Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binde...
Start Learning for Free
In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:
- a)Sodium bentonite
- b)Calcium bentonite
- c)Sodium silicate
- d)Phenol formaldehyde
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium benton...
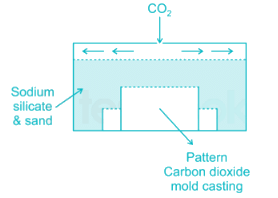
- This process is called sodium silicate moulding process because in this process, the refractory material is coated with a sodium-based binder.
- In this process CO2 gas is passed through the core or mold. The CO2 chemically reacts with the odium silicate to cure or harden the binder.
Most Upvoted Answer
In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium benton...
Carbon Dioxide Moulding Process and the Binder Used
The carbon dioxide moulding process is a type of sand casting process used in foundries to produce intricate and complex metal parts. It is a versatile and cost-effective method that involves the use of a mixture of sand and a binder to create the mould.
Binder
The binder used in the carbon dioxide moulding process is sodium silicate (option C). Sodium silicate, also known as water glass, is a chemical compound composed of sodium oxide (Na2O) and silicon dioxide (SiO2). It is a liquid binder that is mixed with sand to create a mould that can withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the casting process.
Role of the Binder
The binder plays a crucial role in the carbon dioxide moulding process. It has several important functions, including:
1. Bonding: Sodium silicate acts as a binding agent, holding the sand grains together to form a solid mould. It provides the necessary strength and stability to the mould during the casting process.
2. Collapsibility: Sodium silicate has the unique property of being collapsible. This means that when the mould is exposed to carbon dioxide gas, the binder breaks down, allowing the mould to collapse and release the pattern. This collapsibility is essential for easy removal of the pattern from the mould.
3. Heat Resistance: The sodium silicate binder has good heat resistance, which is crucial in withstanding the high temperatures encountered during the casting process. It helps prevent the mould from deforming or breaking down under the intense heat.
4. Dimensional Accuracy: Sodium silicate provides good dimensional accuracy to the mould, ensuring that the final castings have precise dimensions and meet the required specifications.
5. Environmental Friendliness: Sodium silicate is a water-based binder, making it environmentally friendly compared to other binders such as phenol formaldehyde (option D), which is a synthetic resin. It is also non-toxic and does not release harmful fumes during the casting process.
Conclusion
In the carbon dioxide moulding process, sodium silicate is the binder of choice. It provides the necessary bonding, collapsibility, heat resistance, dimensional accuracy, and environmentally friendly properties required for successful casting. By understanding the role of the binder, manufacturers can achieve high-quality castings with complex shapes and intricate details.
The carbon dioxide moulding process is a type of sand casting process used in foundries to produce intricate and complex metal parts. It is a versatile and cost-effective method that involves the use of a mixture of sand and a binder to create the mould.
Binder
The binder used in the carbon dioxide moulding process is sodium silicate (option C). Sodium silicate, also known as water glass, is a chemical compound composed of sodium oxide (Na2O) and silicon dioxide (SiO2). It is a liquid binder that is mixed with sand to create a mould that can withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the casting process.
Role of the Binder
The binder plays a crucial role in the carbon dioxide moulding process. It has several important functions, including:
1. Bonding: Sodium silicate acts as a binding agent, holding the sand grains together to form a solid mould. It provides the necessary strength and stability to the mould during the casting process.
2. Collapsibility: Sodium silicate has the unique property of being collapsible. This means that when the mould is exposed to carbon dioxide gas, the binder breaks down, allowing the mould to collapse and release the pattern. This collapsibility is essential for easy removal of the pattern from the mould.
3. Heat Resistance: The sodium silicate binder has good heat resistance, which is crucial in withstanding the high temperatures encountered during the casting process. It helps prevent the mould from deforming or breaking down under the intense heat.
4. Dimensional Accuracy: Sodium silicate provides good dimensional accuracy to the mould, ensuring that the final castings have precise dimensions and meet the required specifications.
5. Environmental Friendliness: Sodium silicate is a water-based binder, making it environmentally friendly compared to other binders such as phenol formaldehyde (option D), which is a synthetic resin. It is also non-toxic and does not release harmful fumes during the casting process.
Conclusion
In the carbon dioxide moulding process, sodium silicate is the binder of choice. It provides the necessary bonding, collapsibility, heat resistance, dimensional accuracy, and environmentally friendly properties required for successful casting. By understanding the role of the binder, manufacturers can achieve high-quality castings with complex shapes and intricate details.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In carbon dioxide moulding process, the binder used is:a)Sodium bentoniteb)Calcium bentonitec)Sodium silicated)Phenol formaldehydeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















