Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slop...
Start Learning for Free
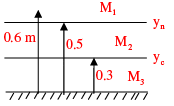
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified as
- a)S1
- b)S2
- c)M1
- d)M2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manni...
yn = 0.5m
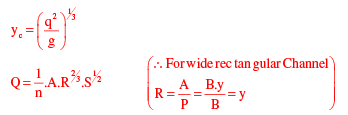
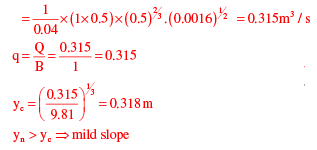
Most Upvoted Answer
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manni...
To determine the classification of the gradually varied flow (GVF) profile at a particular section of a rectangular channel, we need to consider the flow depth and compare it with critical flow depth. The classification is based on the Froude number (Fr) which is calculated using the flow depth, flow velocity, and the gravitational acceleration.
Given data:
Width of the rectangular channel (b) = 1 m
Bed slope (S) = 0.0016
Mannings roughness coefficient (n) = 0.04
Flow depth (y) = 0.6 m
1. Calculate the hydraulic radius (R):
The hydraulic radius is the ratio of the cross-sectional area to the wetted perimeter. For a rectangular channel, the wetted perimeter is equal to the sum of the bottom width and twice the flow depth.
Wetted perimeter (P) = b + 2y
Cross-sectional area (A) = b * y
Hydraulic radius (R) = A / P = (b * y) / (b + 2y)
2. Calculate the flow velocity (V):
The flow velocity can be calculated using Manning's equation:
V = (1 / n) * R^(2/3) * S^(1/2)
3. Calculate the critical flow depth (yc):
The critical flow depth is the flow depth at which the flow transitions from subcritical to supercritical or vice versa. It can be calculated using the following formula:
yc = (Q^2 / (g * A^2))^1/3
4. Calculate the Froude number (Fr):
Fr = V / (g * yc)^0.5
5. Compare the flow depth (y) and critical flow depth (yc):
If y < yc,="" the="" flow="" is="" subcritical="" />
If y > yc, the flow is supercritical (S2).
If y = yc, the flow is critical (M1 or M2).
By comparing the flow depth (y = 0.6 m) and the critical flow depth (yc), we can determine the classification of the GVF profile.
Since the critical flow depth (yc) cannot be calculated without knowing the discharge (Q), we cannot determine the exact classification of the GVF profile. However, if we assume a certain discharge, we can calculate yc and compare it with the given flow depth (y = 0.6 m).
If yc > y, the flow is subcritical (S1).
If yc < y,="" the="" flow="" is="" supercritical="" />
If yc = y, the flow is critical (M1 or M2).
Therefore, without additional information about the discharge, it is not possible to determine the exact classification of the GVF profile. The correct answer cannot be determined based on the given information.
Given data:
Width of the rectangular channel (b) = 1 m
Bed slope (S) = 0.0016
Mannings roughness coefficient (n) = 0.04
Flow depth (y) = 0.6 m
1. Calculate the hydraulic radius (R):
The hydraulic radius is the ratio of the cross-sectional area to the wetted perimeter. For a rectangular channel, the wetted perimeter is equal to the sum of the bottom width and twice the flow depth.
Wetted perimeter (P) = b + 2y
Cross-sectional area (A) = b * y
Hydraulic radius (R) = A / P = (b * y) / (b + 2y)
2. Calculate the flow velocity (V):
The flow velocity can be calculated using Manning's equation:
V = (1 / n) * R^(2/3) * S^(1/2)
3. Calculate the critical flow depth (yc):
The critical flow depth is the flow depth at which the flow transitions from subcritical to supercritical or vice versa. It can be calculated using the following formula:
yc = (Q^2 / (g * A^2))^1/3
4. Calculate the Froude number (Fr):
Fr = V / (g * yc)^0.5
5. Compare the flow depth (y) and critical flow depth (yc):
If y < yc,="" the="" flow="" is="" subcritical="" />
If y > yc, the flow is supercritical (S2).
If y = yc, the flow is critical (M1 or M2).
By comparing the flow depth (y = 0.6 m) and the critical flow depth (yc), we can determine the classification of the GVF profile.
Since the critical flow depth (yc) cannot be calculated without knowing the discharge (Q), we cannot determine the exact classification of the GVF profile. However, if we assume a certain discharge, we can calculate yc and compare it with the given flow depth (y = 0.6 m).
If yc > y, the flow is subcritical (S1).
If yc < y,="" the="" flow="" is="" supercritical="" />
If yc = y, the flow is critical (M1 or M2).
Therefore, without additional information about the discharge, it is not possible to determine the exact classification of the GVF profile. The correct answer cannot be determined based on the given information.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A 1 m wide rectangular channel has a bed slope of 0.0016 and the Manning’s roughness coefficient is 0.04. Uniform flow takes place in the channel at a flow depth of 0.5 m. At a particular section, gradually varied flow (GVF) is observed and the flow depth is measured as 0.6 m. The GVF profile at that section is classified asa)S1b)S2c)M1d)M2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























