Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts ...
Start Learning for Free
Leaching is a process
- a)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :
- b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with water
- c)of draining excess water of irrigation
- d)which controls water-logging
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are d...
Leaching is the process in which land is flooded with adequate depth of water. The alkaii salts' present in soil, get dissolved with this water which percolate down to join the water table or are drained away by sub-surface drains,
Leaching requirement,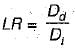
Dd is Depth of water drained out per unit area
Di is Depth of irrigation water applied per unit area
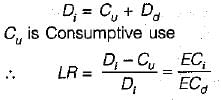
ECi is Electrical conductivity of irrigation water
ECd is Electrical conductivity of drained water.
Leaching requirement,
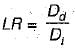
Dd is Depth of water drained out per unit area
Di is Depth of irrigation water applied per unit area
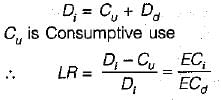
ECi is Electrical conductivity of irrigation water
ECd is Electrical conductivity of drained water.
Most Upvoted Answer
Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are d...
Leaching in Soil Science
Leaching is a process that occurs in soil science and agriculture. It refers to the removal of certain substances, specifically alkali salts, from the soil through the action of water. This process is essential for maintaining healthy soil conditions and preventing soil degradation.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer to the question is option 'A': by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away. This option accurately describes the process of leaching in soil science. Here is a detailed explanation of why this option is correct:
1. Alkali Salts Dissolution
Leaching involves the dissolution of alkali salts that are present in the soil. These salts are primarily composed of sodium, potassium, and other alkali metals. They may accumulate in the soil over time due to various factors such as irrigation practices, excessive use of fertilizers, and the natural mineral content of the soil.
2. Action of Water
The leaching process is facilitated by the action of water. When water is applied to the soil, it percolates through the soil layers, dissolving the alkali salts as it moves downward. This dissolution occurs due to the water's ability to solubilize the salts and carry them along with it.
3. Draining Away
As the water moves through the soil, it carries the dissolved alkali salts with it. Eventually, the water reaches a lower layer of the soil or a drainage system, where it is drained away. This draining process effectively removes the alkali salts from the soil, preventing their accumulation and potential harm to plants and soil fertility.
4. Importance in Soil Health
Leaching plays a crucial role in maintaining soil health. If alkali salts were to accumulate in the soil without being leached, they would lead to soil salinization. Excess salts can hinder plant growth, reduce crop yields, and degrade soil structure. Therefore, leaching helps to maintain a balanced soil environment that is conducive to plant growth.
5. Other Options Explained
Option 'B': by which alkali salts in soil come up with water is incorrect because leaching involves the downward movement of water, carrying the salts away from the root zone, rather than bringing them up to the surface.
Option 'C': of draining excess water of irrigation is incorrect because leaching is not primarily focused on draining excess water. While leaching does involve the movement of water, its main purpose is to remove alkali salts, rather than excess irrigation water.
Option 'D': which controls water-logging is incorrect because leaching is not specifically aimed at controlling water-logging. While leaching may indirectly alleviate water-logging issues by promoting drainage, its primary objective is the removal of alkali salts.
In conclusion, leaching in soil science is a process by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away through the action of water. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy soil conditions and preventing soil degradation.
Leaching is a process that occurs in soil science and agriculture. It refers to the removal of certain substances, specifically alkali salts, from the soil through the action of water. This process is essential for maintaining healthy soil conditions and preventing soil degradation.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer to the question is option 'A': by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away. This option accurately describes the process of leaching in soil science. Here is a detailed explanation of why this option is correct:
1. Alkali Salts Dissolution
Leaching involves the dissolution of alkali salts that are present in the soil. These salts are primarily composed of sodium, potassium, and other alkali metals. They may accumulate in the soil over time due to various factors such as irrigation practices, excessive use of fertilizers, and the natural mineral content of the soil.
2. Action of Water
The leaching process is facilitated by the action of water. When water is applied to the soil, it percolates through the soil layers, dissolving the alkali salts as it moves downward. This dissolution occurs due to the water's ability to solubilize the salts and carry them along with it.
3. Draining Away
As the water moves through the soil, it carries the dissolved alkali salts with it. Eventually, the water reaches a lower layer of the soil or a drainage system, where it is drained away. This draining process effectively removes the alkali salts from the soil, preventing their accumulation and potential harm to plants and soil fertility.
4. Importance in Soil Health
Leaching plays a crucial role in maintaining soil health. If alkali salts were to accumulate in the soil without being leached, they would lead to soil salinization. Excess salts can hinder plant growth, reduce crop yields, and degrade soil structure. Therefore, leaching helps to maintain a balanced soil environment that is conducive to plant growth.
5. Other Options Explained
Option 'B': by which alkali salts in soil come up with water is incorrect because leaching involves the downward movement of water, carrying the salts away from the root zone, rather than bringing them up to the surface.
Option 'C': of draining excess water of irrigation is incorrect because leaching is not primarily focused on draining excess water. While leaching does involve the movement of water, its main purpose is to remove alkali salts, rather than excess irrigation water.
Option 'D': which controls water-logging is incorrect because leaching is not specifically aimed at controlling water-logging. While leaching may indirectly alleviate water-logging issues by promoting drainage, its primary objective is the removal of alkali salts.
In conclusion, leaching in soil science is a process by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away through the action of water. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy soil conditions and preventing soil degradation.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Leaching is a processa)by which alkali salts present in the soil are dissolved and drained away :b)by which alkali salts in soil come up with waterc)of draining excess water of irrigationd)which controls water-loggingCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























