Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stre...
Start Learning for Free
In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress is
- a)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wall
- b)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wall
- c)maximum midway between the centerline and the wall
- d)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the center
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the cen...
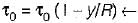 shear stress variation where y is distance from pipe wall, so, the shear stress varies linearly with the distance from the boundary to become zero at the center.
shear stress variation where y is distance from pipe wall, so, the shear stress varies linearly with the distance from the boundary to become zero at the center.Most Upvoted Answer
In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the cen...
Understanding Shear Stress in Turbulent Pipe Flow
In turbulent flow within a pipe, the distribution of shear stress is a critical aspect to understand. The correct answer to the question is option 'D', which states that shear stress is maximum at the wall and decreases to zero at the centerline of the pipe. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Shear Stress Profile
- **Maximum at the Wall**: In turbulent flow, the viscosity of the fluid creates a shear stress that is highest at the pipe walls due to the no-slip condition. This means the fluid in contact with the wall has zero velocity relative to the wall.
- **Decreases Towards the Center**: As you move away from the wall towards the centerline of the pipe, the velocity of the fluid increases. The shear stress, which is a function of the velocity gradient, decreases significantly and approaches zero at the center.
Flow Characteristics
- **Turbulent Flow Dynamics**: In turbulent flow, the fluid exhibits chaotic and irregular movement. This leads to a more complex velocity profile than in laminar flow, where shear stress varies linearly.
- **Velocity Profile**: The velocity profile in turbulent flow is not parabolic like that in laminar flow; instead, it is flatter in the center and steep near the walls, which contributes to the shear stress profile.
Conclusion
In summary, the maximum shear stress occurs at the wall due to the no-slip condition, and it decreases to zero at the centerline. Understanding this concept is crucial in mechanical engineering applications involving fluid dynamics and pipe flow.
In turbulent flow within a pipe, the distribution of shear stress is a critical aspect to understand. The correct answer to the question is option 'D', which states that shear stress is maximum at the wall and decreases to zero at the centerline of the pipe. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Shear Stress Profile
- **Maximum at the Wall**: In turbulent flow, the viscosity of the fluid creates a shear stress that is highest at the pipe walls due to the no-slip condition. This means the fluid in contact with the wall has zero velocity relative to the wall.
- **Decreases Towards the Center**: As you move away from the wall towards the centerline of the pipe, the velocity of the fluid increases. The shear stress, which is a function of the velocity gradient, decreases significantly and approaches zero at the center.
Flow Characteristics
- **Turbulent Flow Dynamics**: In turbulent flow, the fluid exhibits chaotic and irregular movement. This leads to a more complex velocity profile than in laminar flow, where shear stress varies linearly.
- **Velocity Profile**: The velocity profile in turbulent flow is not parabolic like that in laminar flow; instead, it is flatter in the center and steep near the walls, which contributes to the shear stress profile.
Conclusion
In summary, the maximum shear stress occurs at the wall due to the no-slip condition, and it decreases to zero at the centerline. Understanding this concept is crucial in mechanical engineering applications involving fluid dynamics and pipe flow.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a turbulent flow in a pipe, the shear stress isa)maximum at the center and decreases linearly towards the wallb)maximum at the center and decreases logarithmically towards the wallc)maximum midway between the centerline and the walld)maximum at the wall and decreases linearly to a zero value at the centerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























