Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Rankine theory is applicable to the ________....
Start Learning for Free
Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.
- a)Short strut/column
- b)Long column
- c)Both short and long column
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Lon...
For short or long columns Rankine’s Formula is used.
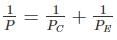
Where P is crippling load by Rankine formula; PC is crushing load; PE is crippling load by Euler’s formula.
For Short column: PE is very large so
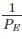 will be very small and negligible as compared to
will be very small and negligible as compared to  so
so 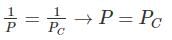
For Long column: PE is small so 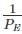 will be large as compared to
will be large as compared to 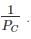
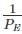 will be large as compared to
will be large as compared to 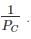
Hence the value of 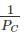 can be neglected. So
can be neglected. So
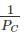 can be neglected. So
can be neglected. So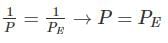
Hence the crippling load by Rankine’s formula for long column is approximately equal to the crippling load by Euler’s formula.
Most Upvoted Answer
Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Lon...
RANKINE THEORY APPLICABILITY TO SHORT AND LONG COLUMNS
The Rankine theory, also known as the Rankine formula or Rankine's theory of columns, is a widely used method for analyzing the stability and strength of columns. It provides a simplified approach to determine the ultimate load-carrying capacity of columns based on their slenderness ratio. The slenderness ratio is the ratio of the effective length of the column to its least radius of gyration.
Applicability of Rankine Theory:
The Rankine theory is applicable to both short and long columns. However, it is important to note that the assumptions and limitations of the theory differ for each type of column.
1. Short Columns:
Short columns are those in which the slenderness ratio is less than a certain critical value. The Rankine theory is most commonly applied to short columns because their behavior is governed by their material strength rather than their slenderness.
The assumptions for applying the Rankine theory to short columns are as follows:
- The column is subjected to axial compression only.
- The column is homogeneous and isotropic.
- The material of the column behaves elastically up to failure.
- The cross-section of the column remains plane and perpendicular to the axis of the column during deformation.
- The load is applied concentrically to the centroid of the cross-section.
Under these assumptions, the Rankine theory provides a reasonably accurate estimate of the ultimate load-carrying capacity of short columns.
2. Long Columns:
Long columns are those in which the slenderness ratio exceeds the critical value. For long columns, the Rankine theory is not directly applicable as it neglects the influence of buckling.
When a long column is subjected to axial compression, it may undergo buckling, which is a sudden lateral deflection caused by the compressive load. The buckling behavior of long columns is more complex and requires a different approach, such as the Euler's theory or the Perry-Robertson formula.
However, the Rankine theory can still be used to estimate the ultimate load-carrying capacity of long columns by considering the additional effect of buckling through appropriate modification factors. These modification factors are typically obtained from experimental data or more advanced analysis methods.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Rankine theory is applicable to both short and long columns. However, it is important to consider the assumptions and limitations of the theory, especially when applying it to long columns where buckling behavior becomes significant.
The Rankine theory, also known as the Rankine formula or Rankine's theory of columns, is a widely used method for analyzing the stability and strength of columns. It provides a simplified approach to determine the ultimate load-carrying capacity of columns based on their slenderness ratio. The slenderness ratio is the ratio of the effective length of the column to its least radius of gyration.
Applicability of Rankine Theory:
The Rankine theory is applicable to both short and long columns. However, it is important to note that the assumptions and limitations of the theory differ for each type of column.
1. Short Columns:
Short columns are those in which the slenderness ratio is less than a certain critical value. The Rankine theory is most commonly applied to short columns because their behavior is governed by their material strength rather than their slenderness.
The assumptions for applying the Rankine theory to short columns are as follows:
- The column is subjected to axial compression only.
- The column is homogeneous and isotropic.
- The material of the column behaves elastically up to failure.
- The cross-section of the column remains plane and perpendicular to the axis of the column during deformation.
- The load is applied concentrically to the centroid of the cross-section.
Under these assumptions, the Rankine theory provides a reasonably accurate estimate of the ultimate load-carrying capacity of short columns.
2. Long Columns:
Long columns are those in which the slenderness ratio exceeds the critical value. For long columns, the Rankine theory is not directly applicable as it neglects the influence of buckling.
When a long column is subjected to axial compression, it may undergo buckling, which is a sudden lateral deflection caused by the compressive load. The buckling behavior of long columns is more complex and requires a different approach, such as the Euler's theory or the Perry-Robertson formula.
However, the Rankine theory can still be used to estimate the ultimate load-carrying capacity of long columns by considering the additional effect of buckling through appropriate modification factors. These modification factors are typically obtained from experimental data or more advanced analysis methods.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Rankine theory is applicable to both short and long columns. However, it is important to consider the assumptions and limitations of the theory, especially when applying it to long columns where buckling behavior becomes significant.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Question Description
Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Rankine theory is applicable to the ________.a)Short strut/columnb)Long columnc)Both short and long columnd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















