Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit...
Start Learning for Free
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.
- a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperature
- b)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature
- c)remains fixed with an increase in temperature
- d)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixe...
The common emitter circuit configuration provides voltage gain combined with a moderate current gain, as well as a medium input and a medium output impedance. As such the common emitter configuration is a good all round circuit for use in many applications.
It is also worth noting at this stage that the common emitter transistor amplifier inverts the signal at the input. Therefore if a waveform that is rising enters the input of the common emitter amplifier, it will cause the output voltage to fall. In other words it has a 180° phase change across the circuit.
Dependent upon the actual electronic circuit design itself, the common emitter does not use too many electronic components, sometimes as few as two resistors, although if the bias needs setting for analogue circuits, then four resistors and three capacitors may be used.
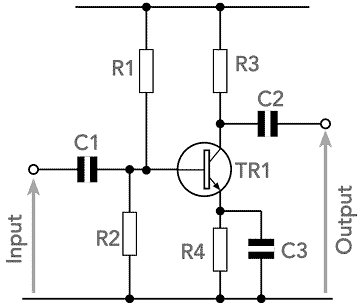
In fixed bias, when temperature is increased, the operating point moves toward the saturation region.
The correct answer is: moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature
The correct answer is: moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature
Most Upvoted Answer
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixe...
In fixed bias, when temperature is increased, the operating point moves toward the saturation region.
The correct answer is: moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature
The correct answer is: moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixe...
In a common emitter transistor amplifier circuit, the operating point refers to the DC bias conditions at which the transistor operates. This biasing is essential to ensure the transistor operates in its active region and produces the desired amplification.
The operating point of a common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is typically set using a fixed bias configuration. This biasing configuration usually consists of a voltage divider network (resistors) connected to the base of the transistor. The purpose of this bias circuit is to establish a stable base current, which determines the operating conditions of the transistor.
Now, let's analyze the given options and determine which one is correct.
a) Moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperature:
When the temperature increases, the forward voltage drop across the base-emitter junction decreases. As a result, the base current increases, which tends to drive the transistor into saturation. Therefore, the operating point moves towards the saturation region. However, this option is incorrect.
b) Moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature:
When the temperature decreases, the forward voltage drop across the base-emitter junction increases. As a result, the base current decreases, which tends to push the operating point towards the cut-off region. Therefore, the operating point moves towards the saturation region. This option is correct.
c) Remains fixed with an increase in temperature:
This option is incorrect because, as mentioned earlier, an increase in temperature causes the forward voltage drop across the base-emitter junction to decrease, leading to a change in the operating point.
d) Moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperature:
This option is incorrect because, as explained earlier, an increase in temperature causes the operating point to move towards the saturation region, not the cut-off region.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' - the operating point of a common emitter transistor amplifier circuit moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature.
The operating point of a common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is typically set using a fixed bias configuration. This biasing configuration usually consists of a voltage divider network (resistors) connected to the base of the transistor. The purpose of this bias circuit is to establish a stable base current, which determines the operating conditions of the transistor.
Now, let's analyze the given options and determine which one is correct.
a) Moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperature:
When the temperature increases, the forward voltage drop across the base-emitter junction decreases. As a result, the base current increases, which tends to drive the transistor into saturation. Therefore, the operating point moves towards the saturation region. However, this option is incorrect.
b) Moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature:
When the temperature decreases, the forward voltage drop across the base-emitter junction increases. As a result, the base current decreases, which tends to push the operating point towards the cut-off region. Therefore, the operating point moves towards the saturation region. This option is correct.
c) Remains fixed with an increase in temperature:
This option is incorrect because, as mentioned earlier, an increase in temperature causes the forward voltage drop across the base-emitter junction to decrease, leading to a change in the operating point.
d) Moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperature:
This option is incorrect because, as explained earlier, an increase in temperature causes the operating point to move towards the saturation region, not the cut-off region.
In summary, the correct answer is option 'B' - the operating point of a common emitter transistor amplifier circuit moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperature.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A common emitter transistor amplifier circuit is operated under a fixed bias. In this circuit, the operating point.a)moves towards the saturation region with an increase in temperatureb)moves towards the saturation region with a decrease in temperaturec)remains fixed with an increase in temperatured)moves toward cut-off region with an increase in temperatureCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















