Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives efferves...
Start Learning for Free
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O (Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both...
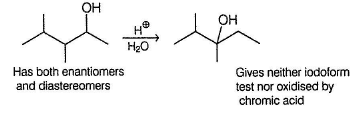
From the give condition, structure of X is derived to be
Most Upvoted Answer
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both...
Minimum number of carbons in the parent chain of X is 5
Explanation:
- The molecular formula of compound X is C7H16O, which suggests that it contains 7 carbon atoms.
- Effervescence with Na indicates the presence of a carboxylic acid group (COOH) in compound X.
- The presence of both enantiomers and diastereomers indicates that compound X contains a chiral center or a double bond.
- Yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution suggests the presence of an alcohol group (OH) in compound X.
- The reaction of X with CrO3 - H2SO4 converts it into compound Y, which has enantiomers but not diastereomers.
- This indicates that compound Y contains a chiral center, but not a double bond.
- Refluxing compound X with H2SO4 isomerizes it to compound Z, which does not give a yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine and does not change the color of CrO3 - H2SO4.
- This suggests that compound Z does not contain an alcohol group and is not a carboxylic acid.
- Therefore, compound Z must be an alkane or an alkene.
- Since compound X is isomerized to compound Z on refluxing with H2SO4, it can be inferred that compound X contains a double bond.
- The only way to have a double bond and a chiral center in a compound with 7 carbon atoms is if the double bond is present in a 5-carbon chain.
- Hence, the minimum number of carbons in the parent chain of X is 5.
Conclusion:
The compound X has a minimum of 5 carbon atoms in its parent chain.
Explanation:
- The molecular formula of compound X is C7H16O, which suggests that it contains 7 carbon atoms.
- Effervescence with Na indicates the presence of a carboxylic acid group (COOH) in compound X.
- The presence of both enantiomers and diastereomers indicates that compound X contains a chiral center or a double bond.
- Yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution suggests the presence of an alcohol group (OH) in compound X.
- The reaction of X with CrO3 - H2SO4 converts it into compound Y, which has enantiomers but not diastereomers.
- This indicates that compound Y contains a chiral center, but not a double bond.
- Refluxing compound X with H2SO4 isomerizes it to compound Z, which does not give a yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine and does not change the color of CrO3 - H2SO4.
- This suggests that compound Z does not contain an alcohol group and is not a carboxylic acid.
- Therefore, compound Z must be an alkane or an alkene.
- Since compound X is isomerized to compound Z on refluxing with H2SO4, it can be inferred that compound X contains a double bond.
- The only way to have a double bond and a chiral center in a compound with 7 carbon atoms is if the double bond is present in a 5-carbon chain.
- Hence, the minimum number of carbons in the parent chain of X is 5.
Conclusion:
The compound X has a minimum of 5 carbon atoms in its parent chain.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An organic compound X (C7H16O) gives effervescence with Na. X has both enantiomers and diastereomers. X gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine solution. With CrO3 - H2SO4 , X is converted into C7H14O(Y) which has enantiom ers but not diastereom ers. X on refluxing with H2SO4 isomerises to Z which neither gives yellow precipitate with alkaline iodine nor changes colour of CrO3 - H2SO4 . What is the minim um number of carbons that can be present in the parent chain of X ?Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















