Physics Exam > Physics Questions > During an integral number of complete cycles,...
Start Learning for Free
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.
Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (sho...
By conservation of energy Q1 = W + Q2 + Q3
i.e., Q2 + Q3 = Q1 - W = 1200 - 200 = 1000 (1)
And as change in entropy in a reversible-process is zero
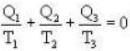 i.e.
i.e. 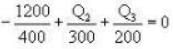
i.e., 2Q2 + 3Q3 = 1800 (2)
Solving equation (1) and (2) for Q2 and Q3, we get
Q2 = 1200 J and Q3 = -200 J
i.e.. the reservoir at temperature T2 absorbs 1200 J of heat while the reservoir at temperature T3 lose 200 J of heat. Hence their sum will be 1400 J
i.e., Q2 + Q3 = Q1 - W = 1200 - 200 = 1000 (1)
And as change in entropy in a reversible-process is zero
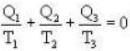 i.e.
i.e. 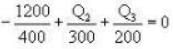
i.e., 2Q2 + 3Q3 = 1800 (2)
Solving equation (1) and (2) for Q2 and Q3, we get
Q2 = 1200 J and Q3 = -200 J
i.e.. the reservoir at temperature T2 absorbs 1200 J of heat while the reservoir at temperature T3 lose 200 J of heat. Hence their sum will be 1400 J
Most Upvoted Answer
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (sho...
Given information:
- A reversible engine absorbs 1200 joules from a reservoir at 400 K.
- The engine performs 200 joules of mechanical work.
- The engine undergoes an integral number of complete cycles.
Assumptions:
- The engine is operating in a Carnot cycle, which consists of two isothermal and two adiabatic processes.
- The engine is in thermal equilibrium with the reservoirs during the isothermal processes.
- The engine is perfectly reversible, meaning there are no losses due to friction or other inefficiencies.
Explanation:
To find the sum of quantities of heat exchanged with the other two reservoirs, we need to consider the energy conservation in the reversible engine.
1. First Law of Thermodynamics:
The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system:
ΔU = Q - W
where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system.
2. Carnot Cycle:
In a Carnot cycle, the engine operates between two heat reservoirs at different temperatures. The efficiency of a Carnot engine is given by:
η = 1 - (T2 / T1)
where η is the efficiency, T1 is the temperature of the hot reservoir, and T2 is the temperature of the cold reservoir.
3. Applying the First Law:
In this problem, the engine absorbs 1200 joules of heat from the hot reservoir and performs 200 joules of work. Therefore, the change in internal energy of the engine is:
ΔU = 1200 J - 200 J = 1000 J
4. Efficiency of the Engine:
The efficiency of a reversible engine is given by:
η = W / Qh = 200 J / 1200 J = 1/6
5. Applying Carnot Efficiency:
Since the engine is operating in a Carnot cycle, its efficiency is also given by:
η = 1 - (T2 / T1)
Let's assume that T2 is the temperature of the cold reservoir. Rearranging the equation, we get:
T2 = T1 - T1 * η
Plugging in the given values, we have:
T2 = 400 K - 400 K * (1/6) = 400 K - 200/6 K = 400 K - 33.33 K = 366.67 K
So, the temperature of the cold reservoir is 366.67 K.
6. Heat Exchange with the Cold Reservoir:
During the isothermal process with the cold reservoir, the engine releases heat to the reservoir. The amount of heat released can be calculated using the equation:
Qc = W / η = 200 J / (1/6) = 1200 J
Therefore, the engine releases 1200 joules of heat to the cold reservoir.
7. Heat Exchange with the Hot Reservoir:
Since the engine is reversible, the heat exchange with the hot reservoir can be calculated using the equation:
Qh = Qc + W = 1200 J +
- A reversible engine absorbs 1200 joules from a reservoir at 400 K.
- The engine performs 200 joules of mechanical work.
- The engine undergoes an integral number of complete cycles.
Assumptions:
- The engine is operating in a Carnot cycle, which consists of two isothermal and two adiabatic processes.
- The engine is in thermal equilibrium with the reservoirs during the isothermal processes.
- The engine is perfectly reversible, meaning there are no losses due to friction or other inefficiencies.
Explanation:
To find the sum of quantities of heat exchanged with the other two reservoirs, we need to consider the energy conservation in the reversible engine.
1. First Law of Thermodynamics:
The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system:
ΔU = Q - W
where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system.
2. Carnot Cycle:
In a Carnot cycle, the engine operates between two heat reservoirs at different temperatures. The efficiency of a Carnot engine is given by:
η = 1 - (T2 / T1)
where η is the efficiency, T1 is the temperature of the hot reservoir, and T2 is the temperature of the cold reservoir.
3. Applying the First Law:
In this problem, the engine absorbs 1200 joules of heat from the hot reservoir and performs 200 joules of work. Therefore, the change in internal energy of the engine is:
ΔU = 1200 J - 200 J = 1000 J
4. Efficiency of the Engine:
The efficiency of a reversible engine is given by:
η = W / Qh = 200 J / 1200 J = 1/6
5. Applying Carnot Efficiency:
Since the engine is operating in a Carnot cycle, its efficiency is also given by:
η = 1 - (T2 / T1)
Let's assume that T2 is the temperature of the cold reservoir. Rearranging the equation, we get:
T2 = T1 - T1 * η
Plugging in the given values, we have:
T2 = 400 K - 400 K * (1/6) = 400 K - 200/6 K = 400 K - 33.33 K = 366.67 K
So, the temperature of the cold reservoir is 366.67 K.
6. Heat Exchange with the Cold Reservoir:
During the isothermal process with the cold reservoir, the engine releases heat to the reservoir. The amount of heat released can be calculated using the equation:
Qc = W / η = 200 J / (1/6) = 1200 J
Therefore, the engine releases 1200 joules of heat to the cold reservoir.
7. Heat Exchange with the Hot Reservoir:
Since the engine is reversible, the heat exchange with the hot reservoir can be calculated using the equation:
Qh = Qc + W = 1200 J +

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer?.
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.Correct answer is '1400'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















