IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Which of the following amino acids are essent...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?
- a)Glycine
- b)Aspartate
- c)Glutamate
- d)Arginine
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and p...
Glycine is needed on in the synthesis of pyrimidine, while aspartate and glutamate is needed for both.
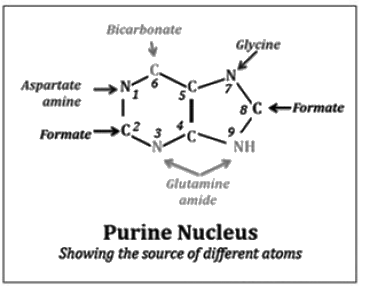
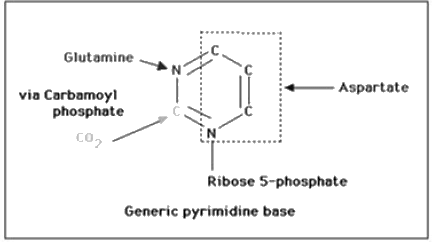


Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and p...
Essential Amino Acids for Purine and Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
Introduction:
Purines and pyrimidines are nucleotide bases that are essential for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. The biosynthesis of these nucleotides requires the presence of specific amino acids. Among the given options, amino acids that are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis are glycine (option A), aspartate (option B), and glutamate (option C).
Amino Acids Involved:
1. Glycine:
- Glycine is an amino acid that is involved in the biosynthesis of both purines and pyrimidines.
- In purine biosynthesis, glycine is required for the formation of 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate (THF), which is an important precursor.
- In pyrimidine biosynthesis, glycine is involved in the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate, which is a key intermediate.
- Therefore, glycine is essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.
2. Aspartate:
- Aspartate is another amino acid that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines.
- In purine biosynthesis, aspartate is required for the formation of adenylosuccinate, which is an intermediate in the pathway.
- In pyrimidine biosynthesis, aspartate is involved in the synthesis of orotate, which is a key precursor.
- Hence, aspartate is essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.
3. Glutamate:
- Glutamate is an amino acid that is necessary for the biosynthesis of both purines and pyrimidines.
- In purine biosynthesis, glutamate is involved in the formation of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), which is a crucial intermediate.
- In pyrimidine biosynthesis, glutamate is required for the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate, a key precursor.
- Thus, glutamate is essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.
Conclusion:
In summary, among the given options, the amino acids that are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis are glycine, aspartate, and glutamate. These amino acids are involved in the formation of important intermediates and precursors required for the synthesis of nucleotide bases.
Introduction:
Purines and pyrimidines are nucleotide bases that are essential for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. The biosynthesis of these nucleotides requires the presence of specific amino acids. Among the given options, amino acids that are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis are glycine (option A), aspartate (option B), and glutamate (option C).
Amino Acids Involved:
1. Glycine:
- Glycine is an amino acid that is involved in the biosynthesis of both purines and pyrimidines.
- In purine biosynthesis, glycine is required for the formation of 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate (THF), which is an important precursor.
- In pyrimidine biosynthesis, glycine is involved in the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate, which is a key intermediate.
- Therefore, glycine is essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.
2. Aspartate:
- Aspartate is another amino acid that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines.
- In purine biosynthesis, aspartate is required for the formation of adenylosuccinate, which is an intermediate in the pathway.
- In pyrimidine biosynthesis, aspartate is involved in the synthesis of orotate, which is a key precursor.
- Hence, aspartate is essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.
3. Glutamate:
- Glutamate is an amino acid that is necessary for the biosynthesis of both purines and pyrimidines.
- In purine biosynthesis, glutamate is involved in the formation of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), which is a crucial intermediate.
- In pyrimidine biosynthesis, glutamate is required for the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate, a key precursor.
- Thus, glutamate is essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.
Conclusion:
In summary, among the given options, the amino acids that are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis are glycine, aspartate, and glutamate. These amino acids are involved in the formation of important intermediates and precursors required for the synthesis of nucleotide bases.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following amino acids are essential for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis?a)Glycineb)Aspartatec)Glutamated)ArginineCorrect answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















