromium (Z = 24): [Ar] 3d5 4s1
c) Manganese (Z = 25): [Ar] 3d5 4s2
d) Iron (Z = 26): [Ar] 3d6 4s2
Factors Affecting Ionization Enthalpy:
1. Effective Nuclear Charge: The greater the effective nuclear charge experienced by an electron, the more energy it will require to remove it.
2. Shielding Effect: The electron-electron repulsion reduces the effective nuclear charge experienced by outer electrons, making them easier to remove.
Factors Affecting Third Ionization Enthalpy:
1. Electron Configuration: The third ionization enthalpy involves removing an electron from a filled inner shell, which requires more energy due to increased electron-electron repulsion.
2. Effective Nuclear Charge: The effective nuclear charge experienced by the third electron will be influenced by the remaining electrons and the shielding effect.
Analysis:
Based on the given electronic configurations, we can observe the following:
1. Vanadium (Z = 23): The third electron is being removed from the 4s orbital, which is farther from the nucleus and experiences less effective nuclear charge.
2. Chromium (Z = 24): The third electron is being removed from the 4s orbital, similar to Vanadium.
3. Manganese (Z = 25): The third electron is being removed from the 3d orbital, which is closer to the nucleus and experiences a higher effective nuclear charge compared to the 4s orbital.
4. Iron (Z = 26): The third electron is being removed from the 3d orbital, similar to Manganese.
Conclusion:
Since Manganese (Z = 25) has the highest effective nuclear charge experienced by the third electron due to its electron configuration, it is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy among the given options. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Four successive members of the first row transition elements are listed below with their atomic numbers. Which one of them is expected to have the highest third ionization enthalpy? [2 00 5]a)Vanadium (Z = 23)b)Chromium (Z = 24)c)Man gan ese (Z = 25)d)Ir on (Z = 26)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















