Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biase...
Start Learning for Free
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as a
- a)voltage source with zero output impedance
- b)voltage source with non-zero output impedance
- c)current source with finite output impedance
- d)current source with infinite output impedance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VD...
If channel length modulation is considered and significant it means λ ≠ 0
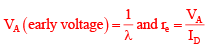
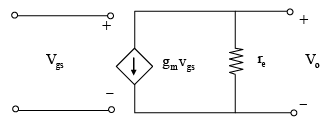
If VAS > VTH and VDS > (VDS - VTH) then it indicates that MOSFET is working in saturation region and it can be used as an amplifier. So it can act as current source with finite output impedance.
If VAS > VTH and VDS > (VDS - VTH) then it indicates that MOSFET is working in saturation region and it can be used as an amplifier. So it can act as current source with finite output impedance.
Most Upvoted Answer
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VD...
Explanation:
MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device that operates in the saturation region when the gate-to-source voltage (VGS) is greater than the threshold voltage (VTH) and the drain-to-source voltage (VDS) is also greater than zero. However, when the drain-to-source voltage increases, the width of the depletion region near the drain also increases, reducing the effective channel length and, hence, increasing the channel resistance. This phenomenon is known as channel length modulation and it affects the MOSFET output impedance.
Current Source with Finite Output Impedance:
When the MOSFET is biased in the saturation region, it behaves like a current source, and the output impedance depends on the channel length modulation effect:
- As the drain-to-source voltage (VDS) increases, the channel length modulation effect reduces the effective channel length, leading to an increase in channel resistance, which in turn increases the output impedance.
- Therefore, the MOSFET behaves like a current source with finite output impedance.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'C,' i.e., the MOSFET behaves like a current source with finite output impedance due to channel length modulation effect.
MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device that operates in the saturation region when the gate-to-source voltage (VGS) is greater than the threshold voltage (VTH) and the drain-to-source voltage (VDS) is also greater than zero. However, when the drain-to-source voltage increases, the width of the depletion region near the drain also increases, reducing the effective channel length and, hence, increasing the channel resistance. This phenomenon is known as channel length modulation and it affects the MOSFET output impedance.
Current Source with Finite Output Impedance:
When the MOSFET is biased in the saturation region, it behaves like a current source, and the output impedance depends on the channel length modulation effect:
- As the drain-to-source voltage (VDS) increases, the channel length modulation effect reduces the effective channel length, leading to an increase in channel resistance, which in turn increases the output impedance.
- Therefore, the MOSFET behaves like a current source with finite output impedance.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'C,' i.e., the MOSFET behaves like a current source with finite output impedance due to channel length modulation effect.
Attention Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET is biased at VGS > VTH and VDS > (VGS - VTH) , where VGS is the gate-to-source voltage, VDS is the drain-to-source voltage and VTH is the threshold voltage. Considering channel length modulation effect to be significant, the MOSFET behaves as aa)voltage source with zero output impedanceb)voltage source with non-zero output impedancec)current source with finite output impedanced)current source with infinite output impedanceCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























