Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A conventional drained triaxial compression t...
Start Learning for Free
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________
Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a no...
1st Specimen : Drained condition

Let pore pressure developed is u
∴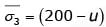
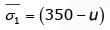
From stress relationship
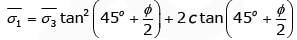
∴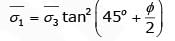
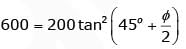
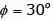
For second specimen,
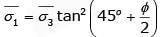
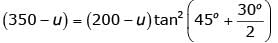
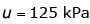

Let pore pressure developed is u
∴
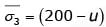
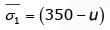
From stress relationship
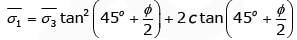
∴
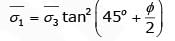
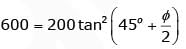
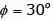
For second specimen,
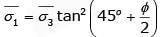
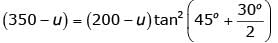
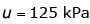
Most Upvoted Answer
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a no...
Given information:
- Conventional drained triaxial compression test on normally consolidated clay sample.
- Effective confining pressure = 200 kPa.
- Deviator stress at failure = 400 kPa.
Required information:
- Pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial compression test.
- Deviator stress at failure = 150 kPa.
Solution:
To find the pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial compression test, we need to consider the principle of effective stress.
Principle of effective stress:
The principle of effective stress states that the total stress in a soil mass is divided into two components: the effective stress and the pore water pressure.
Total stress = Effective stress + Pore water pressure
In an undrained triaxial compression test, the pore water pressure remains constant throughout the test. Therefore, the change in effective stress is equal to the change in total stress.
Step 1: Calculate the change in effective stress during the drained triaxial test.
Deviator stress at failure during the drained triaxial test = 400 kPa
Effective confining pressure = 200 kPa
Effective stress at failure = Deviator stress at failure + Effective confining pressure
Effective stress at failure = 400 kPa + 200 kPa = 600 kPa
Step 2: Calculate the change in total stress during the undrained triaxial test.
Deviator stress at failure during the undrained triaxial test = 150 kPa
Change in effective stress = Deviator stress at failure during the drained triaxial test - Deviator stress at failure during the undrained triaxial test
Change in effective stress = 600 kPa - 150 kPa = 450 kPa
Step 3: Calculate the pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial test.
Change in total stress = Change in effective stress + Change in pore water pressure
Change in pore water pressure = Change in total stress - Change in effective stress
Change in pore water pressure = 450 kPa - 450 kPa = 0 kPa
Therefore, the pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial compression test is 0 kPa.
- Conventional drained triaxial compression test on normally consolidated clay sample.
- Effective confining pressure = 200 kPa.
- Deviator stress at failure = 400 kPa.
Required information:
- Pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial compression test.
- Deviator stress at failure = 150 kPa.
Solution:
To find the pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial compression test, we need to consider the principle of effective stress.
Principle of effective stress:
The principle of effective stress states that the total stress in a soil mass is divided into two components: the effective stress and the pore water pressure.
Total stress = Effective stress + Pore water pressure
In an undrained triaxial compression test, the pore water pressure remains constant throughout the test. Therefore, the change in effective stress is equal to the change in total stress.
Step 1: Calculate the change in effective stress during the drained triaxial test.
Deviator stress at failure during the drained triaxial test = 400 kPa
Effective confining pressure = 200 kPa
Effective stress at failure = Deviator stress at failure + Effective confining pressure
Effective stress at failure = 400 kPa + 200 kPa = 600 kPa
Step 2: Calculate the change in total stress during the undrained triaxial test.
Deviator stress at failure during the undrained triaxial test = 150 kPa
Change in effective stress = Deviator stress at failure during the drained triaxial test - Deviator stress at failure during the undrained triaxial test
Change in effective stress = 600 kPa - 150 kPa = 450 kPa
Step 3: Calculate the pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial test.
Change in total stress = Change in effective stress + Change in pore water pressure
Change in pore water pressure = Change in total stress - Change in effective stress
Change in pore water pressure = 450 kPa - 450 kPa = 0 kPa
Therefore, the pore pressure developed during the undrained triaxial compression test is 0 kPa.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer?.
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A conventional drained triaxial compression test was conducted on a normally consolidated clay sample under an effective confining pressure of 200 KPa. The deviator stress at failure was found to be 400 kPa. An identical specimen of the same clay sample is isotropically consolidated to a confining pressure of 200 kPa and subjected to standard undrained triaxial compression test. If the deviator stress at failure is 150 kPa, the pore pressure developed (in kPa, up to one decimal place) is _______________Correct answer is '(125)'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























