Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Which complex is likely to show optical activ...
Start Learning for Free
Which complex is likely to show optical activity
- a)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4 ]+
- b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+
- c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2 ]3+
- d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2 ]3+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+...
Cis [Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
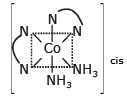
No POS optically active rest compound has POS.
No POS optically active rest compound has POS.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+...
Understanding Optical Activity in Coordination Compounds
Optical activity refers to the ability of a compound to rotate plane-polarized light, which usually occurs in chiral molecules. In coordination chemistry, the geometry and arrangement of ligands around a central metal ion are crucial in determining chirality.
Analyzing the Given Complexes
- Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+
- This complex has a symmetrical arrangement, which lacks chirality. Therefore, it does not show optical activity.
- [Cr(H2O)6]3+
- This octahedral complex is also symmetrical with identical ligands (water), leading to no optical activity.
- Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
- Here, "en" refers to ethylenediamine, a bidentate ligand. The cis arrangement allows for a non-superimposable mirror image, making this complex chiral. Thus, it exhibits optical activity.
- Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
- Similar to the previous complex, but in the trans configuration, it is symmetric and does not possess chirality, resulting in no optical activity.
Conclusion
The only complex that displays optical activity is Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+ due to its chiral nature resulting from the arrangement of ligands, which creates non-superimposable mirror images.
Optical activity refers to the ability of a compound to rotate plane-polarized light, which usually occurs in chiral molecules. In coordination chemistry, the geometry and arrangement of ligands around a central metal ion are crucial in determining chirality.
Analyzing the Given Complexes
- Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+
- This complex has a symmetrical arrangement, which lacks chirality. Therefore, it does not show optical activity.
- [Cr(H2O)6]3+
- This octahedral complex is also symmetrical with identical ligands (water), leading to no optical activity.
- Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
- Here, "en" refers to ethylenediamine, a bidentate ligand. The cis arrangement allows for a non-superimposable mirror image, making this complex chiral. Thus, it exhibits optical activity.
- Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
- Similar to the previous complex, but in the trans configuration, it is symmetric and does not possess chirality, resulting in no optical activity.
Conclusion
The only complex that displays optical activity is Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+ due to its chiral nature resulting from the arrangement of ligands, which creates non-superimposable mirror images.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which complex is likely to show optical activitya)Trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]+b)[Cr(H2O)6]3+c)Cis-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+d)Trans-[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















