IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Which of the following anomeric form of Gluco...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starch
- a)Alpha D glucose
- b)Beta D glucose
- c)Alpha L glucose
- d)Beta L glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)...
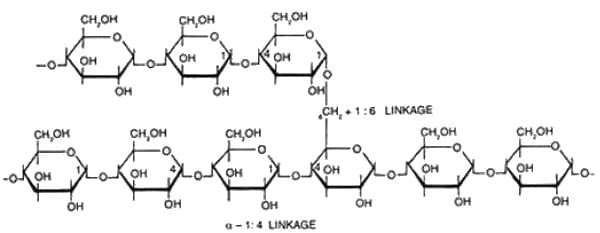
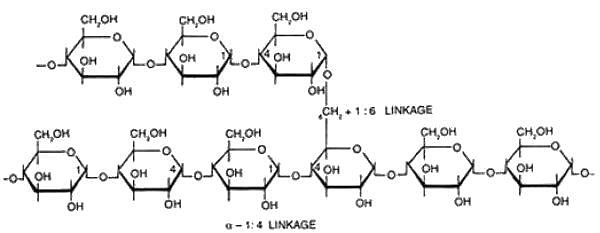
Starch is made up of repeating units of alpha D glucose. In aqueous solution, glucose occurs predominantly as cyclic (ring) structure in which the carbonyl group of glucose forms a covalent bond with oxygen of hydroxyl group at C-5 position of the same glucose molecule, resulting in formation of hemiacetal winch contains an additional asymmetric carbon atom. Thus cyclic form of glucose can exist in two stereoisomeric forms called α and β. Therefore, anomers are isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon atom

Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)...
Answer:
Introduction:
Starch is a polysaccharide composed of repeating units of glucose molecules. It is a storage form of energy in plants and is the most abundant carbohydrate in our diet. The glucose molecules in starch can exist in two different anomeric forms - alpha and beta. These anomers differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon atom.
Explanation:
Starch is composed of two main polysaccharides: amylose and amylopectin. Both amylose and amylopectin are made up of glucose molecules linked together through glycosidic bonds.
Alpha and Beta Anomers:
1. Alpha Anomer: In the alpha form, the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) is in a downward position.
2. Beta Anomer: In the beta form, the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) is in an upward position.
Presence of Anomeric Forms in Starch:
In starch, the glucose molecules are predominantly present in the alpha form. This means that the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) of glucose is in a downward position. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Alpha D glucose.
Reasoning:
Starch is a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules linked together. The glycosidic bonds between the glucose molecules determine the orientation of the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1). In starch, the predominant form of glucose is the alpha form, with the hydroxyl group in a downward position. The beta form is less common in starch.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the alpha D glucose anomeric form is predominantly present in starch. This form is characterized by the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) being in a downward position. It is important to note that starch can also contain small amounts of the beta form, but the alpha form is the major constituent.
Introduction:
Starch is a polysaccharide composed of repeating units of glucose molecules. It is a storage form of energy in plants and is the most abundant carbohydrate in our diet. The glucose molecules in starch can exist in two different anomeric forms - alpha and beta. These anomers differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon atom.
Explanation:
Starch is composed of two main polysaccharides: amylose and amylopectin. Both amylose and amylopectin are made up of glucose molecules linked together through glycosidic bonds.
Alpha and Beta Anomers:
1. Alpha Anomer: In the alpha form, the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) is in a downward position.
2. Beta Anomer: In the beta form, the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) is in an upward position.
Presence of Anomeric Forms in Starch:
In starch, the glucose molecules are predominantly present in the alpha form. This means that the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) of glucose is in a downward position. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Alpha D glucose.
Reasoning:
Starch is a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules linked together. The glycosidic bonds between the glucose molecules determine the orientation of the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1). In starch, the predominant form of glucose is the alpha form, with the hydroxyl group in a downward position. The beta form is less common in starch.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the alpha D glucose anomeric form is predominantly present in starch. This form is characterized by the hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon (C1) being in a downward position. It is important to note that starch can also contain small amounts of the beta form, but the alpha form is the major constituent.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)...
Starch is made up of repeating units of alpha D glucose. In aqueous solution, glucose occurs predominantly as cyclic (ring) structure in which the carbonyl group of glucose forms a covalent bond with oxygen of hydroxyl group at C-5 position of the same glucose molecule, resulting in formation of hemiacetal winch contains an additional asymmetric carbon atom. Thus cyclic form of glucose can exist in two stereoisomeric forms called α and β. Therefore, anomers are isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon atom


|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starcha)Alpha D glucoseb)Beta D glucosec)Alpha L glucosed)Beta L glucoseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















