Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a...
Start Learning for Free
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:
- a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span length
- b)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span length
- c)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span length
- d)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span length
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and ...
Sag is defined as the difference in level between points of supports and the lowest point on the conductor.
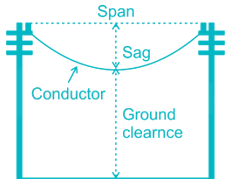
Sag of conductor’s between two poles can be determined by
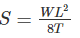
Where, S is the sag of conductors
W is the weight per unit length of the conductor
L is the length of span
T is the tension in the conductor
Most Upvoted Answer
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and ...
Weight of Conductor and its Relationship with Sag
Introduction:
The sag of a transmission line refers to the vertical distance between the highest point of the conductor and the lowest point of the sag curve. It is an important factor to consider in the design and installation of transmission lines as it affects the overall performance and safety of the line. The sag of a transmission line is influenced by several factors, including the weight of the conductor and the span length.
Weight of Conductor:
The weight of the conductor plays a significant role in determining the sag of a transmission line. The conductor is typically made of materials such as aluminum or copper, which have a certain weight per unit length. This weight exerts a downward force on the conductor, causing it to sag under its own weight.
Directly Proportional to Span Length:
The sag of a transmission line is directly proportional to the span length. A longer span length means that the conductor is stretched over a greater distance, resulting in a larger sag. This relationship can be intuitively understood by considering a simple example: if we have a long piece of string and we hold it at both ends, the string will sag more in the middle compared to a shorter piece of string held under the same tension.
Directly Proportional to Square of Span Length:
However, the relationship between the weight of the conductor and the sag is not linear with respect to the span length. Instead, it is directly proportional to the square of the span length. This means that doubling the span length will result in a four-fold increase in the sag.
Explanation:
The reason for this non-linear relationship is the distribution of the conductor's weight along the span length. As the span length increases, the weight of the conductor is distributed over a larger distance. This distribution causes the sag to increase at an exponential rate, rather than a linear one.
Visual Representation:
Visually, this relationship can be represented by a sag curve. As the span length increases, the sag curve becomes more pronounced, with a larger vertical distance between the highest and lowest points of the curve.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the sag of a transmission line is influenced by the weight of the conductor and its relationship with the span length. The weight of the conductor causes it to sag under its own weight, and the sag is directly proportional to the square of the span length. Understanding this relationship is crucial for designing and installing transmission lines that meet safety and performance requirements.
Introduction:
The sag of a transmission line refers to the vertical distance between the highest point of the conductor and the lowest point of the sag curve. It is an important factor to consider in the design and installation of transmission lines as it affects the overall performance and safety of the line. The sag of a transmission line is influenced by several factors, including the weight of the conductor and the span length.
Weight of Conductor:
The weight of the conductor plays a significant role in determining the sag of a transmission line. The conductor is typically made of materials such as aluminum or copper, which have a certain weight per unit length. This weight exerts a downward force on the conductor, causing it to sag under its own weight.
Directly Proportional to Span Length:
The sag of a transmission line is directly proportional to the span length. A longer span length means that the conductor is stretched over a greater distance, resulting in a larger sag. This relationship can be intuitively understood by considering a simple example: if we have a long piece of string and we hold it at both ends, the string will sag more in the middle compared to a shorter piece of string held under the same tension.
Directly Proportional to Square of Span Length:
However, the relationship between the weight of the conductor and the sag is not linear with respect to the span length. Instead, it is directly proportional to the square of the span length. This means that doubling the span length will result in a four-fold increase in the sag.
Explanation:
The reason for this non-linear relationship is the distribution of the conductor's weight along the span length. As the span length increases, the weight of the conductor is distributed over a larger distance. This distribution causes the sag to increase at an exponential rate, rather than a linear one.
Visual Representation:
Visually, this relationship can be represented by a sag curve. As the span length increases, the sag curve becomes more pronounced, with a larger vertical distance between the highest and lowest points of the curve.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the sag of a transmission line is influenced by the weight of the conductor and its relationship with the span length. The weight of the conductor causes it to sag under its own weight, and the sag is directly proportional to the square of the span length. Understanding this relationship is crucial for designing and installing transmission lines that meet safety and performance requirements.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The sag of a transmission line depends upon:a)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to span lengthb)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to span lengthc)Weight of conductor and directly proportional to square of span lengthd)Weight of conductor and inversely proportional to square of span lengthCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























