Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A plane monochromatic light wave falls normal...
Start Learning for Free
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with tw...
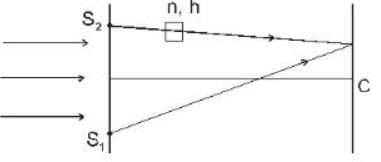
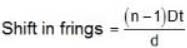
D = 10 cm = 1 m
d = 2.5 mm = 2.5 x 10-3 m
t = 10 x 10-6 m , n = 1.5
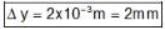
Most Upvoted Answer
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with tw...
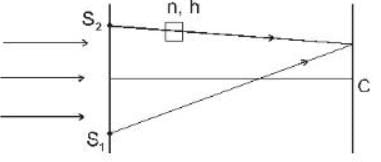
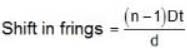
D = 10 cm = 1 m
d = 2.5 mm = 2.5 x 10-3 m
t = 10 x 10-6 m , n = 1.5
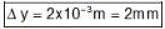
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with tw...
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of interference of light waves. When light passes through two narrow slits, it creates an interference pattern on a screen.
Without the glass plate covering one of the slits, we have a double-slit interference pattern. The interference pattern consists of bright fringes (maxima) and dark fringes (minima). The bright fringes are formed where constructive interference occurs, while the dark fringes are formed where destructive interference occurs.
When one of the slits is covered by a glass plate, it introduces a phase difference between the waves passing through the two slits. This phase difference leads to a shift in the interference pattern.
The phase difference introduced by the glass plate can be calculated using the equation:
Δφ = (2π/h) * h,
where h is the thickness of the glass plate.
In this case, h = 10 mm = 10^-2 m.
Δφ = (2π/10^-2) * 10^-2
Δφ = 2π
The phase difference Δφ of 2π corresponds to a shift of one fringe. Therefore, the fringes will be displaced by a distance corresponding to the wavelength of light.
The distance between adjacent fringes (displacement) can be calculated using the equation:
δx = λ * I / d,
where λ is the wavelength of light, I is the distance between the screen and the diaphragm, and d is the distance between the two slits.
In this case, I = 100 cm = 1 m and d = 2.5 mm = 2.5 * 10^-3 m.
Using the equation, we can rearrange it to solve for λ:
λ = δx * d / I
Substituting the values, we get:
λ = (2π) * (2.5 * 10^-3) / 1
Calculating this, we find:
λ ≈ 0.0157 m
Therefore, the fringes will be displaced by a distance of approximately 0.0157 m (or 1.57 cm) in the direction perpendicular to the direction of the slits.
Without the glass plate covering one of the slits, we have a double-slit interference pattern. The interference pattern consists of bright fringes (maxima) and dark fringes (minima). The bright fringes are formed where constructive interference occurs, while the dark fringes are formed where destructive interference occurs.
When one of the slits is covered by a glass plate, it introduces a phase difference between the waves passing through the two slits. This phase difference leads to a shift in the interference pattern.
The phase difference introduced by the glass plate can be calculated using the equation:
Δφ = (2π/h) * h,
where h is the thickness of the glass plate.
In this case, h = 10 mm = 10^-2 m.
Δφ = (2π/10^-2) * 10^-2
Δφ = 2π
The phase difference Δφ of 2π corresponds to a shift of one fringe. Therefore, the fringes will be displaced by a distance corresponding to the wavelength of light.
The distance between adjacent fringes (displacement) can be calculated using the equation:
δx = λ * I / d,
where λ is the wavelength of light, I is the distance between the screen and the diaphragm, and d is the distance between the two slits.
In this case, I = 100 cm = 1 m and d = 2.5 mm = 2.5 * 10^-3 m.
Using the equation, we can rearrange it to solve for λ:
λ = δx * d / I
Substituting the values, we get:
λ = (2π) * (2.5 * 10^-3) / 1
Calculating this, we find:
λ ≈ 0.0157 m
Therefore, the fringes will be displaced by a distance of approximately 0.0157 m (or 1.57 cm) in the direction perpendicular to the direction of the slits.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?.
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















