IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determin...
Start Learning for Free
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?
- a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridges
- b)heterodimeric with disulphide bridges
- c)tetrameric with disuphide bridges
- d)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridges
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular we...
Size exclusion chromatography, also known as molecular sieve chromatography, is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size and molecular weight.
Molecular weight of the protein was found to be 60 kDa by size exclusion chromatography. So, 60 kDa is the molecular weight of intact native protein.
6 M urea will denature the protein, that is protein will lose its secondary and tertiary structure, however its disulphide bonds will remain intact in the presence of urea. Urea does not reduce the disulphide bonds. Urea belongs to a class of compounds known as chaotropic denaturants, which unravel the tertiary structure of proteins by destabilizing internal, non-covalent bonds between atoms.
So when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea, 30 kDa species was obtained, it’s because, urea denatures the proteins, so subunits of proteins (each subunit 30 kDa) were separated from each other in the presence of urea.
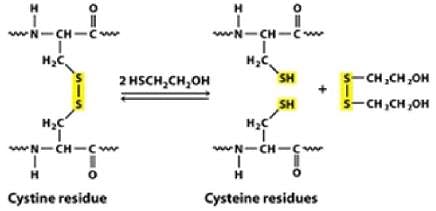
However, when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea and Beta mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kDa was obtained. It’s because, beta mercaptoethanol is a reducing agent. It reduces the disulphide bonds (that form between thiol groups of cysteine residues) present in the protein.
Each single 30 kDa subunit of protein was further made up of 2 single 15 kDa subunits that were held together by disulphide bond, which was reduced in the presence of beta mercaptoethanol.
Hence 60 kDa protein is a tetrameric protein held together by disulphide bridge.
Molecular weight of the protein was found to be 60 kDa by size exclusion chromatography. So, 60 kDa is the molecular weight of intact native protein.
6 M urea will denature the protein, that is protein will lose its secondary and tertiary structure, however its disulphide bonds will remain intact in the presence of urea. Urea does not reduce the disulphide bonds. Urea belongs to a class of compounds known as chaotropic denaturants, which unravel the tertiary structure of proteins by destabilizing internal, non-covalent bonds between atoms.
So when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea, 30 kDa species was obtained, it’s because, urea denatures the proteins, so subunits of proteins (each subunit 30 kDa) were separated from each other in the presence of urea.
However, when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea and Beta mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kDa was obtained. It’s because, beta mercaptoethanol is a reducing agent. It reduces the disulphide bonds (that form between thiol groups of cysteine residues) present in the protein.
Each single 30 kDa subunit of protein was further made up of 2 single 15 kDa subunits that were held together by disulphide bond, which was reduced in the presence of beta mercaptoethanol.
Hence 60 kDa protein is a tetrameric protein held together by disulphide bridge.

Most Upvoted Answer
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular we...
Structure of the molecule:
- The size exclusion chromatography result indicates that the protein has a molecular weight of 60 kD, suggesting that it is a monomer or a multimer with a molecular weight of 60 kD.
- Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species, which indicates that the protein is partially unfolded and has lost some of its tertiary or quaternary structure.
- When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results, indicating that the protein has been completely denatured and the subunits have dissociated.
Based on these results, we can conclude that the protein is a tetrameric protein with disulfide bridges. The dissociation of the protein into subunits in the presence of urea and b-mercaptoethanol suggests that the subunits are held together by disulfide bonds, which are disrupted by the reducing agent. The tetrameric structure is supported by the fact that the dissociation of the protein into subunits results in a 30-kd species, which is consistent with a dimeric subunit, and the final product is a 15-kd species, which suggests that the protein is composed of four subunits of approximately equal size. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
- The size exclusion chromatography result indicates that the protein has a molecular weight of 60 kD, suggesting that it is a monomer or a multimer with a molecular weight of 60 kD.
- Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species, which indicates that the protein is partially unfolded and has lost some of its tertiary or quaternary structure.
- When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results, indicating that the protein has been completely denatured and the subunits have dissociated.
Based on these results, we can conclude that the protein is a tetrameric protein with disulfide bridges. The dissociation of the protein into subunits in the presence of urea and b-mercaptoethanol suggests that the subunits are held together by disulfide bonds, which are disrupted by the reducing agent. The tetrameric structure is supported by the fact that the dissociation of the protein into subunits results in a 30-kd species, which is consistent with a dimeric subunit, and the final product is a 15-kd species, which suggests that the protein is composed of four subunits of approximately equal size. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular we...
Size exclusion chromatography, also known as molecular sieve chromatography, is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size and molecular weight.
Molecular weight of the protein was found to be 60 kDa by size exclusion chromatography. So, 60 kDa is the molecular weight of intact native protein.
6 M urea will denature the protein, that is protein will lose its secondary and tertiary structure, however its disulphide bonds will remain intact in the presence of urea. Urea does not reduce the disulphide bonds. Urea belongs to a class of compounds known as chaotropic denaturants, which unravel the tertiary structure of proteins by destabilizing internal, non-covalent bonds between atoms.
So when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea, 30 kDa species was obtained, it’s because, urea denatures the proteins, so subunits of proteins (each subunit 30 kDa) were separated from each other in the presence of urea.
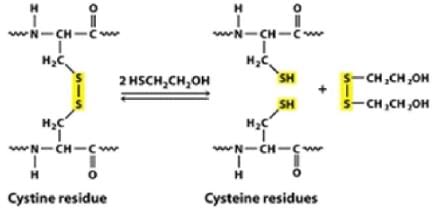
However, when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea and Beta mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kDa was obtained. It’s because, beta mercaptoethanol is a reducing agent. It reduces the disulphide bonds (that form between thiol groups of cysteine residues) present in the protein.
Each single 30 kDa subunit of protein was further made up of 2 single 15 kDa subunits that were held together by disulphide bond, which was reduced in the presence of beta mercaptoethanol.
Hence 60 kDa protein is a tetrameric protein held together by disulphide bridge.
Molecular weight of the protein was found to be 60 kDa by size exclusion chromatography. So, 60 kDa is the molecular weight of intact native protein.
6 M urea will denature the protein, that is protein will lose its secondary and tertiary structure, however its disulphide bonds will remain intact in the presence of urea. Urea does not reduce the disulphide bonds. Urea belongs to a class of compounds known as chaotropic denaturants, which unravel the tertiary structure of proteins by destabilizing internal, non-covalent bonds between atoms.
So when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea, 30 kDa species was obtained, it’s because, urea denatures the proteins, so subunits of proteins (each subunit 30 kDa) were separated from each other in the presence of urea.
However, when size exclusion chromatography was carried out in the presence of 6 M urea and Beta mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kDa was obtained. It’s because, beta mercaptoethanol is a reducing agent. It reduces the disulphide bonds (that form between thiol groups of cysteine residues) present in the protein.
Each single 30 kDa subunit of protein was further made up of 2 single 15 kDa subunits that were held together by disulphide bond, which was reduced in the presence of beta mercaptoethanol.
Hence 60 kDa protein is a tetrameric protein held together by disulphide bridge.


|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Protein was purified to homogeneity. Determination of the molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography yields 60 kD. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30-kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM b-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. Describe the structure of the molecule?a)homodimeric with no di sulphide bridgesb)heterodimeric with disulphide bridgesc)tetrameric with disuphide bridgesd)Polymeric with nodisuphide bridgesCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















