Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 ...
Start Learning for Free
A long solenoid of diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec. Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.
Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the c...
As field inside, a solenoid is given by
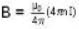
so here.
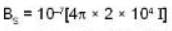
And hence flux linked with the coil
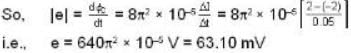
Further as the coil has a resistance of 10π2 ohm. the current induced in it.
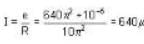
and as,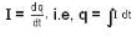
So,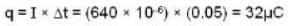
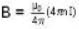

so here.
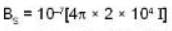
And hence flux linked with the coil
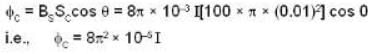
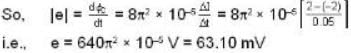
Further as the coil has a resistance of 10π2 ohm. the current induced in it.
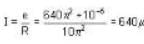
and as,
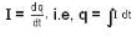
So,
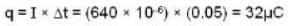
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Physics courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Physics courses
Most Upvoted Answer
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the c...
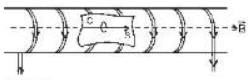
As field inside, a solenoid is given by
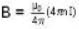

so here.
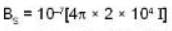
And hence flux linked with the coil
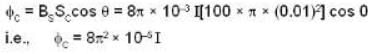
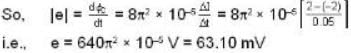
Further as the coil has a resistance of 10π2 ohm. the current induced in it.
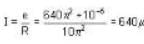
and as,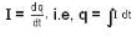
So,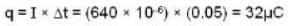
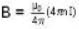

so here.
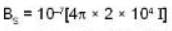
And hence flux linked with the coil
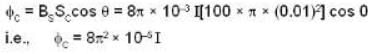
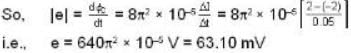
Further as the coil has a resistance of 10π2 ohm. the current induced in it.
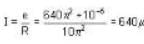
and as,
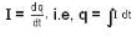
So,
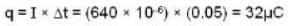
Community Answer
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the c...
To find the total charge, we can use Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction:
EMF = -N * dΦ/dt
Where EMF is the electromotive force induced in the coil, N is the number of turns in the coil, and dΦ/dt is the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil.
Since the coil is placed at the center of the solenoid, the magnetic field through the coil is constant and given by:
B = μ₀ * N * I
Where μ₀ is the permeability of free space, N is the number of turns per meter in the solenoid, and I is the current in the solenoid.
The magnetic flux through the coil is then given by:
Φ = B * A
Where A is the area of the coil.
Since the coil has a circular shape, the area can be calculated as:
A = π * r²
Where r is the radius of the coil.
Substituting the values given:
A = π * (0.01 m)² = 0.000314 m²
B = (4π * 10⁻⁷ T * 2 * 10⁴ turns/m * 2 A) = 5.03 * 10⁻³ T
Φ = (5.03 * 10⁻³ T) * (0.000314 m²) = 1.58 * 10⁻⁶ Wb
The rate of change of magnetic flux can be calculated as:
dΦ/dt = (Φ₂ - Φ₁) / (t₂ - t₁)
Where Φ₂ and Φ₁ are the final and initial flux values, and t₂ and t₁ are the final and initial times.
Substituting the values given:
dΦ/dt = (1.58 * 10⁻⁶ Wb - 0) / (0.05 s - 0) = 3.16 * 10⁻⁵ Wb/s
Now we can calculate the electromotive force induced in the coil:
EMF = -N * dΦ/dt = -100 turns * 3.16 * 10⁻⁵ Wb/s = -3.16 * 10⁻³ V
To find the total charge, we can use the equation:
Q = ∫ EMF * dt
Integrating from t₁ to t₂:
Q = ∫ (-3.16 * 10⁻³ V) * dt
Q = (-3.16 * 10⁻³ V) * (t₂ - t₁)
Substituting the values given:
Q = (-3.16 * 10⁻³ V) * (0.05 s - 0) = -1.58 * 10⁻⁴ C
Since charge is a scalar quantity, we take the absolute value:
|Q| = 1.58 * 10⁻⁴ C
Therefore, the total charge induced in the coil is 1.58 * 10⁻⁴ C.
EMF = -N * dΦ/dt
Where EMF is the electromotive force induced in the coil, N is the number of turns in the coil, and dΦ/dt is the rate of change of magnetic flux through the coil.
Since the coil is placed at the center of the solenoid, the magnetic field through the coil is constant and given by:
B = μ₀ * N * I
Where μ₀ is the permeability of free space, N is the number of turns per meter in the solenoid, and I is the current in the solenoid.
The magnetic flux through the coil is then given by:
Φ = B * A
Where A is the area of the coil.
Since the coil has a circular shape, the area can be calculated as:
A = π * r²
Where r is the radius of the coil.
Substituting the values given:
A = π * (0.01 m)² = 0.000314 m²
B = (4π * 10⁻⁷ T * 2 * 10⁴ turns/m * 2 A) = 5.03 * 10⁻³ T
Φ = (5.03 * 10⁻³ T) * (0.000314 m²) = 1.58 * 10⁻⁶ Wb
The rate of change of magnetic flux can be calculated as:
dΦ/dt = (Φ₂ - Φ₁) / (t₂ - t₁)
Where Φ₂ and Φ₁ are the final and initial flux values, and t₂ and t₁ are the final and initial times.
Substituting the values given:
dΦ/dt = (1.58 * 10⁻⁶ Wb - 0) / (0.05 s - 0) = 3.16 * 10⁻⁵ Wb/s
Now we can calculate the electromotive force induced in the coil:
EMF = -N * dΦ/dt = -100 turns * 3.16 * 10⁻⁵ Wb/s = -3.16 * 10⁻³ V
To find the total charge, we can use the equation:
Q = ∫ EMF * dt
Integrating from t₁ to t₂:
Q = ∫ (-3.16 * 10⁻³ V) * dt
Q = (-3.16 * 10⁻³ V) * (t₂ - t₁)
Substituting the values given:
Q = (-3.16 * 10⁻³ V) * (0.05 s - 0) = -1.58 * 10⁻⁴ C
Since charge is a scalar quantity, we take the absolute value:
|Q| = 1.58 * 10⁻⁴ C
Therefore, the total charge induced in the coil is 1.58 * 10⁻⁴ C.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer?.
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A long solenoidof diameter 0.1 m has 2 * 104 turns per meter. At the centre of, the solenoid a 100 turn coil of radius 0.01m is placed with its axis coinciding with that of the solenoid. The current in the solenoid is decreasing at a constant rate from +2A to -2A in 0.05 sec.Find the total charge (in μC ) flowing through the coil during this time if the resistance of the coil is 10 π2 ohm.Correct answer is '32'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















