Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric aci...
Start Learning for Free
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals of metalion present in product B is
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Whic...

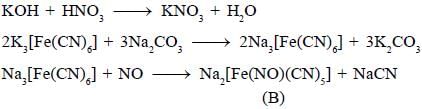
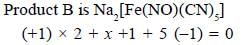
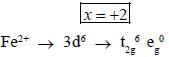
Most Upvoted Answer
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Whic...
Potassium ferrocyanide (K4[Fe(CN)6]) is a coordination compound that consists of a central iron atom coordinated to six cyanide ligands. When it reacts with nitric acid (HNO3), it undergoes a redox reaction, resulting in the formation of product A.
1. Reaction between potassium ferrocyanide and nitric acid:
- The nitric acid donates a proton (H+) to the ferrocyanide ion, resulting in the formation of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and a complex containing the iron center.
- The balanced equation for this reaction is:
K4[Fe(CN)6] + 6HNO3 -> 4KNO3 + Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6] + 6HCN
2. Formation of product A:
- In the reaction between potassium ferrocyanide and nitric acid, one of the products is a complex containing the iron center, Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6].
- This complex is known as a double salt, where the iron atom is coordinated to six water molecules and one ferrocyanide ion.
- The double salt is the product A formed in the reaction.
3. Reaction between product A and sodium carbonate:
- Product A, Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6], further reacts with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) to form product B.
- The balanced equation for this reaction is:
Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6] + 3Na2CO3 -> 6NaOH + FeCO3 + 6H2O + 2CO2
4. Formation of product B:
- In the reaction between product A and sodium carbonate, one of the products is iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3).
- The iron atom in FeCO3 is in the +2 oxidation state and is coordinated to three carbonate ions.
- The coordination number of iron in FeCO3 is 6, as it is coordinated to six oxygen atoms (three from carbonate ions and three from water molecules).
- The total number of electrons in the t2g orbitals of the metal ion present in product B (FeCO3) is 6.
- This is because the t2g orbitals (dxy, dyz, and dzx) can accommodate a maximum of six electrons.
In conclusion, the total number of electrons in the t2g orbitals of the metal ion present in product B (FeCO3) is 6.
1. Reaction between potassium ferrocyanide and nitric acid:
- The nitric acid donates a proton (H+) to the ferrocyanide ion, resulting in the formation of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and a complex containing the iron center.
- The balanced equation for this reaction is:
K4[Fe(CN)6] + 6HNO3 -> 4KNO3 + Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6] + 6HCN
2. Formation of product A:
- In the reaction between potassium ferrocyanide and nitric acid, one of the products is a complex containing the iron center, Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6].
- This complex is known as a double salt, where the iron atom is coordinated to six water molecules and one ferrocyanide ion.
- The double salt is the product A formed in the reaction.
3. Reaction between product A and sodium carbonate:
- Product A, Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6], further reacts with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) to form product B.
- The balanced equation for this reaction is:
Fe(H2O)6[Fe(CN)6] + 3Na2CO3 -> 6NaOH + FeCO3 + 6H2O + 2CO2
4. Formation of product B:
- In the reaction between product A and sodium carbonate, one of the products is iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3).
- The iron atom in FeCO3 is in the +2 oxidation state and is coordinated to three carbonate ions.
- The coordination number of iron in FeCO3 is 6, as it is coordinated to six oxygen atoms (three from carbonate ions and three from water molecules).
- The total number of electrons in the t2g orbitals of the metal ion present in product B (FeCO3) is 6.
- This is because the t2g orbitals (dxy, dyz, and dzx) can accommodate a maximum of six electrons.
In conclusion, the total number of electrons in the t2g orbitals of the metal ion present in product B (FeCO3) is 6.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Potassium ferrocyanide reacts with nitric acid to form product A. Which further reacts with sodium carbonate to form product B. The total number of elections in t2g orbitals ofmetalion present inproduct B isCorrect answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















