IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Which of the following is an example of hemia...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetal
- a)Linear structure of Glucose
- b)Cyclic structure of Glucose
- c)Linear structure of Fructose
- d)Cyclic structure of Fructose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure o...
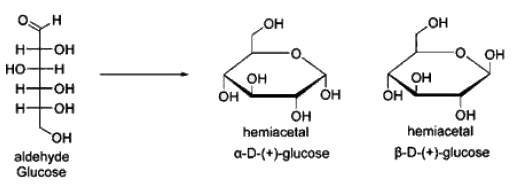
Hemiacetal is forimed due to reaction between aldehyde and internal hydroxyl groups of the carbohydrates. If hemiacetal reacts with one more sugar through alcohol group they lead to the formation of acetal hi linear structure carbohydrates are neither hemiacetal nor acetal. Glucose is a aldehyde sugar and aldehyde sugars on cyclization tonus hemiacetal. Fructose is a ketose sugar and ketose sugars on cyclization form Hemiketal. Hemiacetals / Hemiketal contain an additional asymmetric carbon atom and thus can exist in 2 stereo isomeric forms α and β.

Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure o...
Introduction:
Hemiacetals are a class of organic compounds that contain both an alcohol functional group (-OH) and an aldehyde or ketone functional group (>C=O). They are formed when a carbonyl compound reacts with an alcohol. In this question, we are asked to identify an example of a hemiacetal.
Explanation:
Among the given options, the cyclic structure of glucose (option B) is an example of a hemiacetal. Glucose is a monosaccharide, which means it is a simple sugar. It exists in both linear and cyclic forms due to the presence of hemiacetal formation.
Linear and Cyclic Forms of Glucose:
Glucose can exist in a linear form, which is an open-chain structure. In this form, the carbonyl group (C=O) is present at one end of the molecule. However, in aqueous solutions, glucose predominantly exists in its cyclic form due to the reaction between the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group on the same molecule.
Hemiacetal Formation:
In the cyclic form of glucose, the carbonyl group reacts with the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of a hemiacetal. Specifically, the aldehyde group on the glucose molecule reacts with the hydroxyl group on the fifth carbon atom, forming a cyclic hemiacetal. This reaction involves the formation of a new carbon-oxygen bond, converting the carbonyl group into a hemiacetal functional group.
Importance of Hemiacetal Formation in Glucose:
The formation of the hemiacetal in glucose is crucial for its stability and reactivity. It allows glucose to form glycosidic bonds with other molecules, leading to the formation of more complex carbohydrates such as disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Conclusion:
In summary, the cyclic structure of glucose (option B) is an example of a hemiacetal. In this form, the carbonyl group reacts with a hydroxyl group on the same molecule, resulting in the formation of a cyclic hemiacetal. This hemiacetal formation is important for the stability and reactivity of glucose, allowing it to participate in various biological processes.
Hemiacetals are a class of organic compounds that contain both an alcohol functional group (-OH) and an aldehyde or ketone functional group (>C=O). They are formed when a carbonyl compound reacts with an alcohol. In this question, we are asked to identify an example of a hemiacetal.
Explanation:
Among the given options, the cyclic structure of glucose (option B) is an example of a hemiacetal. Glucose is a monosaccharide, which means it is a simple sugar. It exists in both linear and cyclic forms due to the presence of hemiacetal formation.
Linear and Cyclic Forms of Glucose:
Glucose can exist in a linear form, which is an open-chain structure. In this form, the carbonyl group (C=O) is present at one end of the molecule. However, in aqueous solutions, glucose predominantly exists in its cyclic form due to the reaction between the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group on the same molecule.
Hemiacetal Formation:
In the cyclic form of glucose, the carbonyl group reacts with the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of a hemiacetal. Specifically, the aldehyde group on the glucose molecule reacts with the hydroxyl group on the fifth carbon atom, forming a cyclic hemiacetal. This reaction involves the formation of a new carbon-oxygen bond, converting the carbonyl group into a hemiacetal functional group.
Importance of Hemiacetal Formation in Glucose:
The formation of the hemiacetal in glucose is crucial for its stability and reactivity. It allows glucose to form glycosidic bonds with other molecules, leading to the formation of more complex carbohydrates such as disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Conclusion:
In summary, the cyclic structure of glucose (option B) is an example of a hemiacetal. In this form, the carbonyl group reacts with a hydroxyl group on the same molecule, resulting in the formation of a cyclic hemiacetal. This hemiacetal formation is important for the stability and reactivity of glucose, allowing it to participate in various biological processes.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is an example of hemiacetala)Linear structure of Glucoseb)Cyclic structure of Glucosec)Linear structure of Fructosed)Cyclic structure of FructoseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















