Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined con...
Start Learning for Free
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.
Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined...
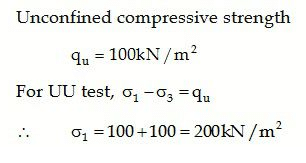
Most Upvoted Answer
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined...
Given information:
- Unconfined compressive strength of clay soil specimen = 100 kN/m2
- Specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2
To find:
- Axial stress at failure in the UU triaxial test
Solution:
Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) is the maximum compressive stress that a soil sample can sustain under unconfined conditions. In other words, it is the strength of the soil when it is not confined by any external pressure.
In the UU triaxial test, the soil sample is confined by a cell pressure (also known as confining pressure) in addition to the axial stress. The cell pressure is applied uniformly from all sides of the soil sample, simulating the in-situ stress conditions.
The failure in the UU triaxial test occurs when the soil sample reaches its maximum shear strength, which is affected by both the axial stress and the confining pressure. The relationship between the axial stress, confining pressure, and shear strength of the soil is described by the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion.
The Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion can be expressed as follows:
τ = c + σtan(φ)
where,
τ = shear stress
c = cohesion intercept
σ = normal stress (which is equal to the confining pressure in the UU triaxial test)
φ = angle of internal friction
In the UU triaxial test, the confining pressure is 100 kN/m2, which is equal to the cell pressure. The UCS of the soil is also given as 100 kN/m2.
From the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, we can calculate the shear strength of the soil as follows:
τ = c + σtan(φ)
τ = 0 + 100tan(φ)
τ = 100tan(φ)
The maximum shear stress (τmax) that the soil can sustain is equal to the UCS. Therefore,
UCS = τmax = 100tan(φ)
From this equation, we can find the angle of internal friction of the soil as follows:
tan(φ) = UCS/100
tan(φ) = 1
Therefore, φ = 45 degrees.
Now, we can calculate the axial stress (σa) at failure in the UU triaxial test using the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion:
τ = c + σtan(φ)
τmax = c + σatan(φ)
100 = 0 + σa(1)
Therefore, σa = 100 kN/m2.
Hence, the axial stress at failure in the UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2 is 200 kN/m2 (sum of the confining pressure and axial stress).
- Unconfined compressive strength of clay soil specimen = 100 kN/m2
- Specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2
To find:
- Axial stress at failure in the UU triaxial test
Solution:
Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) is the maximum compressive stress that a soil sample can sustain under unconfined conditions. In other words, it is the strength of the soil when it is not confined by any external pressure.
In the UU triaxial test, the soil sample is confined by a cell pressure (also known as confining pressure) in addition to the axial stress. The cell pressure is applied uniformly from all sides of the soil sample, simulating the in-situ stress conditions.
The failure in the UU triaxial test occurs when the soil sample reaches its maximum shear strength, which is affected by both the axial stress and the confining pressure. The relationship between the axial stress, confining pressure, and shear strength of the soil is described by the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion.
The Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion can be expressed as follows:
τ = c + σtan(φ)
where,
τ = shear stress
c = cohesion intercept
σ = normal stress (which is equal to the confining pressure in the UU triaxial test)
φ = angle of internal friction
In the UU triaxial test, the confining pressure is 100 kN/m2, which is equal to the cell pressure. The UCS of the soil is also given as 100 kN/m2.
From the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, we can calculate the shear strength of the soil as follows:
τ = c + σtan(φ)
τ = 0 + 100tan(φ)
τ = 100tan(φ)
The maximum shear stress (τmax) that the soil can sustain is equal to the UCS. Therefore,
UCS = τmax = 100tan(φ)
From this equation, we can find the angle of internal friction of the soil as follows:
tan(φ) = UCS/100
tan(φ) = 1
Therefore, φ = 45 degrees.
Now, we can calculate the axial stress (σa) at failure in the UU triaxial test using the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion:
τ = c + σtan(φ)
τmax = c + σatan(φ)
100 = 0 + σa(1)
Therefore, σa = 100 kN/m2.
Hence, the axial stress at failure in the UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2 is 200 kN/m2 (sum of the confining pressure and axial stress).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer?.
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A clay soil specimen tested in unconfined condition gave an unconfined compressive strength of 100 kN/m2. A specimen of the same clay with the same initial condition is subjected to a UU triaxial test under a cell pressure of 100 kN/m2. The axial stress (in kN/m2) at failure would be ____________.Correct answer is '200'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























