Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Which of the following is true?a)the slope of...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is true?
- a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipe
- b)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipe
- c)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the pipe
- d)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipe
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be great...
Explanation: EGL is obtained by plotting total head at various points along the axis of the pipe.
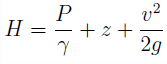
where H is the total head, P ⁄ γ is the pressure head, z is the potential head, , and v2 / 2g is the velocity head.
Hence, there is no relation whatsoever between the slope of EGL and that of the axis of the pipe.
where H is the total head, P ⁄ γ is the pressure head, z is the potential head, , and v2 / 2g is the velocity head.
Hence, there is no relation whatsoever between the slope of EGL and that of the axis of the pipe.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be great...
The correct answer is option D: the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipe.
Explanation:
To understand why the slope of EGL (Energy Grade Line) is independent of the slope of the axis of the pipe, let's first define what each of these terms represents:
1. Slope of the axis of the pipe:
The slope of the axis of the pipe represents the change in elevation of the pipe axis per unit length. It can be positive (upward slope) or negative (downward slope) depending on the direction of flow.
2. Slope of EGL:
The slope of EGL represents the change in total energy head (including both pressure head and elevation head) per unit length. It is related to the hydraulic gradient and the friction losses experienced by the fluid flowing through the pipe.
Now, let's discuss why the slope of EGL is independent of the slope of the axis of the pipe:
1. Flow in a pipe:
When fluid flows through a pipe, it experiences various forces such as pressure forces and friction forces. These forces result in energy losses, causing a decrease in the total energy head along the pipe. This decrease in energy head is reflected by the slope of the EGL.
2. Conservation of Energy:
According to the principle of conservation of energy, the total energy of a fluid remains constant along a streamline. This means that the sum of the pressure head and the elevation head at any point along the pipe will be equal to the sum of the pressure head and the elevation head at any other point along the same streamline.
3. EGL and Hydraulic Gradient:
The EGL represents the total energy head at different points along the pipe. The hydraulic gradient, on the other hand, represents the pressure head at different points along the pipe. The hydraulic gradient is directly related to the slope of the axis of the pipe.
4. Friction Losses:
Friction losses occur due to the interaction between the fluid and the pipe walls. These losses depend on factors such as the pipe roughness, flow velocity, and pipe diameter. Friction losses cause a decrease in the total energy head, resulting in a negative slope of the EGL.
5. Conclusion:
The slope of EGL is independent of the slope of the axis of the pipe because the EGL represents the total energy head and is influenced by various factors such as friction losses, while the slope of the axis of the pipe represents the change in elevation and is influenced by the hydraulic gradient.
Explanation:
To understand why the slope of EGL (Energy Grade Line) is independent of the slope of the axis of the pipe, let's first define what each of these terms represents:
1. Slope of the axis of the pipe:
The slope of the axis of the pipe represents the change in elevation of the pipe axis per unit length. It can be positive (upward slope) or negative (downward slope) depending on the direction of flow.
2. Slope of EGL:
The slope of EGL represents the change in total energy head (including both pressure head and elevation head) per unit length. It is related to the hydraulic gradient and the friction losses experienced by the fluid flowing through the pipe.
Now, let's discuss why the slope of EGL is independent of the slope of the axis of the pipe:
1. Flow in a pipe:
When fluid flows through a pipe, it experiences various forces such as pressure forces and friction forces. These forces result in energy losses, causing a decrease in the total energy head along the pipe. This decrease in energy head is reflected by the slope of the EGL.
2. Conservation of Energy:
According to the principle of conservation of energy, the total energy of a fluid remains constant along a streamline. This means that the sum of the pressure head and the elevation head at any point along the pipe will be equal to the sum of the pressure head and the elevation head at any other point along the same streamline.
3. EGL and Hydraulic Gradient:
The EGL represents the total energy head at different points along the pipe. The hydraulic gradient, on the other hand, represents the pressure head at different points along the pipe. The hydraulic gradient is directly related to the slope of the axis of the pipe.
4. Friction Losses:
Friction losses occur due to the interaction between the fluid and the pipe walls. These losses depend on factors such as the pipe roughness, flow velocity, and pipe diameter. Friction losses cause a decrease in the total energy head, resulting in a negative slope of the EGL.
5. Conclusion:
The slope of EGL is independent of the slope of the axis of the pipe because the EGL represents the total energy head and is influenced by various factors such as friction losses, while the slope of the axis of the pipe represents the change in elevation and is influenced by the hydraulic gradient.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is true?a)the slope of EGL will always be greater than that of the axis of the pipeb)the slope of EGL will always be smaller than that of the axis of the pipec)the slope of EGL will always be equal to that of the axis of the piped)the slope of EGL will always be independent of that of the axis of the pipeCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























