Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohm...
Start Learning for Free
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.
Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward bia...
Reverse current at t = 0 when the voltage
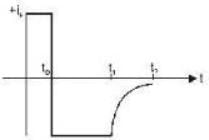
is instantaneously reversed to - VR = - 10 V is

Negative sign indicating reversal of current and voltage.
∴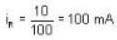

is instantaneously reversed to - VR = - 10 V is

Negative sign indicating reversal of current and voltage.
∴
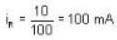
Most Upvoted Answer
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward bia...
Analysis:
To determine the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0, we need to consider the behavior of the diode in both the forward and reverse biased conditions.
Forward Bias:
When the p-n junction diode is forward biased, the positive terminal of the voltage source is connected to the p-side of the diode, and the negative terminal is connected to the n-side. This causes the diode to conduct current.
Given:
- Forward current (I) = 100 mA
- Resistance (R) = 100 Ω
Using Ohm's Law, we can determine the voltage (V) across the resistor:
V = I * R
V = 100 mA * 100 Ω
V = 10 V
Therefore, when the diode is forward biased, the voltage across the combination is 10 V.
Reverse Bias:
When the voltage across the combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0, the positive terminal of the voltage source is now connected to the n-side of the diode, and the negative terminal is connected to the p-side. This causes the diode to be reverse biased.
In reverse bias, the diode does not conduct current unless the reverse voltage exceeds the diode's breakdown voltage. However, we can assume that the reverse voltage of 10 V is below the breakdown voltage of the diode.
Answer:
The reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately 100 mA.
To determine the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0, we need to consider the behavior of the diode in both the forward and reverse biased conditions.
Forward Bias:
When the p-n junction diode is forward biased, the positive terminal of the voltage source is connected to the p-side of the diode, and the negative terminal is connected to the n-side. This causes the diode to conduct current.
Given:
- Forward current (I) = 100 mA
- Resistance (R) = 100 Ω
Using Ohm's Law, we can determine the voltage (V) across the resistor:
V = I * R
V = 100 mA * 100 Ω
V = 10 V
Therefore, when the diode is forward biased, the voltage across the combination is 10 V.
Reverse Bias:
When the voltage across the combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0, the positive terminal of the voltage source is now connected to the n-side of the diode, and the negative terminal is connected to the p-side. This causes the diode to be reverse biased.
In reverse bias, the diode does not conduct current unless the reverse voltage exceeds the diode's breakdown voltage. However, we can assume that the reverse voltage of 10 V is below the breakdown voltage of the diode.
Answer:
The reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately 100 mA.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer?.
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A p-n junction diode in series with a 100 ohms resistor is forward biased so that a current of 100 mA flows. If the voltage across this combination is instantaneously reversed to 10 V at t = 0. the reverse current that flows through the diode at t = 0 is approximately________ mA.Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















