JEE Exam > JEE Questions > When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydrox...
Start Learning for Free
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :
- a)Mn
- b)Cr
- c)V
- d)Ti
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxi...
Most Upvoted Answer
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxi...
Introduction
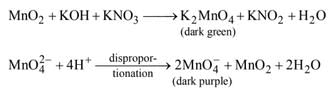
The reaction involving the fusion of XO2 with alkali metal hydroxide and an oxidizing agent like KNO3 leads to a dark green product that subsequently disproportions in acidic conditions, yielding a dark purple solution. Here, we will identify X as Manganese (Mn).
Reaction Overview
- XO2 represents a metal oxide, where X is the metal.
- In this case, we are considering manganese dioxide (MnO2).
Formation of Dark Green Product
- When MnO2 is fused with alkali metal hydroxide in the presence of KNO3, a complex manganese species is formed.
- This dark green product typically contains manganese in a higher oxidation state, possibly as a manganate ion (MnO4^2-).
Disproportionation Reaction
- In acidic solutions, the dark green manganate undergoes disproportionation:
- 2 MnO4^2- → MnO4^- (purple) + MnO2 (brown).
- The dark purple solution formed is due to the presence of permanganate ions (MnO4^-), which are well-known for their deep purple color.
Conclusion
- Based on these reactions, the metal X that leads to the formation of such products is indeed Manganese (Mn).
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
This process highlights the intriguing chemistry of manganese and its ability to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions, exemplifying its versatile oxidation states.
The reaction involving the fusion of XO2 with alkali metal hydroxide and an oxidizing agent like KNO3 leads to a dark green product that subsequently disproportions in acidic conditions, yielding a dark purple solution. Here, we will identify X as Manganese (Mn).
Reaction Overview
- XO2 represents a metal oxide, where X is the metal.
- In this case, we are considering manganese dioxide (MnO2).
Formation of Dark Green Product
- When MnO2 is fused with alkali metal hydroxide in the presence of KNO3, a complex manganese species is formed.
- This dark green product typically contains manganese in a higher oxidation state, possibly as a manganate ion (MnO4^2-).
Disproportionation Reaction
- In acidic solutions, the dark green manganate undergoes disproportionation:
- 2 MnO4^2- → MnO4^- (purple) + MnO2 (brown).
- The dark purple solution formed is due to the presence of permanganate ions (MnO4^-), which are well-known for their deep purple color.
Conclusion
- Based on these reactions, the metal X that leads to the formation of such products is indeed Manganese (Mn).
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
This process highlights the intriguing chemistry of manganese and its ability to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions, exemplifying its versatile oxidation states.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxi...


|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When XO2 is fused with an alkali metal hydroxide in presence of an oxidizing agent such as KNO3 ; a dark green product is formed which disproportioates in acidic solution to afford a dark purple solution. X is :a)Mnb)Crc)Vd)TiCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















